Embolism
Embolism
Airways
This is the name of the 'sign' seen below suggesting pulmonary embolus.
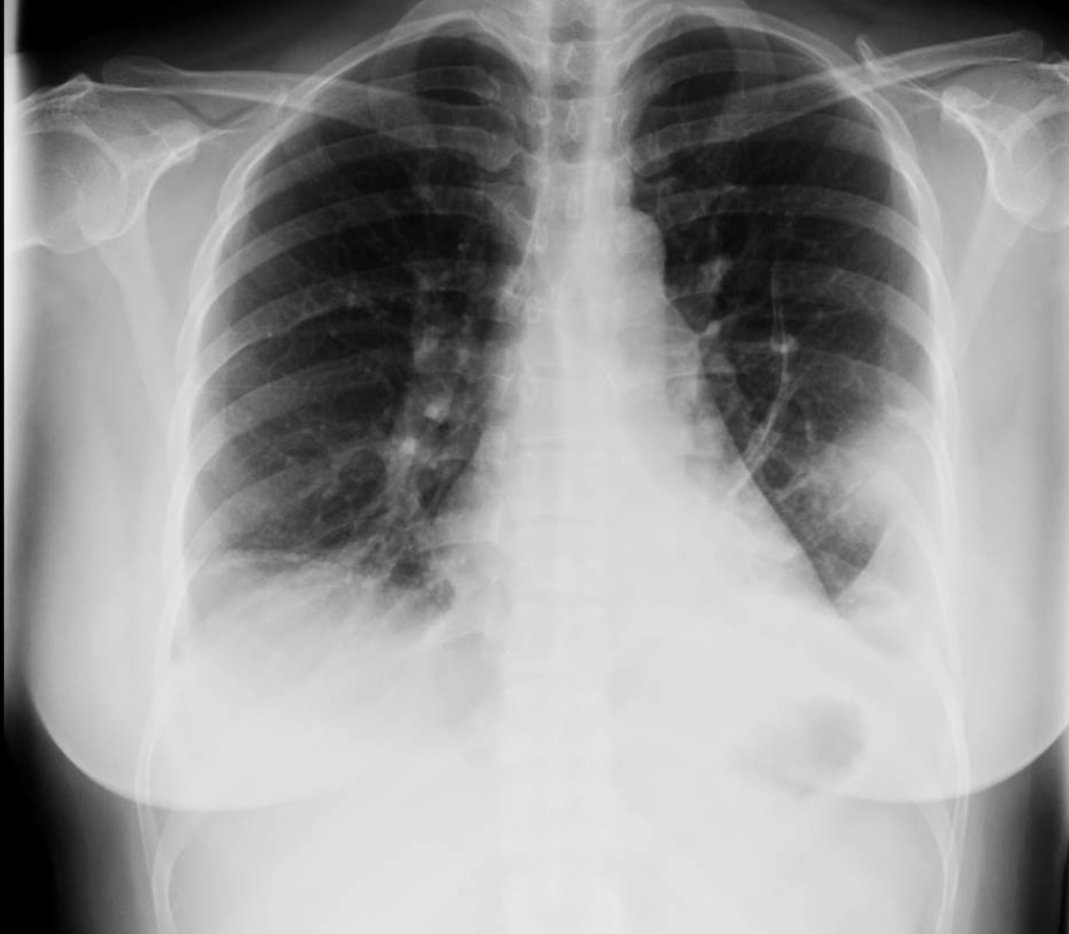
Hamptons Hump
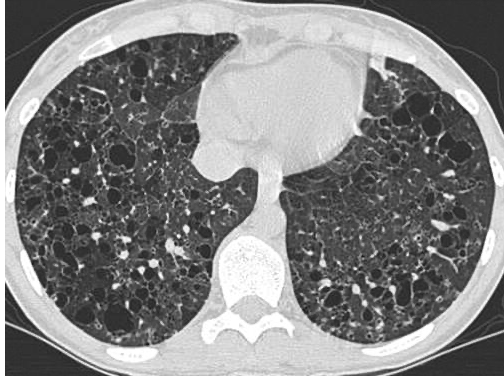
1. The CT below shows this type of pattern.
2. Name 2 conditions where this pattern is seen. 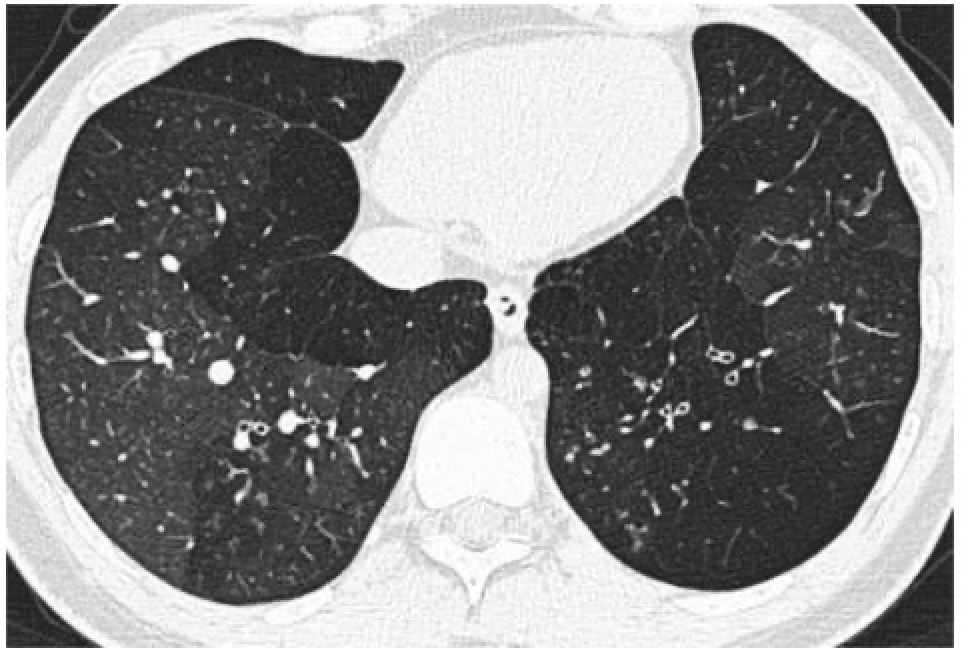
