How should the CR be angled for a lateral knee on an average sized patient?
5-7 degrees cephalic
How many bones in the appendicular skeleton?
126
What are the two main landmarks for chest positioning?
vertebra prominens and jugular notch
Why should a chest x-ray be taken erect?
the diaphragm can move farther down, to visualize fluid levels, to prevent engorgement of vessels
What are kidney stones a clinical indication for?
KUB
How much of the patella needs to be free of superimposition by the femur for an oblique knee?
about half
Why is it important to include the correct marker on an image?
legal/liability purposed, to validate the part being examined
How many lobes are in the left and right lungs?
left 2, right 3
What is a pneumothorax a clinical indication for?
chest x-ray
Where is the central ray for a routine thumb exam?
1st MCP
Regarding the anatomy of the knee, why is it important to angle the x-ray tube 5-7 degrees for a lateral knee?
the medial condyle is longer
What patient position is described with the patient’s head lower than the feet?
Trendelenburg
What is the area where the thymus gland, heart and great vessels, trachea and esophagus are located in the medial portion of the thoracic cavity?
mediastinum
Which kidney is lower due to the liver?
right
What fracture is most common in the 5th metacarpal in which the closed fist comes into contact with an object?
Boxers fracture
What is the proper way to view a foot x-ray?
toes up
What synovial joint movement allows the greatest freedom of motion (hip or shoulder joints)?
spheroidal (ball and socket)
Which plane is perpendicular to the IR for a PA chest?
midsagittal
In which of the four major quadrants of the abdomen would the appendix be found?
right lower
What anatomy is visualized with an internal (medial) oblique elbow projection?
trochlea and coronoid process
You performed a Tib/Fib exam and the distal portion of the leg is clipped on both views. What should you do for the to ensure all the anatomy is present?
take an AP and Lateral ankle and collimate down
What patient position is this?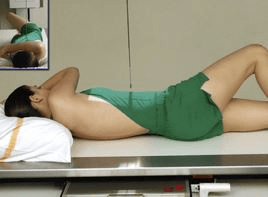
LPO
How many ribs should be visualized for a PA chest?
10
Which vertebral level is the xiphoid process?
T10
What position is the hand when the radial tuberosity (tubercle) is seen posteriorly, adjacent to the ulna?
Thumb down/hand with maximal internal rotation