Where two tectonic plates rub against each other.
What is the transform plate boundary?
This type of tectonic plate boundary results in the formation of mountains
What is convergent plate boundary?
Majority of earthquakes take place at this depth.
What is shallow?
Volcanism is defined as ______________
What is movement of magma to the surface of the earth?
The circle area around the Pacific Ocean where most volcanic eruption and earthquakes are found.
What is the Ring of Fire?
Process by which the denser crust sinks into the asthenosphere and melts into magma.
What is subduction?
Name the 3 types of rock deformation?
What are compression, tension and shear?
Name two features of P waves.
Travel is all media.
Travel the fastest.
Compression.
Type of renewable energy harness from the heat inside the earth.
What is geothermal energy?
He was the weather man who proposed the plate tectonic theory.
This type of boundary is constructive.
What is divergent boundary?
Raised flat areas are called_______ (usually found near mountain ranges)
What is plateau?
The scale that tells the amount of energy released during an earthquake.
What is the moment scale?
For this physical property, felsic magma results in more explosive eruptions
What is low viscosity?
This is the total number of tectonic plates.
What is 15?
The reason why oceanic plate subducts under the continental plate.
What is the greater density of oceanic plate?
What one will you find a graben and what is the type of mountain called?
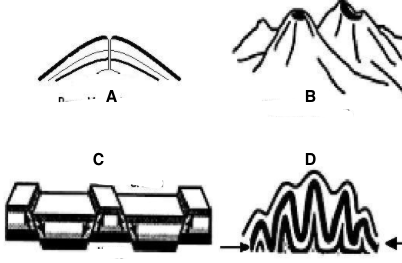
What is C and it is called a fault-block mountain?
Please identify each volcano.

What are composite, cinder cone, and shield volcanoes?
This is where magma plumes rise up through the crust that can result in the formation of volcanoes
What are hotspots?
The islands of Hawaii only have this type of volcano that are the result of hotspots.
What are shield volcanoes?
Identify Points A and C.
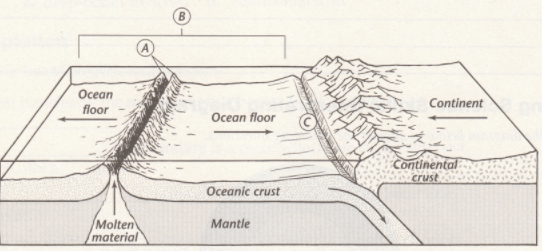
What are the mid-ocean ridge and trench?
Identify syncline that has the youngest layer of rock in the core.
A. B. C.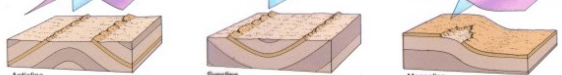
What is B?
Name the type of fault and the rock above (A) and below (B) the fault plane.
A B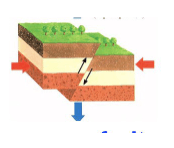
What are normal fault, hanging wall, and footwall?
This is a dense, fast-moving flow of solidified lava pieces, volcanic ash, and hot gases as a result of a violent eruption.
What is a pyroclastic flow?
This island country in Asia has the most earthquake activities
What is Japan?
Explain paleomagnetism and why it is important.
The study of ancient magnetism preserved in rock and helps support the sea floor spreading theory.
Explain isostasy.
Isostasy is the rising or settling of a portion of the Earth's lithosphere that occurs when weight is removed or added in order to maintain equilibrium between buoyancy forces that push the lithosphere upward and gravity forces that pull the lithosphere downward.
Name 3 factors that affect the intensity of an earthquake.
Name two areas where volcanic eruption can occur.
Mid-ocean ridge
oceanic-continental convergent boundary (subduction zone)
Hotspots
The only place on earth where you will find the plate tectonic and mid-ocean ridge exposed. Name one of the two plates.
What is Iceland which sits on Eurasian and North American tectonic plates?