Transport
???
What makes the body react to changes to keep conditions inside the body the same (balanced)?
(Vocabulary Choices: Homeostasis, Nervous System, Stimulus, Response, Neuron)
What is Homeostasis?
The number of molecules in an area (High concentration = more
Low concentration = less)
(Vocabulary Choices: Concentration, Passive Transport, Diffusion, Active Transport)
What is concentration?
The organ system that exchanges (moves) the gases oxygen and carbon dioxide
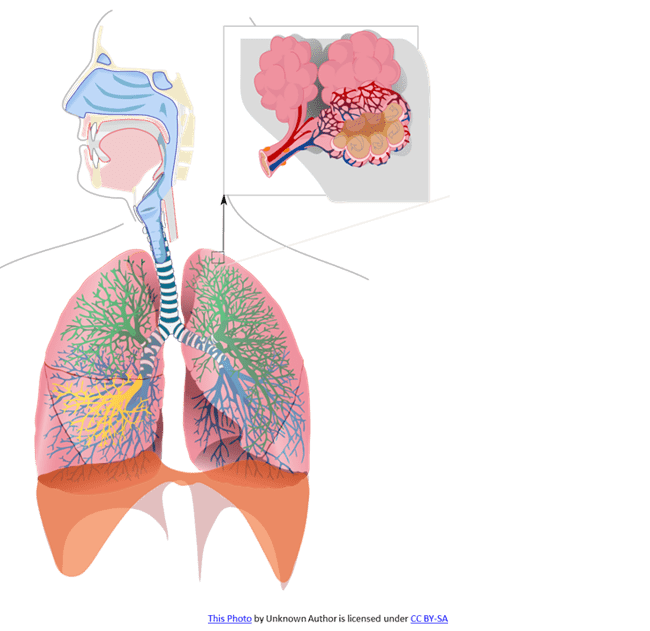
(Vocabulary Choices: Exchange, Alveoli, Respiratory System)
What is the respiratory system?
Tubes that transport blood to all parts of the body

(Vocabulary Choices: Blood, Circulatory System, Blood Vessel, Respiratory System, Oxygen)
What is a blood vessel?
Which side has the highest concentration of molecules?
A B
What is side A has the highest concentration of molecules?
The organ system that carries messages between the brain and the body.
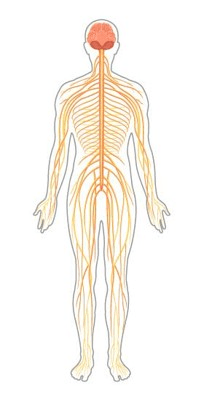
(Vocabulary Choices: Homeostasis, Nervous System, Stimulus, Response, Neuron)
What is the Nervous System?
When molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
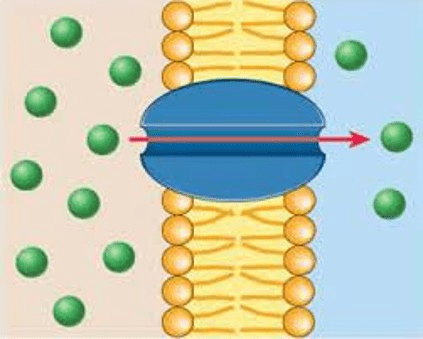
(Vocabulary Choices: Concentration, Passive Transport, Diffusion, Active Transport)
What is diffusion?
The location of gas exchange in the lungs
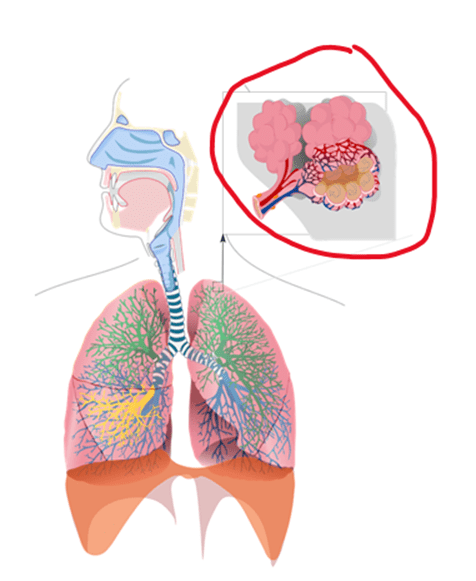
(Vocabulary Choices: Exchange, Alveoli, Respiratory System)
What is alveoli?
The organ system that carries oxygen and nutrients to the cells and removes waste.
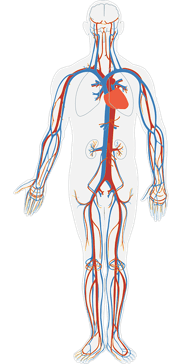
(Vocabulary Choices: Blood, Circulatory System, Blood Vessel, Respiratory System, Oxygen)
What is the circulatory system?
Which picture is the stimulus and what picture is the response.
