The meninge layer closest to the brain's surface
What is pia mater?

This is the relay station for most sensations
What is the thalamus?

A neuron with its axon projecting to the brain is known as this.
What is (an) afferent (neuron)

Delta waves appear in the slow-wave sleep of this stage
What is stage 4? (N3 in book
A dog salivating after hearing the bell that signals for his food is this type of learning.
What is Pavlovian?
(Also what is the cephalic phase?)

Tight junctions in brain capillaries form this, which prevents harmful substances in the blood from entering the interstitial fluid
What is the blood-brain barrier?

This diffuse modulatory system is responsible for pleasure, in addition to motor control
What is dopamine?

The ventral roots of the spinal chord contain information coming from this place
What is the brain (or CNS)? 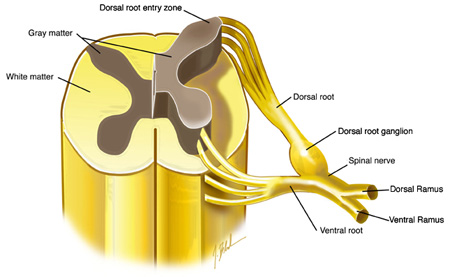 Efferent neurons
Efferent neurons
As you approach morning (after a long sleep) do you spend more time in REM or deep sleep?
REM sleep

This type of memory requires higher cognitive skills and conscious attention for recall.
What is declarative memory?

Non-declarative aka reflexive
A person who had damage here might be able to think of a word but not be able to say it (lack of communication between hemispheres)
What is the corpus callosum? 
A patient who has damage to this area might nod in understanding but only respond to your questions with the word "ball"
What is Broca's Area?

This reaction activates muscle movement without input of the brain.
What is a Spinal Reflex
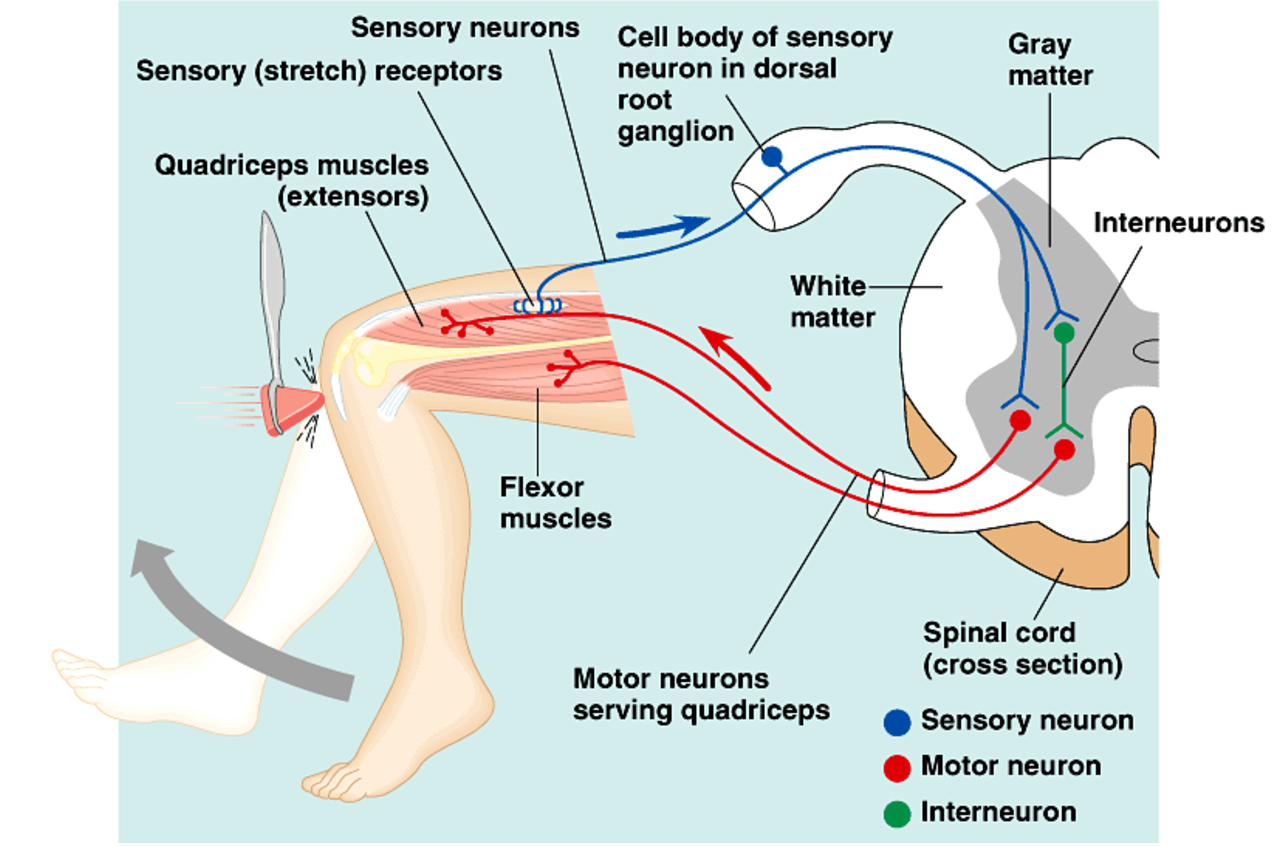
Circadian rhythms are controlled by this internal clock in the hypothalamus
What is the suprachiasmatic nucleus?
This principle of plasticity states that "neurons that fire together, wire together"
What is the Hebbian principle?