Explain the advantages of having both lipid and carbohydrate as energy stores in the human body.
a. lipid is long-term energy storage
OR
carbohydrate is short-term energy storage/readily available ✔
b. lipids are insoluble, so easier to store
OR
carbohydrates/sugars are soluble, so easy to transport by blood ✔
c. lipids store more energy «per gram»
OR
lipids occupy less space «per energy/kJ» ✔
OWTTE
What maintains the concentration gradient for ventilation
dense networks of blood vessels, continuous blood flow, and ventilation with air for lungs and
with water for gills.
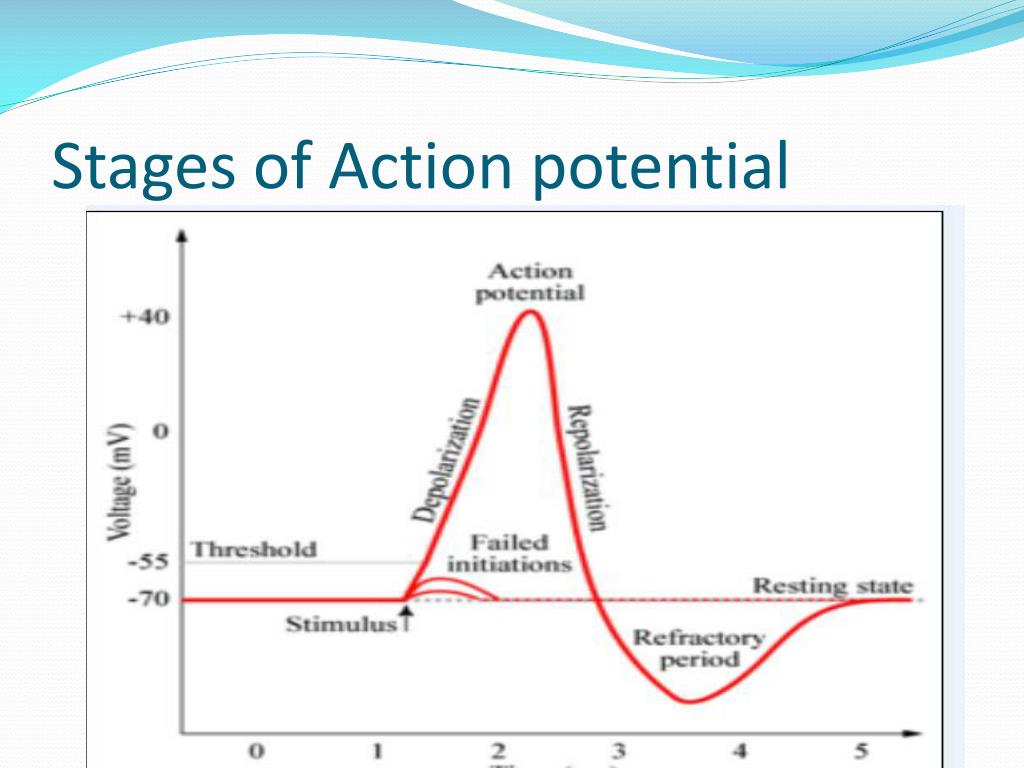
 Which Ions are involved in action potentials
Which Ions are involved in action potentials
Na, K
What are some adaptions of gas exchange surfaces
Surfactants, high surface area to volume ration, permeability, thin tissue layer
Describe the structure and function of starch in plants. [3]
a. «starch» is a polysaccharide/is composed of glucose molecules
b. contains amylose which is a linear/helical molecule
c. contains amylopectin which is a branched molecule
Function:
d. storage of glucose/energy in plants
e. storage form that does not draw water
How does the diaphragm do to facilitate gas exchange
Change the volume of the lungs to create a pressure difference, so gases move from low to high concentration
 What drives the movement of sodium and potassium ions against their concentration gradient
What drives the movement of sodium and potassium ions against their concentration gradient
ATP
What is an essential amino acid
One that needs to be obtained from your diet
Outline the function of three named protein
a. Rubisco fixes CO2 from atmosphere during photosynthesis;
b. insulin controls blood glucose levels;
c. collagen forms connective tissue/ligaments;
d. spider silk forms the spider web;
e. rhodopsin involved in photoreceptor;
f. immunoglobulins/antibodies attach to antigens/pathogens;
g. actin/myosin performs muscle contraction;
h. hemoglobin carries oxygen in red blood cells;
Accept any other correct three named proteins
If an enzyme is named, the correct substrate must be stated
What is one adaption for gas exchange
waxy cuticle, epidermis, air spaces, spongy mesophyll,
stomatal guard cells and veins.
What does the world polar mean?
Opposite
How does pH impact protein
denatures them changing their function
Distinguish between the structure of amylose and the structure of amylopectin. [1]
amylose unbranched/helical while amylopectin branched / vice versa
What is the function of the stomata
Control rate of transpiration (water loss) from plants
What is transmitted along a nerve
Electricity
This is the voltage difference between the inside of the cell membrane and outside the cell membrane
What is membrane potential?
What is the monomer of cellulose
Beta Glucose
State two structural features that differ between RNA and DNA. [2]
a. number of strands
OR
(usually) only one strand in RNA/two strands in DNA
b. base composition
OR
uracil only in RNA / thymine only in DNA
c. type of pentose
OR
ribose only in RNA / deoxyribose only in DNA
What is expiratory reserves
the amount of extra air above normal that you exhale during a forceful breath out
This is a structure that is a cell that grows and wraps around the neuron axon; it functions in speeding up the nerve impulse, nourishing the cell, and helping to remove metabolic waste from the neuron.
What is the myelin sheath? (produced by Schwann Cells in the PNS or oligodendrocytes in the CNS)
 What voltage is the resting potential
What voltage is the resting potential
What reaction is used to build molecules
condensation (dehydration) reaction