Leading cause of death ages 1-44,
A. suicide
B drug overdose
C. Trauma
D. murder
C Trauma
Most common cause TBI related ED visits
A falls
B MVA
C violence
D sports injury
A falls
A Epidural hematoma
B subdural hematoma
C Subarachnoid hemorrhage
D intraparenchymal hemorrhage
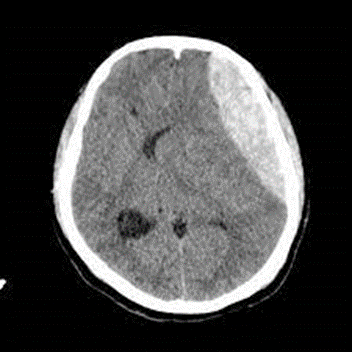
A Epidural hematoma
Severity of TBI, severe(coma),moderate,mild GCS
A <8, 8-12, >12
B <9, 9-12, >12
C <8, 8-13, >13
D <9, 9-13, >13
B <9, 9-12, >12
Which is not example of recovering brain?
A neuronal regeneration/collateral sprouting
B Redundancy
C Functional/behavioral substitution
D Vicariation
C Functional/behavioral substitution
Discuss diaschisis
Annual TBI in US
A < 1 million
B 1-2 million
C 2-3 million
D 3-4 million
C 2-3 million
Annual TBI deaths 1979-1992
A <20,000
B 20,000 - 40,000
C 40,000 - 60,000
D > 60,000
C 40,000 - 60,000
A Epidural hematoma
B subdural hematoma
C Subarachnoid hemorrhage
D intraparenchymal hemorrhage
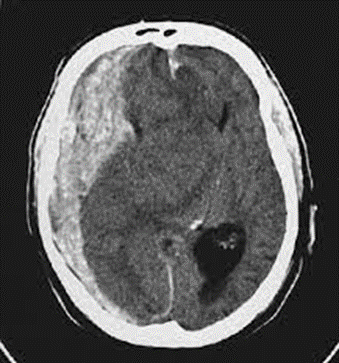
B subdural hematoma
Of items in GCS, best predictor of final outcome
A best eye at 24 hour
B motor at 2 weeks
C verbal at 1 week
D best total at 24 hour
B motor at 2 weeks
RLA LCFS; localized response to stimuli, confused and agitated, confused but appropriate, Generalized response to stimuli
A II,IV,VI,I C III, IV, VI, II
B III, IV V, II D III, V, VI, II
C III, IV, VI, II
Age distribution TBI
A unimodal skewed left
B unimodal skewed right
C level
D bimodal
D bimodal
Trends in TBI 1979-1992 MVA vs firearms
A both down
B both up
C MVA down, firearms up
D MVA up, firearms down
C MVA down firearms up
A Epidural hematoma
B subdural hematoma
C Subarachnoid hemorrhage
D intraparenchymal hemorrhage
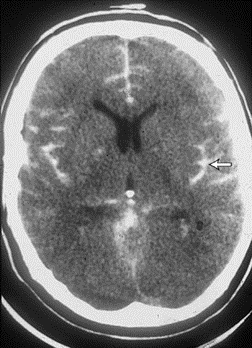
C Subarachnoid hemorrhage
A Severe disability unlikely when coma < 2 weeks
B Good recovery unlikely when coma > 4 weeks
C Anoxic causes of coma better prognosis than metabolic
D longer duration coma associated with poorer outcomes
C Anoxic causes of coma better prognosis than metabolic
Not a risk factor for late posttraumatic seizures
A penetrating injury
B immediate seizure
C Depressed skull fracture
D coma >24h
B immediate seizure
Gender distribution TBI, M:F
A 0.5:1
B 1:1
C 2.5:1
D 4:1
C 2.5:1
Where do parenchymal contusions frequently occur
A parietal lobe
B vertex
C inferior frontal and anterior temporal lobes
D occipital lobe
C inferior frontal and anterior temporal lobes
Which is untrue of Diffuse Axonal Injury
A occurs at time of injury
B most often in midline structures
C unrelated to loss of consciousness
D not always seen on imaging
C unrelated to loss of consciousness
Duration of post traumatic amnesia
A time of injury to 2 consecutive GOAT score >75
B time of end coma to 2 consecutive GOAT score<75
C time of end coma to GOAT score<75
D time of end coma to 2 consecutive GOAT score<75
D time of end coma to 2 consecutive GOAT score>75
Only Cranial N which may be affected in mild TBI
A I
B II
C VII
D VIII
A I
I, VII, VIII most commonly affected
Most common cause of death and injury in MVA
A crush injury to head
B Crush injury to torso
C amputation
D ejection from vehicle
D ejection from vehicle
On CT, blood appearance over time
A isointense, hypointense, hyperintense
B hypointense, hyperintense, isointense
C hyperintense, isointense, hypointense
D hypointense, isointense, hyperintense
C hyperintense, isointense, hypointense
Which is not positive predictor of outcome
A younger vs older age
B SAH rather than metabolic cause of coma
C reactive vs nonreactive pupils
D eyes deviate vs not deviate during caloric testing
B SAH rather than metabolic cause of coma
Which is not part of diagnostic criteria for paroxysmal sympathetic hyperactivity
A tachycardia
B urinary retention
C fever
D extensor posturing/sever dystonia
B urinary retention
In addition to other 3, HTN, tachypnea, excessive diaphoresis are 6 signs, 4 of which present in absence of other possible causes (sepsis, airway obstruction) leads to diagnosis