Information or data that supports the claim.
What is the first step in using a triple beam balance?
Make sure the pointer aligns to the zero mark.
This type of data describes qualities or characteristics that cannot be measured with numbers.
What is qualitative data?
You see that the classroom lights are off. Is this an observation or an inference?
What is an observation?
What should be included in your claim?
A clear answer based on the investigation or data.
Connecting evidence to claim using scientific ideas.
What is Reasoning?
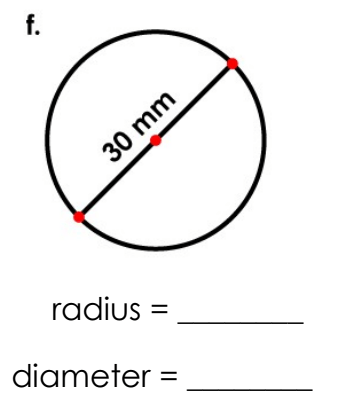
radius : 15 mm
Diameter : 30 mm
A student says, “The solution is blue.” Is this an example of qualitative or quantitative data?
What is qualitative data?
You see smoke rising from the kitchen and say, “Something is burning.” Is this an observation or an inference?
What is an inference?
People could spread misinformation
The experiment demonstrated that plants need sunlight to grow.
What is a claim?
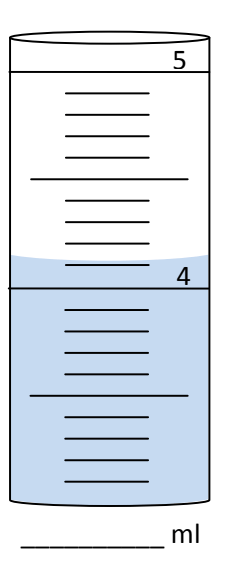
4.1 ml
During an experiment, a student notes that the candle wax melted at 60°C and also that the wax had a sweet smell. Which type(s) of data are included here?
What is both quantitative (60°C) and qualitative (sweet smell) data?
Describe the difference between observation and inference.
An observation is information you gather through your five senses. An inference is a conclusion you reach after making an observation.
A student writes: “Because plants need sunlight for photosynthesis, the plant placed near the window grew taller.” Which part of CER is this sentence?
What is reasoning?
Be specific—avoid vague phrases like “there was a change.”
What is evidence?
What are the side lengths of a cube who's volume is 27 cm^3?
3 cm
A student measures the length of 10 seeds and also writes down that they are “oval-shaped.” Which type of data is each example?
Length = quantitative data; shape = qualitative data.
During an experiment, you hear bubbling and see gas being released from a test tube. You say, “A chemical reaction is happening.” Identify the observation(s) and the inference.
Observations = bubbling, gas release; Inference = chemical reaction is happening.
A student observes that ice melts faster in warm water than in cold water. What type of evidence would best support this claim?
Timed measurements of ice melting in different water temperatures
Where do you usually get evidence from?
experiment, graph, data table, published research studies, reliable sources.
Why is it important to use units in calculations? Give an example.
Units give numbers meaning and help us use them correctly.
You cant add 5 meters and 3 seconds.
Describe the quantitative data from this survey. 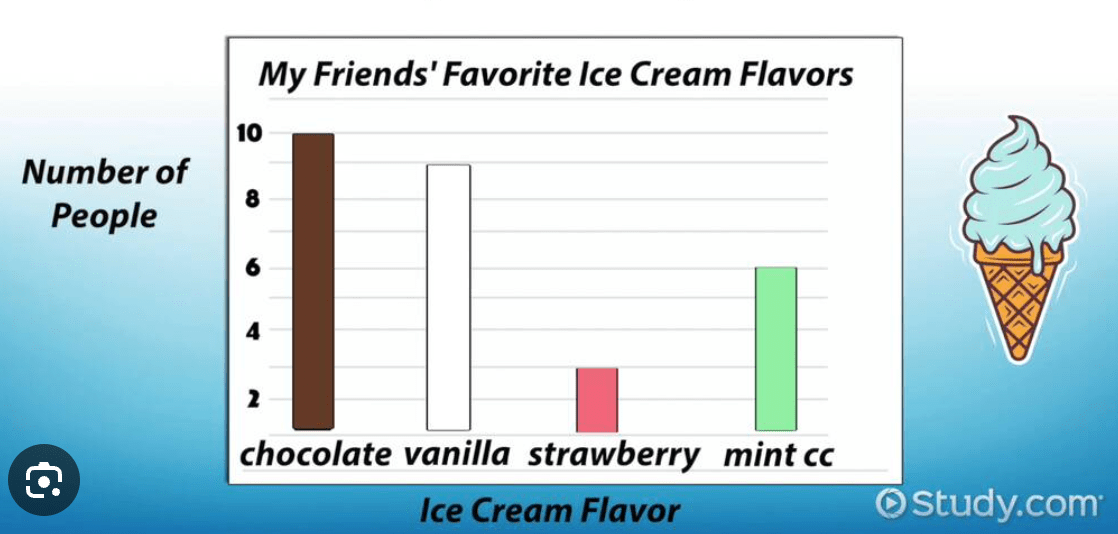
10 friends like chocolate
9 friends like vanilla
3 friends like strawberry
6 friends like mint cc
28 friends were surveyed.
Why is it important to separate observations and inferences in science.
Scientists must separate them because observations are direct evidence, while inferences are interpretations that could change with new evidence.
Why is evidence important in science?
Evidence-backed claims are verifiable. If another scientist repeats the experiment, they should see the same results. This creates credibility and trust.