1. Mosaic or Geographical pattern
2. Pulmonary Hypertension (due to perfusion abnormality), sarcoid (bronchial involvement), Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (due to air trapping)
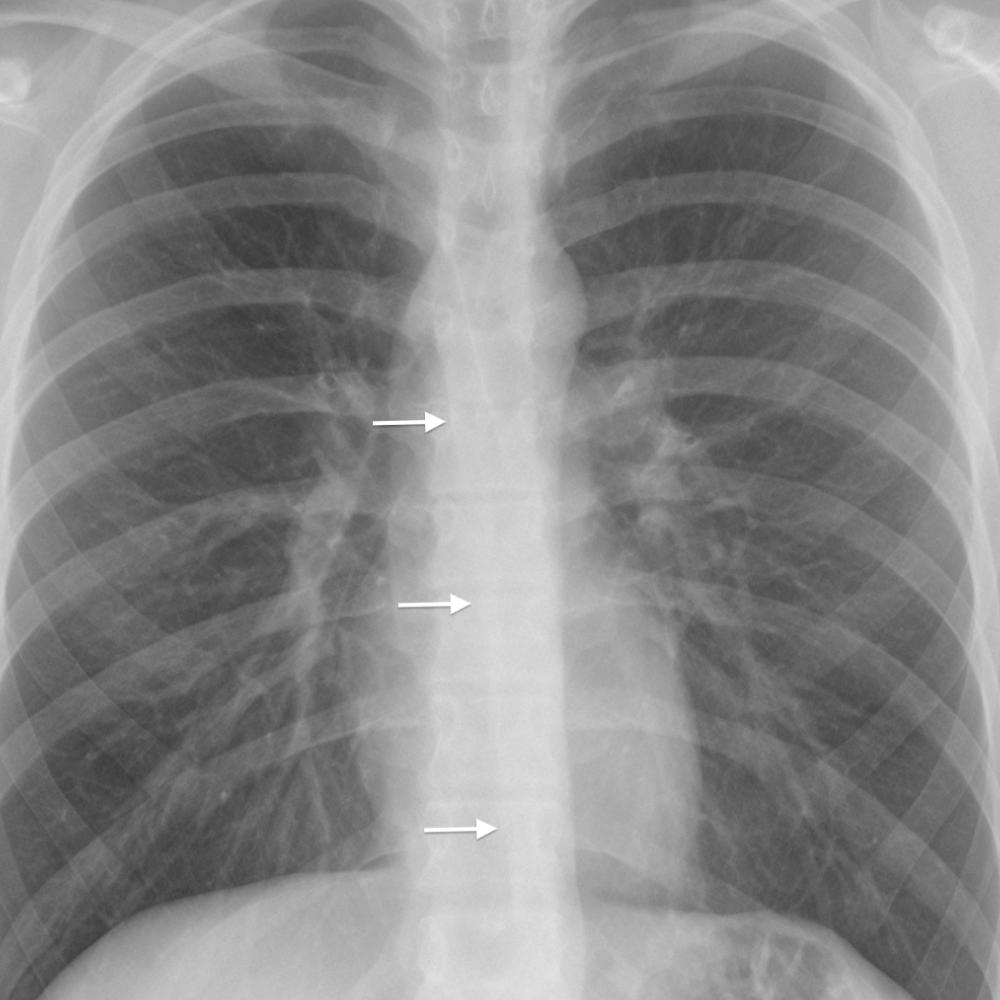
This is the name of the tagged structure below.
