What is the primary function of the left hemisphere?
The left hemisphere primarily handles language and analytical tasks.
What function is associated with the occipital lobe?
The occipital lobe is primarily responsible for vision.
Where is the motor cortex located?
The motor cortex is located in the rear part of the frontal lobe.
What is the primary function of Wernicke’s area?
The primary function of Wernicke’s area is language comprehension.
What does an EEG measure?
An EEG measures electrical activity in the brain. It uses electrodes placed on the scalp to detect and record these brainwave patterns
Name a function that is predominantly managed by the right hemisphere.
The right hemisphere is predominantly involved in spatial awareness and creativity.
What is the function of the frontal lobe?
The frontal lobe is involved in reasoning and problem-solving.
What is the location of the cerebellum?
The cerebellum is located at the back of the brain, under the occipital lobes.
What is the primary function of Broca’s area?
The primary function of Broca’s area is speech production.
What is the purpose of an MRI scan?
The purpose of an MRI scan is to provide detailed images of the brain's structure.
How do the two hemispheres communicate?
The two hemispheres communicate through the corpus callosum.
Name a key function of the parietal lobe
A key function of the parietal lobe is spatial orientation and sensory integration.
Describe the role and location of the sensory cortex.
The sensory cortex processes sensory information and is located in the parietal lobe
Where is Broca’s area located? (hemisphere and lobe location)
Broca’s area is located in the left frontal lobe.
What does a PET scan show?
A PET scan shows metabolic processes in the brain by using radioactive tracers.
What is hemispheric lateralization?
Hemispheric lateralization refers to the specialization of certain functions in one hemisphere over the other.
What is a major function of the temporal lobe?
A major function of the temporal lobe involves auditory processing and memory.
What is the location of the amygdala?
The amygdala is located near the hippocampus in the temporal lobe.
Where is Wernicke's area located? (hemisphere and lobe location)
Wernicke's area is located in the left temporal lobe.
What are the advantages of using a CAT scan?
Advantages of a CAT scan include its ability to quickly provide detailed images of brain structures, often used in emergency situations.
Describe a condition that may result from damage to one hemisphere.
Conditions like aphasia may result from damage to one hemisphere.
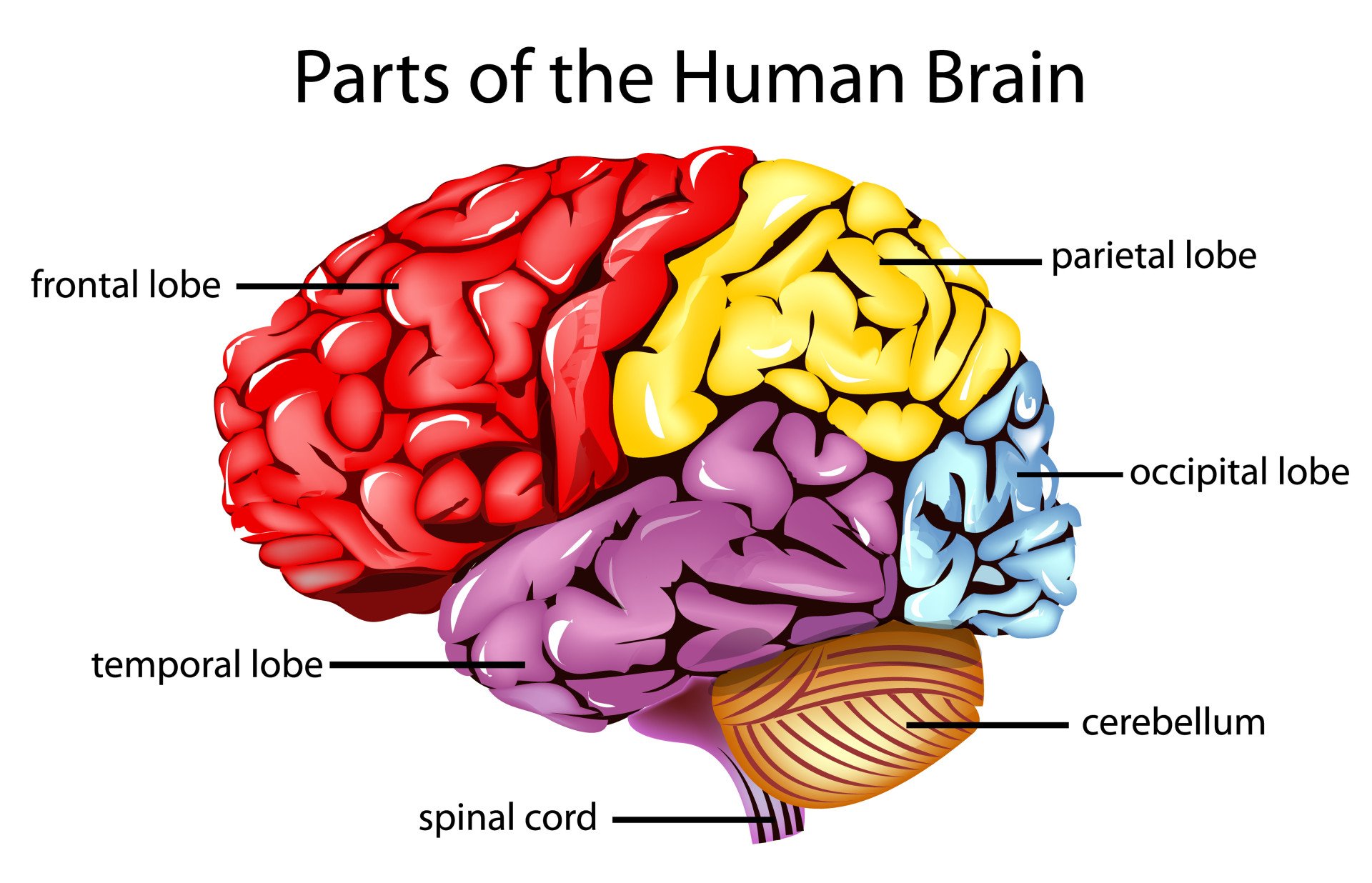
Label the 4 brain lobes,cerebellum, and spinal cord
The four main lobes are the frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes.
What are the key functions of the cerebellum?
The cerebellum has several functions relating to movement and coordination, including:
- Maintaining balance: The cerebellum has special sensors that detect shifts in balance and movement. It sends signals for the body to adjust and move.
- Coordinating movement: Most body movements require the coordination of multiple muscle groups. The cerebellum times muscle actions so that the body can move smoothly.
- Vision: The cerebellum coordinates eye movements.
- Motor learning: The cerebellum helps the body to learn movements that require practice and fine-tuning. For example, the cerebellum plays a role in learning to ride a bicycle or play a musical instrument.
What happens when Broca's and Wernicke's areas are damaged?
Damage to Broca's area can result in difficulty in speech production (known as Broca's aphasia)
Symptoms of damage to Wernicke's area include the production of nonsensical speech (known as Wernicke's aphasia).
How does an fMRI differ from a standard MRI?
An fMRI shows brain activity by measuring changes in blood flow, while a standard MRI captures static images.