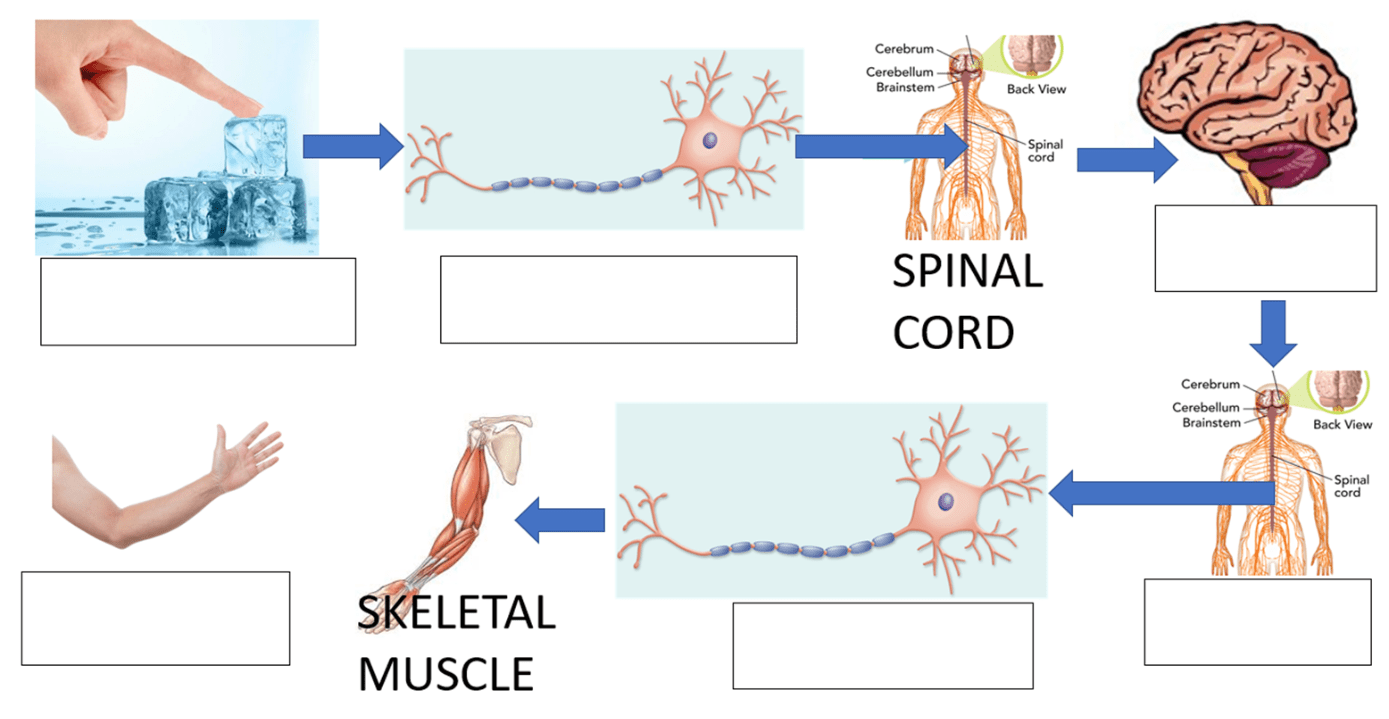
The ice = stimulus
The moving hand = response
The reaction to the stimulus

(Vocabulary Choices: Homeostasis, Nervous System, Stimulus, Response, Neuron)
What is a response?
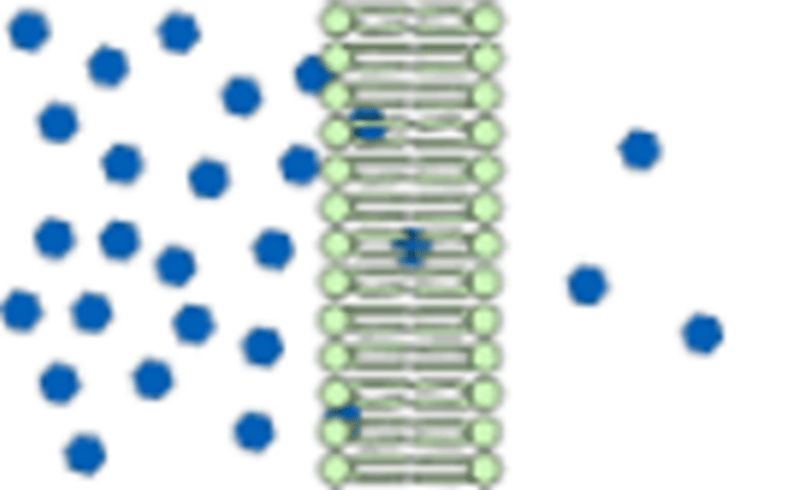
Molecules moving across a cell membrane without using energy (ATP)
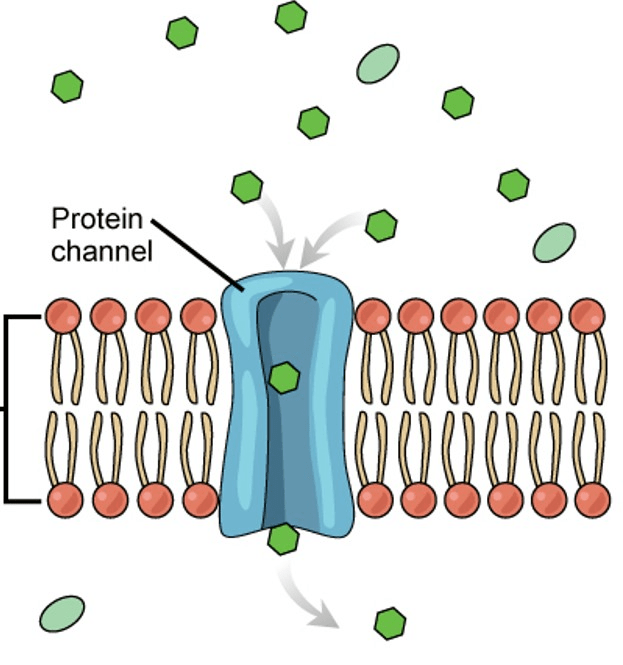
(Vocabulary Choices: Concentration, Passive Transport, Diffusion, Active Transport)
What is passive transport?