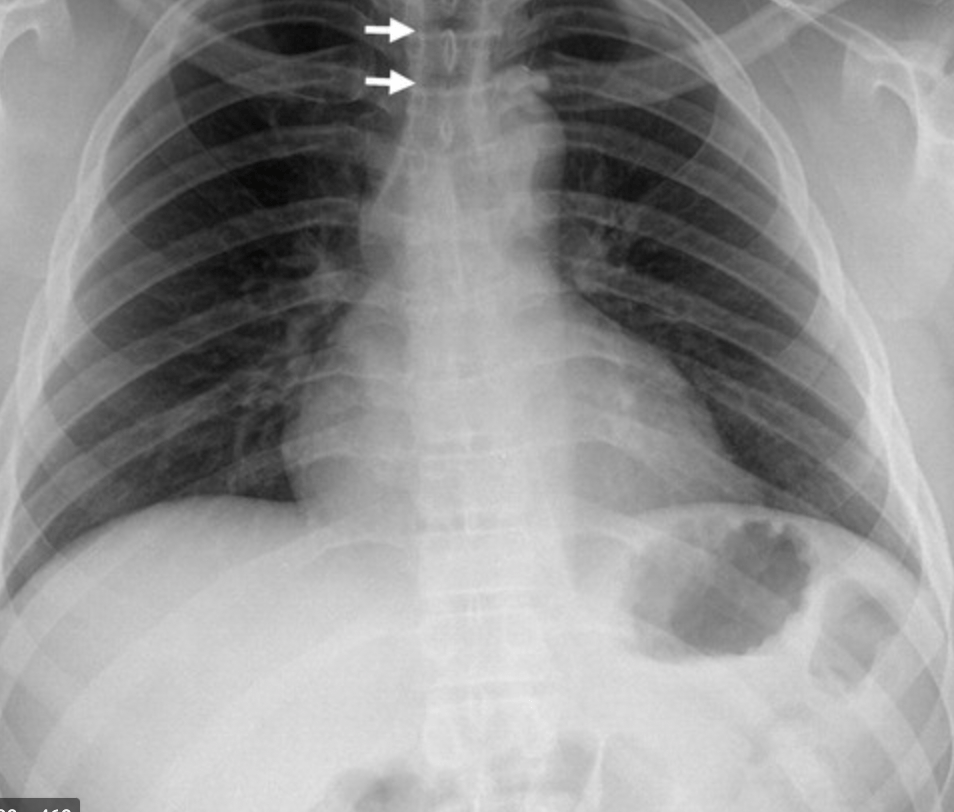
Right paratracheal line.
Distortion suggests Middle mediastinal mass.
The image finding below is classically found in this chronic irreversible lung disease.
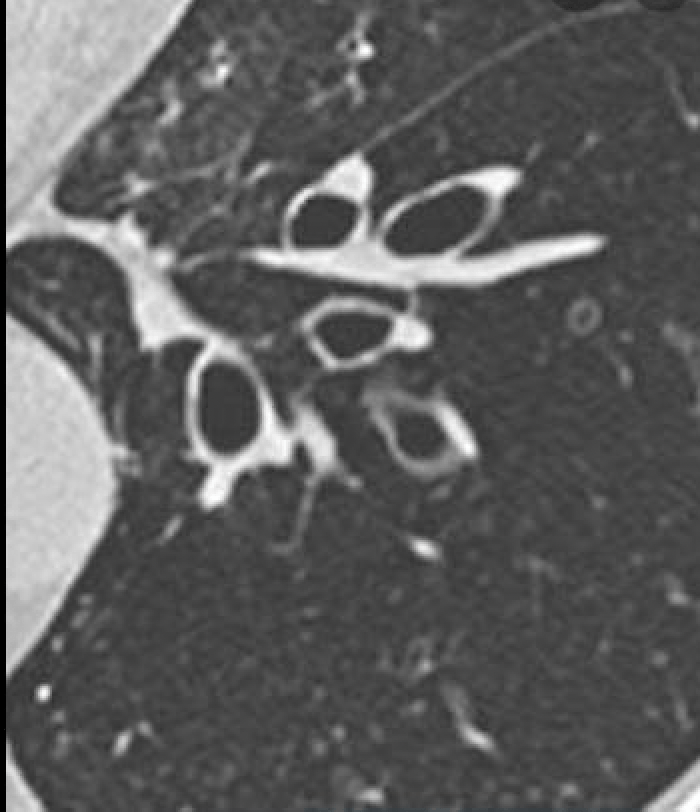
Bronchiectasis.
This is the signet ring sign- dilated bronchus next to accompanying pulmonary artery.
