Please write an example of a Single-Sample t-Test
Comparing the sample mean to the population mean, however YOU DON'T KNOW THE POPULATION STANDARD DEVIATION!
Please list the 3 Statistics we use to make sure a find is MEANINGFUL
Confidence Intervals
Effect Sizes
Statistical Power
I believe that Women at UNL are smarter (have higher I.Q) than they have ever been in UNL's history. If I were to run a two-tailed Z-test, please state the Null Hypothesis. WORDS ONLY
There is no significant difference between today's UNL Women, and the Population of UNL Women in I.Q.
Why would I use a Single Sample t-Test instead of a Single Sample z-Test?
What percentile is a Z-score of 0?
50th Percentile
Please write an example study for a Paired-Sample's t-Test
Comparing two means for a within-groups design (every participant is exposed to BOTH levels of the I.V)
Effect Size
I want to find if Frogs in the world who use my drug will eat more bugs. Before I run this study, I need to make sure that my population of frogs eats the same average number of bugs as the population. I grab 75 frogs from the local lake to participate in my study. I know the population eats 15 bugs a day with a standard deviation of 4. My sample eats 17 bugs with a standard deviation of 6.
How many assumptions are SATISFIED and name them!
Scaled DV
Approximately Normal Distribution
What is the formula for Degrees of Freedom?
N-1
What percentile is a Z score of 1.25? (Round to 2 Decimal Places)
89.44th Percentile
Please write an example of a Z-test
Comparing the sample mean to the population mean in which WE KNOW THAT POPULATION STANDARD DEVIATION
Assume I am talking about a Z test, If I increase my alpha from .05 to .15, what does this do to my Statistical Power? How do you know?
Increases Power
You are increasing the shaded area, meaning you are more likely to reject the null, thus decreasing my chance of Type II error, ergo Increasing Power
I want to find if Frogs in the world who use my drug will eat more bugs. Before I run this study, I need to make sure that my population of frogs eats the same average number of bugs as the population. I grab 75 frogs from the local lake to participate in my study. I know the population eats 15 bugs a day with a standard deviation of 4. My sample eats 17 bugs with a standard deviation of 6.
Using Symbols, right the Alternative Hypothesis for this study
H1: 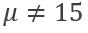
If I did a study on 60 people and set alpha=.20, what are my t-critical values?
-1.296 and 1.296
I got a score of 18. I know that the population mean is 16 with a standard deviation of 3.6. Calculate the Percentile of my raw score? (Round ALL VALUES to 2 Decimal Places)
71.23rd Percentile
Please write an example of an Independent Samples t-Test
comparing two means for a between-groups design (participants are exposed to only 1 level of the I.V)
Assume I am talking about a Z test, If my sample mean increases, so much so that it now is higher than my population mean, what does this do to my Statistical Power? How do you know?
Increases Power
Increasing sample mean, increases my Zstat, which means I am more likely to reject the null, decreasing my chance of a Type II error, ergo increasing power
What is the goal of a Z-test? Give me two scenarios in which you would want to run a Z-test
Making sure my sample represents the population
Seeing if the population is changing
I believe 3rd graders are better at math than 9th graders. I give both groups of kids a math test and compare there percent scores. If I'm running a ONE-TAILED test, please state the alternative hypotheses in words and symbols
H1: Mean of 3rd grade math scores > Mean of 9th grade math scores
The average 3rd grade math score is significantly higher than the average 9th grade math score
I got a score of 10. I know the population mean is 14 with a standard deviation of 6.6. Calculate the percentile of my raw score. (Round ALL VALUES to 2 Decimal places)
27.09th Percentile
What type of chart should not be shown at an Alcoholics' Anonymous Meeting
Bar Chart
Assume I am talking about a Z test, If I decrease my sample size, what does this do to my Statistical Power? How do you know?
Decreases Power
Decreasing my sample size increases my standard error term. If my standard error term gets bigger, my Zstat gets smaller, meaning I'm less likely to reject the null, which increases my chance of a Type II error, ergo decreasing power
If i have a p-value of .03, interpret what that means?
There is a 3% chance of making a Type 1 error if I were to reject the null
Please explain the difference between a Single Sample t-Test, a Paird Sample t-Test, and Independent Samples t-Test
Single Sample- comparing a sample to the population
Paired Sample- comparing one sample on two different conditions/levels of the IV
Independent Sample- Comparing two samples on one condition/level of the IV
I know that my raw score is in the 3.51st percentile. Given that I know the population mean is 10 with a standard deviation of 5, find my raw score. (Round ALL VALUES to 2 Decimal Places)
.95