To replace one thing for another

(Vocabulary Choices: Exchange, Alveoli, Respiratory System)
What is exchange?
A fluid that circulates through the body carrying nutrients and wastes.
(Vocabulary Choices: Blood, Circulatory System, Blood Vessel, Respiratory System, Oxygen)
What is blood?
Cells use ______ for the active transportation of some molecules.
(Vocabulary Choices: Passive Transport, ATP, Diffusion, Response, Alveoli)
What is ATP?
a change that causes something to happen

(Vocabulary Choices: Homeostasis, Nervous System, Stimulus, Response, Neuron)
What is a stimulus?
Molecules need energy (ATP) to move across a cell membrane.
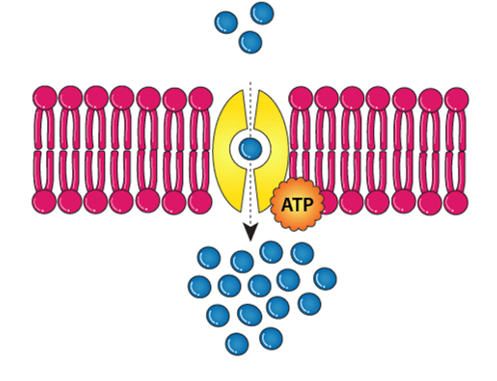
(Vocabulary Choices: Concentration, Passive Transport, Diffusion, Active Transport)
What is active transport?
The lungs exchange ________ and ________ __________.
(Vocabulary Choices: Carbon Dioxide, Exchange, Alveoli, Respiratory System, Oxygen)
What is oxygen and carbon dioxide?
The function of the circulatory system is to carry _____ and ______ to the cells and remove _________.
(Vocabulary Choices: Nutrients, Blood, Circulatory System, Blood Vessel, Oxygen, Wastes)
What is carrying oxygen and nutrients to cells and removing wastes?
The ________ is inside the lungs and functions to exchange gases between the respiratory and circulatory systems.
(Vocabulary Choices: Blood, Diffusion, Response, Alveoli)
What is Alveoli?
A specialized cell in the nervous system that sends impulses (messages)
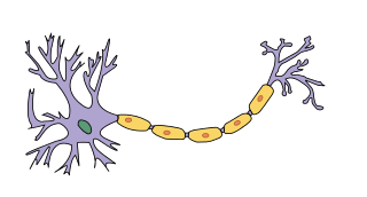
(Vocabulary Choices: Homeostasis, Nervous System, Stimulus, Response, Neuron)
What is a neuron?
Which picture shows active transport and why?
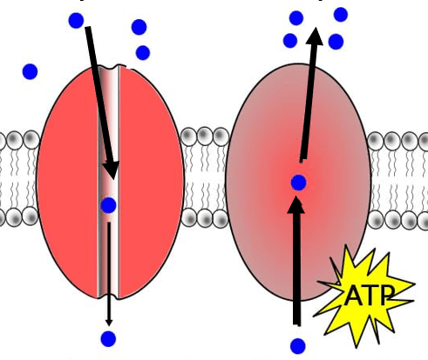
A B
What is B, because cells use ATP for the active transport of some molecules?
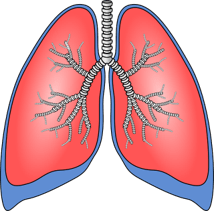
An organ in the respiratory system that exchanges gases, oxygen, and carbon dioxide.
What are the lungs?
The function of the ________ is to transport nutrients, oxygen, and carbon dioxide around the body.
What is blood?
What two body systems work with the circulatory system?
(Vocabulary Choices: Nervous System, Respiratory System, Digestive System)
What are the respiratory and digestive systems?