The name of the common finding on the image below suggesting a later stage of pulmonary fibrosis. 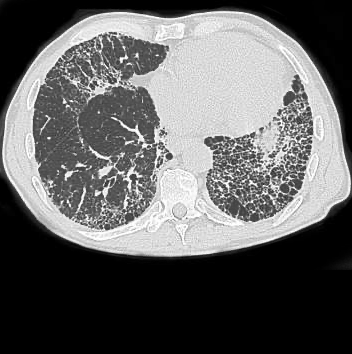
Honeycombing
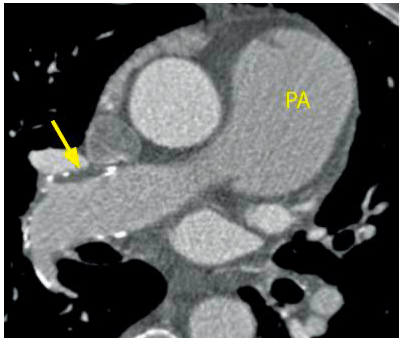
The name of the "sign" that shows widening of the pulmonary arteries due to clot burden.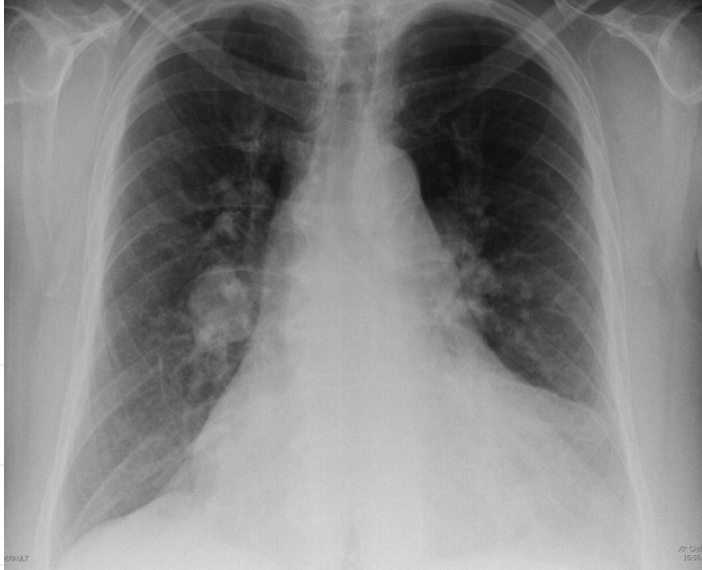
Fleischner Sign
According to the WHO, pulmonary hypertension caused by this mechanism is classified as Group 3.
Pulmonary hypertension secondary to chronic hypoxemia (COPD, sleep apnea, ILD)
This is the name of this structure.
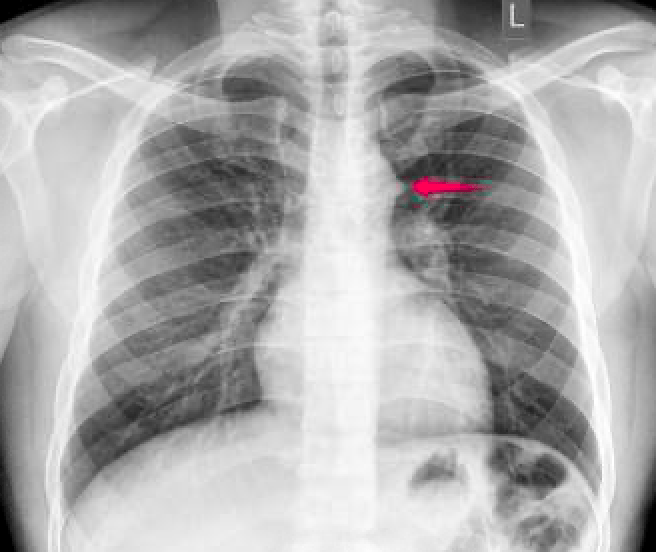
Aortic Nipple.
Fun fact: It represents the left superior intercostal vein.
This is the name of this type of emphysema shown below.
