What is the term for the outer layer of the epidermis?
Stratum Corneum
Which type of bone protects organs and provides attachment points for muscles? Name an example.
Flat bones. Ex. Scapula, Skull, Ribs, Sternum
Which type of gland is shown on the left hand side of the diagram?
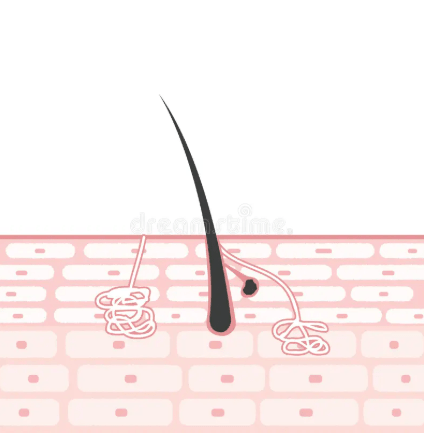
Eccrine
Name all six bones of the cranium.
Parietal, temporal, occipital, frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid.
Name the three structures of the scapula and their functions.
Acromion process: articulates with the clavicle, attachment point for the arm and the scapula to the rest of the body
Coracoid process: attachment point for muscles of the arm
Glenoid cavity: the socket that articulates with the head of the femur.
What are the two functions of sweat?
Maintain a constant core temperature and help eliminate wastes.
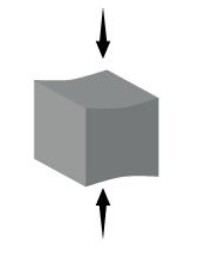
Which type of strength is being demonstrated and what component of bone contributes to this strength?
Compressional and calcium salts.
How are bone injuries able to heal quickly despite bone's hardened matrix?
Because bone cells are well supplied with oxygen and nutrients.
Which bones does the lambdoid suture connect?
Occipital and parietal.
Describe this phalanx using its number and location.
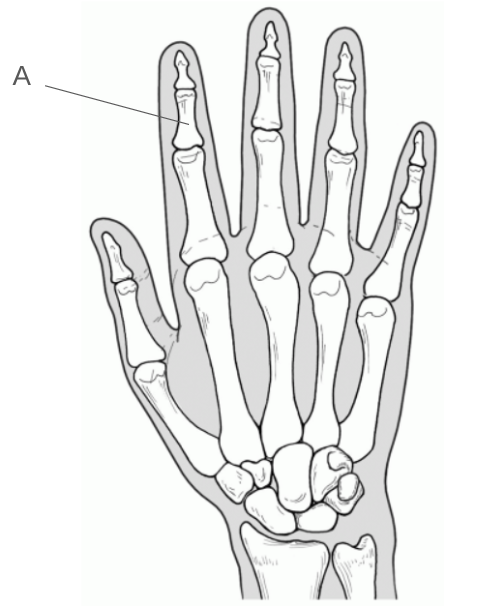
Middle phalanx II
What is a consequence of an over abundance of sebum?
Acne.
What is the differences between osteoblasts and osteocytes?
Osteocytes are mature osteoblasts that are entrapped in bone matrix. Osteocytes can also build and break down where osteoblasts only build bone.
What is the name of the small bony projection located on the temporal bone? What is its function?
Styloid process. It is an attachment point for neck muscles.
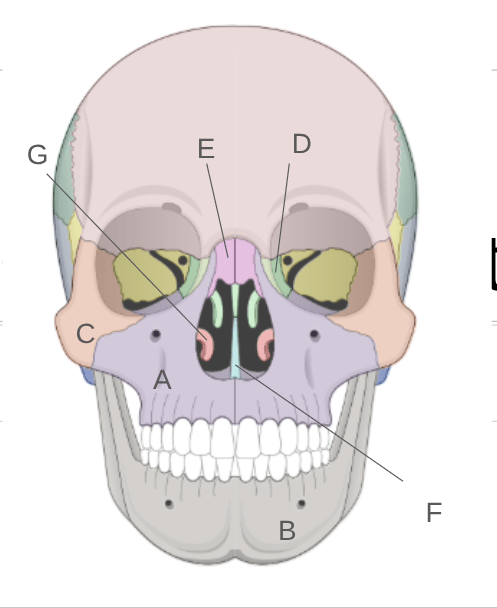 Identify A-G on this diagram
Identify A-G on this diagram
A: Maxillae
B: Mandible
C: Zygomatic Bone
D: Lacrimal Bone
E: Nasal Bone
F: Vomer
G: Inferior Nasal Conchae
Identify the two labeled carpals.
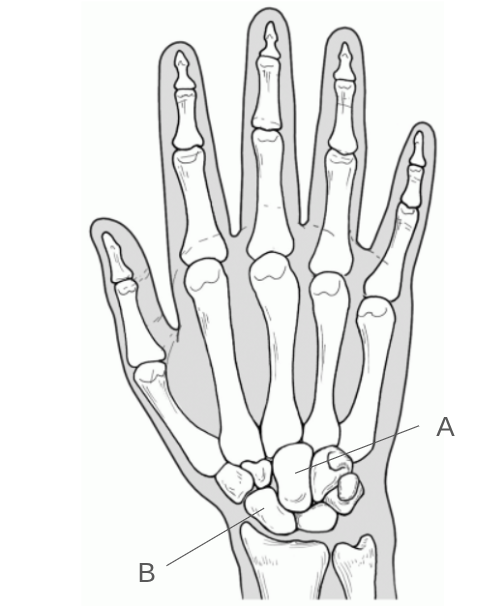
A: Capitate
B: Scaphoid
Where are apocrine glands located and what are their function other than sweat production?