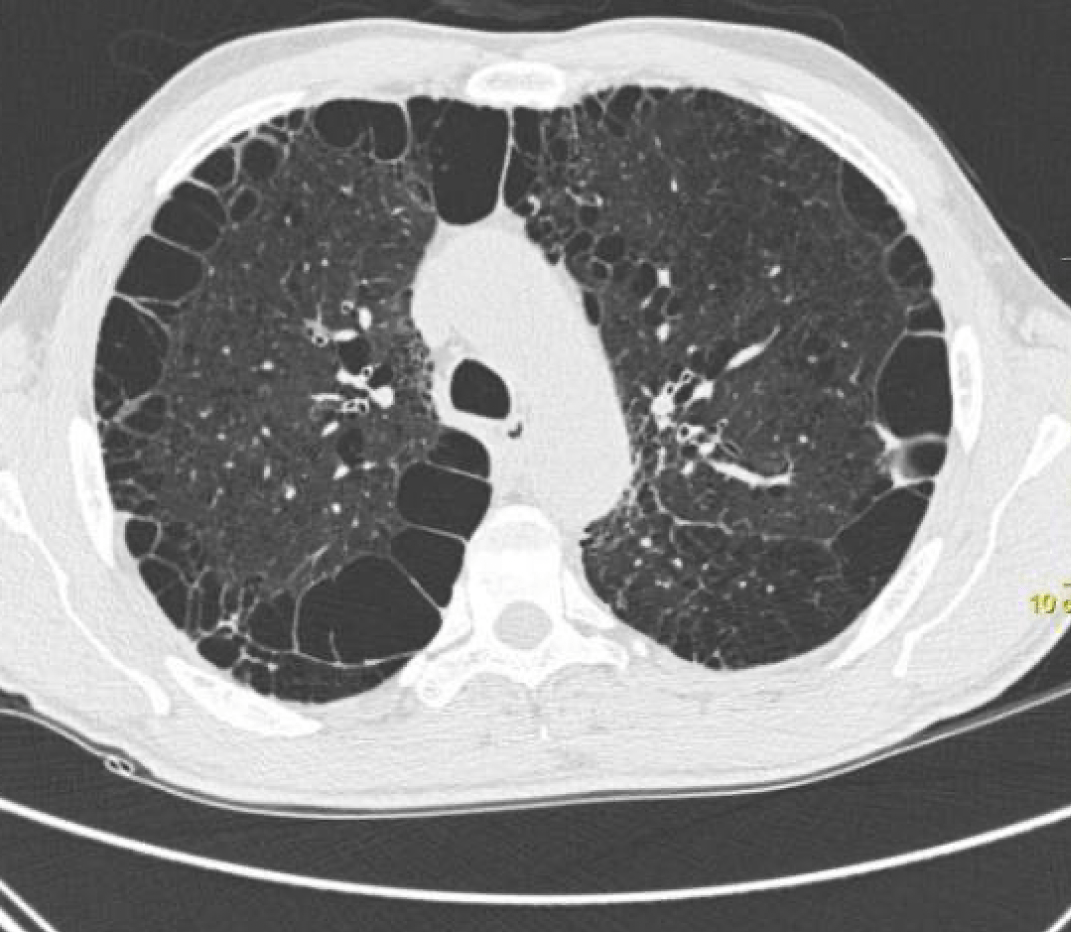
Paraseptal Emphysema.
These pathologic conditions could produce the pathology shown in this image. Name 2
1. Silicosis
2. Sarcoidosis
3. TB
4. Histoplasmosis
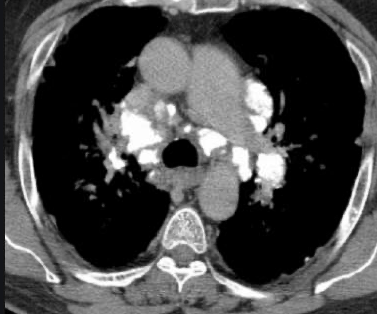
Representing right heart strain, elevation of this has a linear correlation with increased mortality.
RV:LV ratio
The imaging below would make it easy for you to suggest the patient had which condition, chronically?
Pulmonary Hypertension
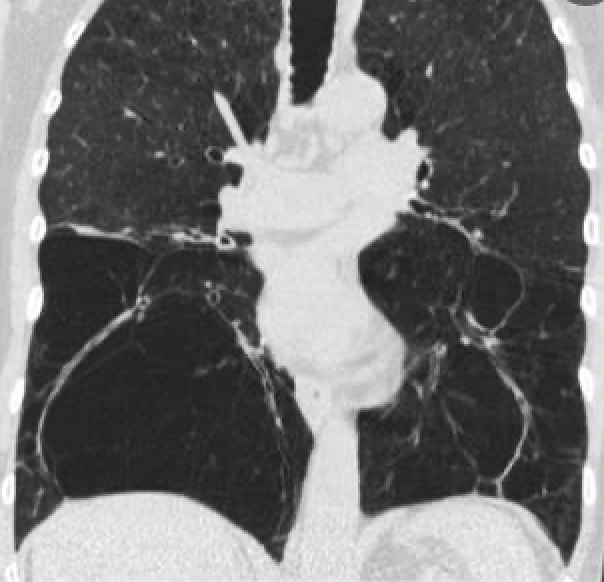
1. Name this line.
2. Name a pathology that could distort this line.
Azygoesophageal Recess.
Posterior mediastinal pathologies:
1. esophageal mass
2. hiatal hernia
3. left atrial enlargement
4. adenopathy
This type of emphysema imaged below occurs with the deficiency an anti-trypsin enzyme.
Panacinar or panlobular emphysema.
Name this sign.
Diagnosis?
1.Donut sign
2. Sarcoidosis
Name 2 findings that would suggest pulmonary embolism that can be seen on x-ray imaging.
1. wedge shaped consolidation
2. pleural effusion
3. linear bands of subsegmental atelectasis
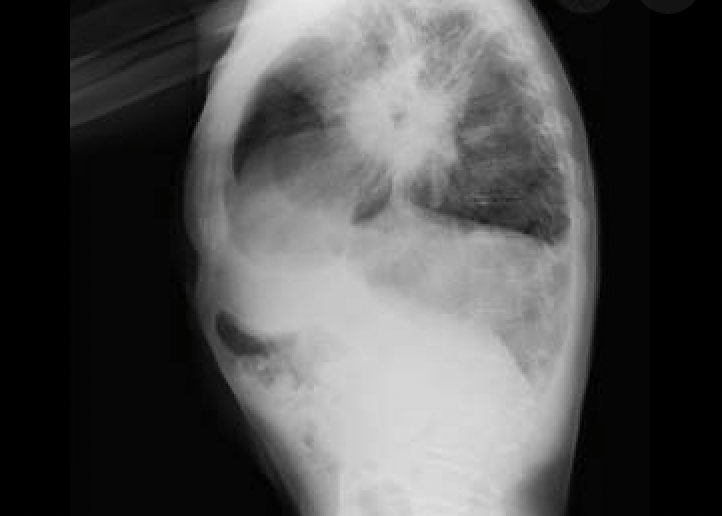
This smoking related disease will cause lung findings as shown below - upper lobe predominant cysts. (no, not emphysema)
Pulmonary Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis.
This is later stage with the natural progression being nodules-->cavitary nodules-->irregular cysts
Name the sign portrayed on this frontal radiograph. Which part of the mediastinum is this mass NOT in?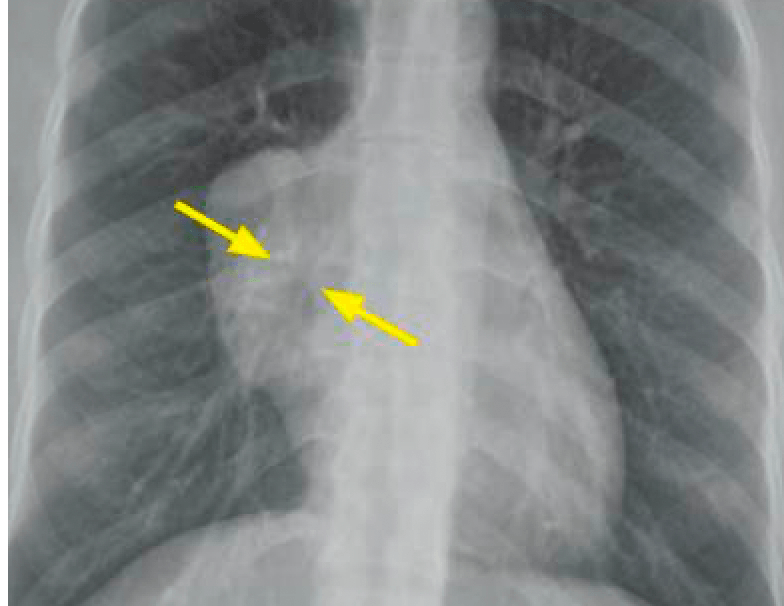
The hilum overlay sign.
The mass must not be in the middle mediastinum.
These are the three types of bronchiectasis..in order of increasing severity of disease.
1. cylindrical
2. varicose
3. cystic 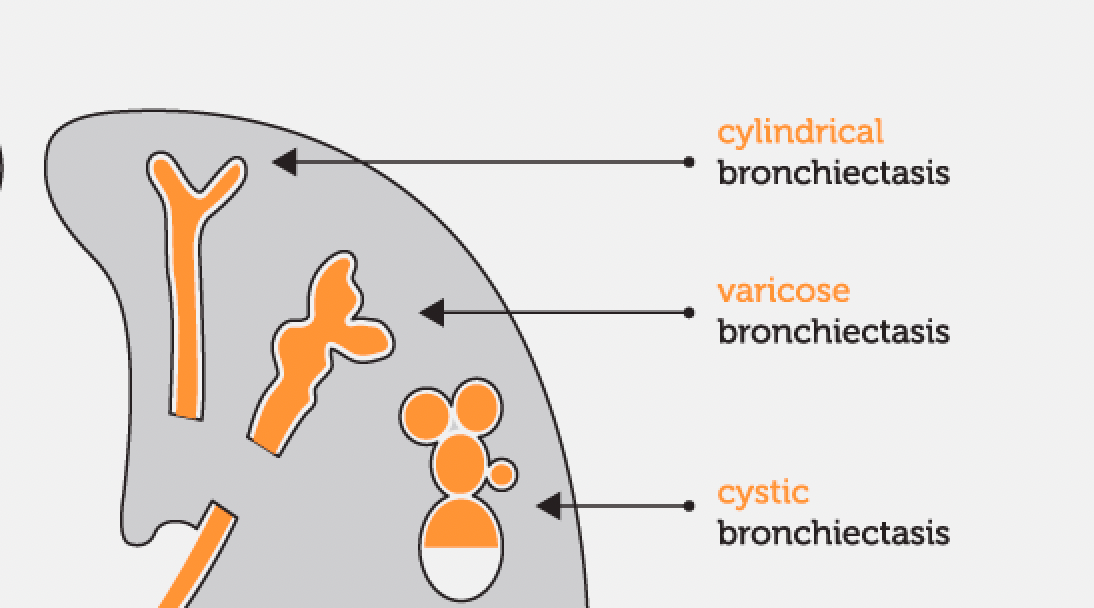
Seeing the sign below will prompt this diagnosis.