Located in axillary and anogenital region and they are scent glands.
What is the name of the circular structure in this diagram. What are the two main parts of the structure?
Osteon. Lamellar and haversian/osteonic canals.
What joint connects the os coxae to the spine? Which two bones articulate at that joint?
The sacroiliac joint. The sacrum and the illium.
Name the two structures labeled on this diagram. Explain what the structures are? When do they go away?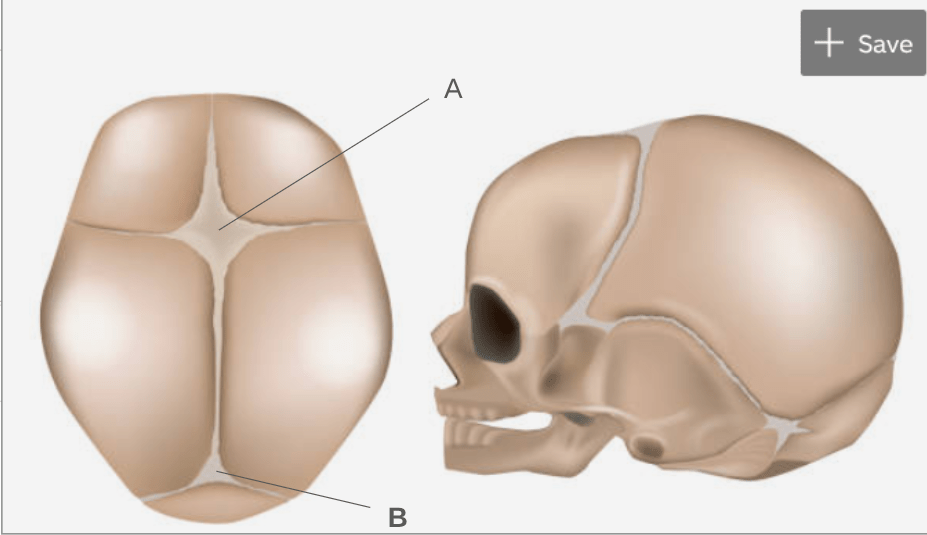
A: Anterior Fontanel
B: Posterior/Occipital Fontanel
Fontanels are areas between unfused bones covered by fibrous membranes. They close by age 2.
How does the female pelvis change in order for the pelvic outlet to widen during childbirth?
The pubis symphysis softens.
Which type of burn results in blisters, severe pain, and swelling?
Second degree/partial thickness burns.
Which type of fracture tends to happen after high impact trauma, such as car accidents?
Comminuted.
What is the name of the largest tarsal bone and what is its function?
Calcaneus, it bears weight.
Name this spinal condition. Name the three causes of this condition. 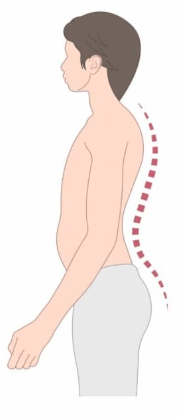
Lordosis. Can result from osteoporosis, poor posture, and abdominal weight gain.
Identify the following structures of the pelvis
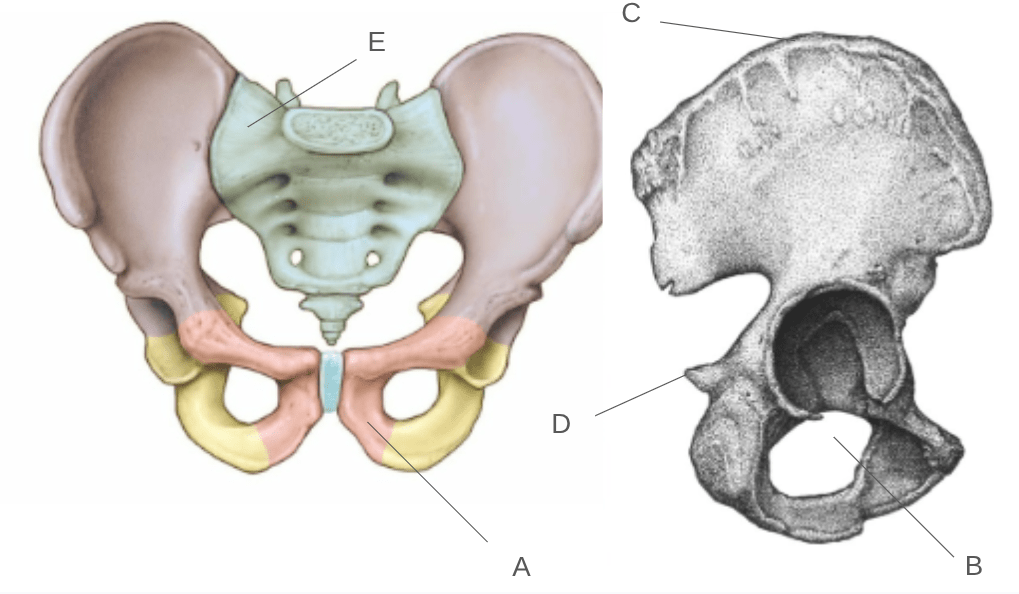
A: Pubis
B: Obturator foramen
C: Iliac crest
D: Ischial spine
E: Sacrum