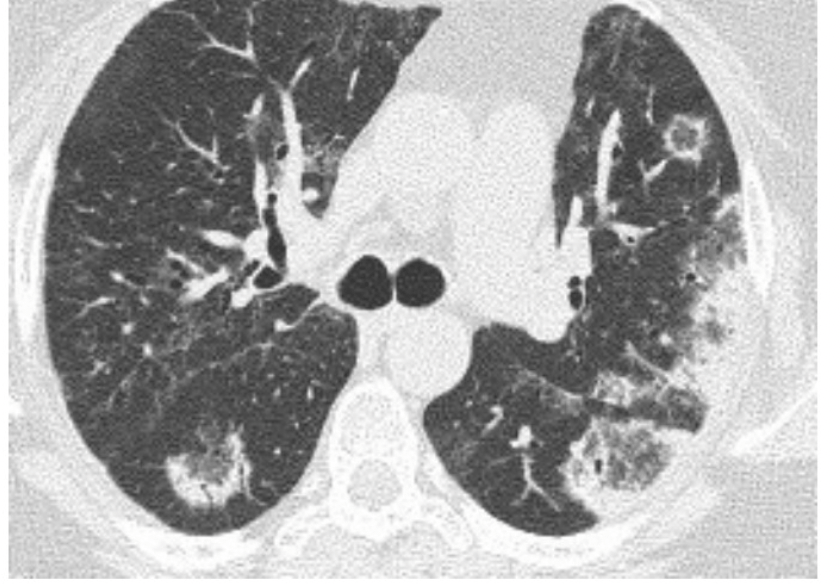
COP
These are the THREE classic signs of significant right heart strain post pulmonary embolism.
1. Elevated RV:LV ratio.
2. Bowing of the intraventricular septum into the left ventricle
3. right ventricular dilation
The image below shows the classic look of this type of interstitial pneumonia when immune cell infiltration causes alveolar distortion.
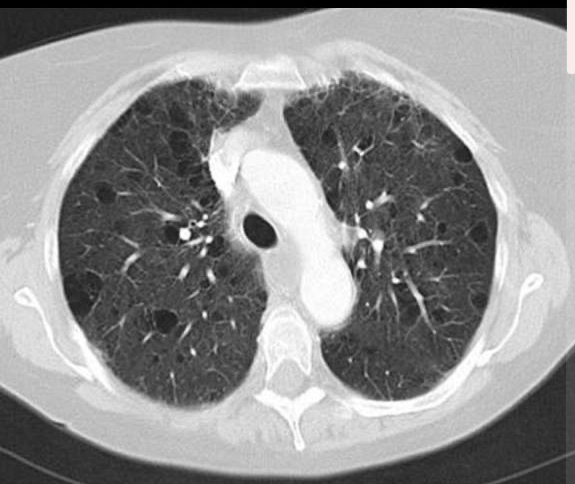
Lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia (LIP)
Associated with Sjogrens syndrome or HIV.
What compartment of the mediastinum is this mass, associated with myasthenia gravis, located in? Diagnosis?
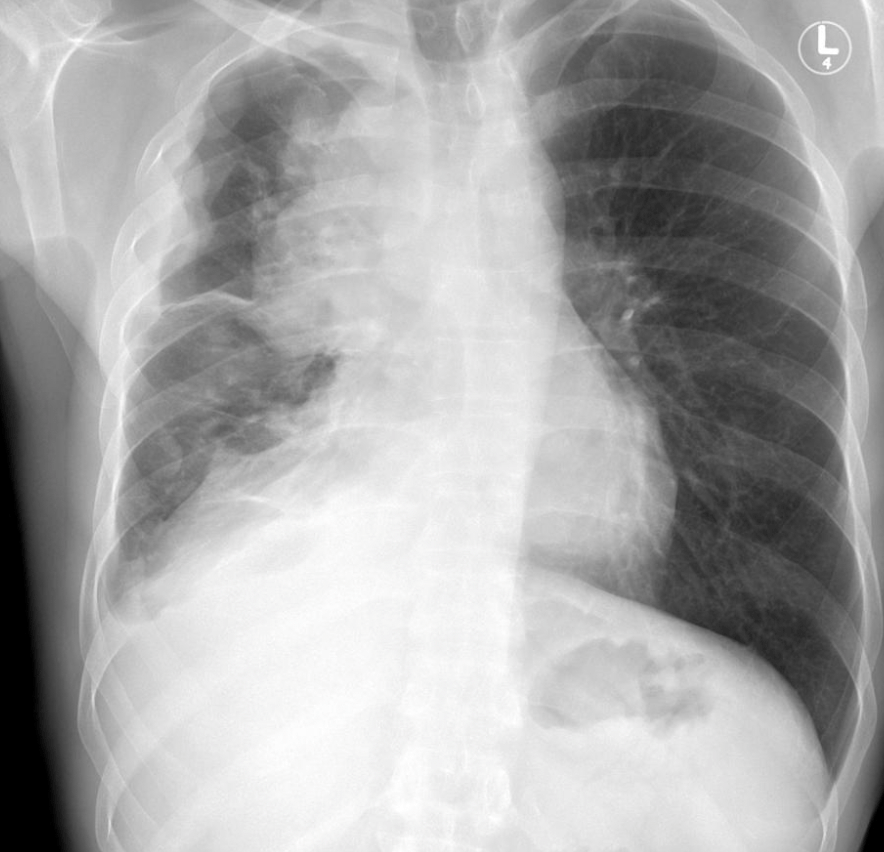
Anterior Mediastinum. Thymoma.
This relatively rare endobronchial tumor shown below can cause increased cortisol levels in your blood.
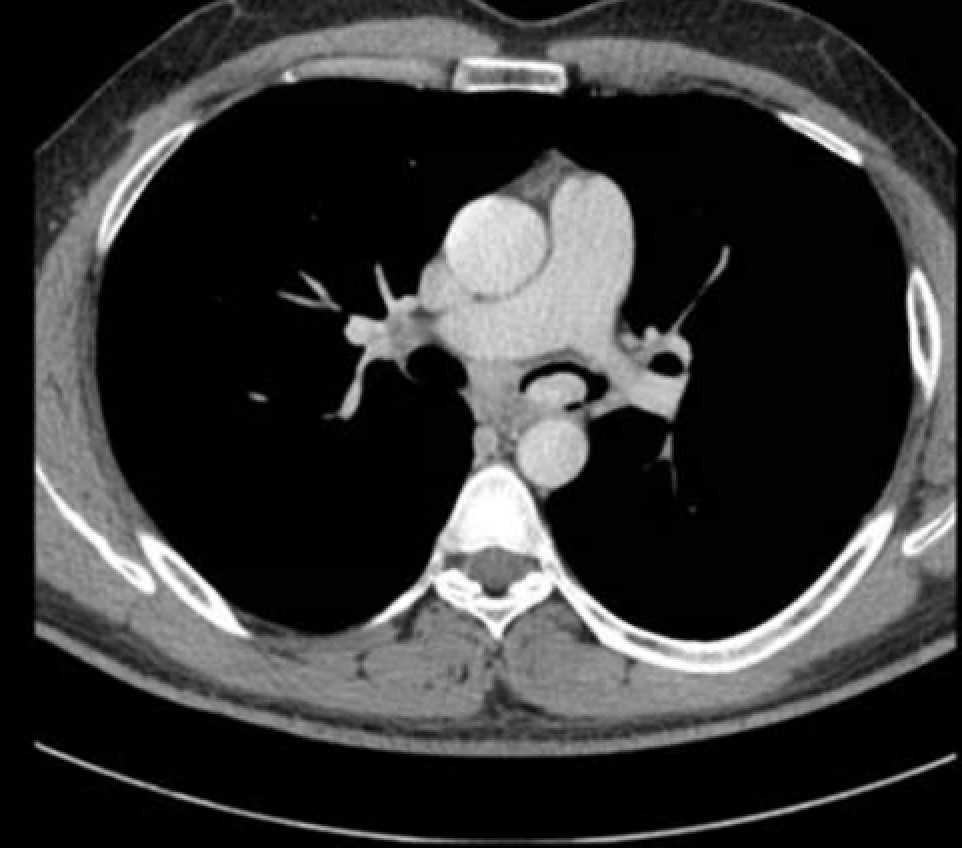
Carcinoid.
Fun facts:
Cacinoid is rare in adults,however, it is the most common bronchial tumor in children.
Carcinoid almost always occurs distal to the carina.
CT shows an endoluminal bronchial mass with homogeneous arterial enhancement.
1. Name the sign.
2. Diagnosis?
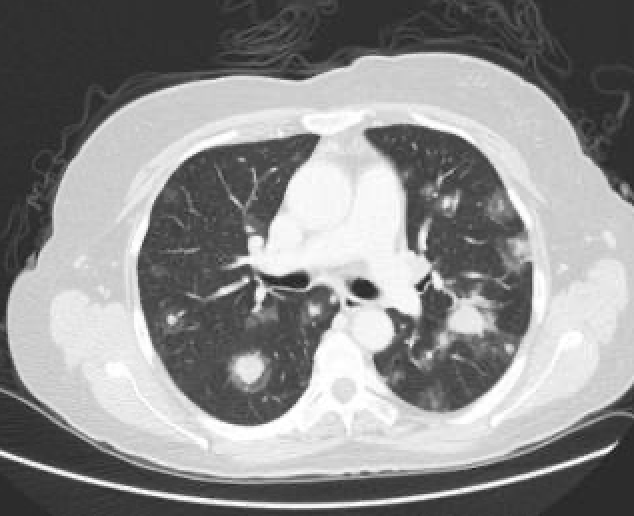
1. Halo Sign
2. angioinvasive aspergillosis