What are actionable genes?
If there is therapy to improve life and reduce symptoms caused by pathogenic mutations (variants) in a gene, that gene is actionable.
What is the central dogma?
DNA in a gene is transcribed into mRNA that is then translated into a protein.
Jews are divided into three groups (descendants of tribes). What are their names and ancient roles.
Kohen--priests
Levi-- served in the temple
Israelites- everyone else, the common people
What does mRNA stand for?
messenger RNA
What was one of the things Norman repeatedly told his daughter (the author?)
Do your best and leave the rest.
OR
Aim to be satisfied.
How is the chance of a gene causing illness categorized when it is sequenced?
Benign, likely benign, of uncertain significance, likely pathogenic, pathogenic
What is an exon?
The DNA sequence in a gene that codes for a protein.
What is a mitzvah? Give an example.
A commandment from God to be followed e.g. honor your parents
What does rRNA stand for?
Ribosomal RNA
What did the author's sister Diane tell the parents of her students?
Celebrate your child.
What are introns?
DNA sequences inserted into genes that need to be spliced out before the mRNA can be translated into the protein.
What is an afikomen?
Piece of matzah hidden and ransomed by children during the Passover seder. It is broken and shared with everyone at the table as the final dessert at the end of the festive Passover meal.
What does DCM stand for?
dilated cardiomyopathy
Who liked to say, "This too will pass."
The author's mother Cyrilla
What is the difference between genetic testing and genetic screening?
Genetic testing is in response to family history or a disease or symptom in patient likely to be caused by a gene mutation (pathogenic variant.)
Genetic Screening is done without above causes to catch unknown mutations.
Why is yeast a better model to use to study human disease than bacteria?
Yeast cells have a nucleus just like human cells, but bacteria don't have a nucleus.
What was the 1949 Operation Magic Carpet (also called On Wings of Eagles)?
Israel airlifted 45,000 Yemenite Jews to Israel.
What does ACMG stand for?
American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics
Who is the child in this picture and how did he die?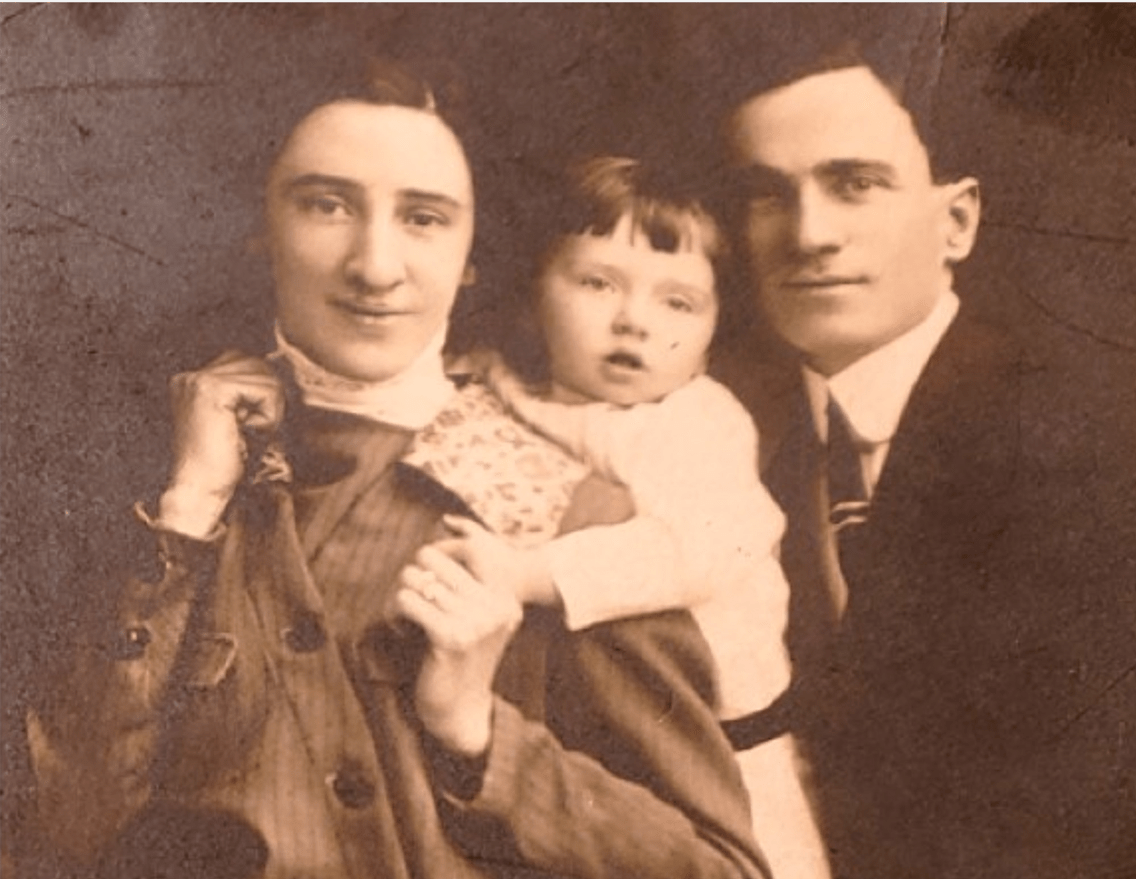 
The author's uncle Eugene who died of heart failure.
What is cascade genetic testing?
Testing relatives for a patient's mutation and if they have the mutation testing their relatives until no more people with the mutation are found.
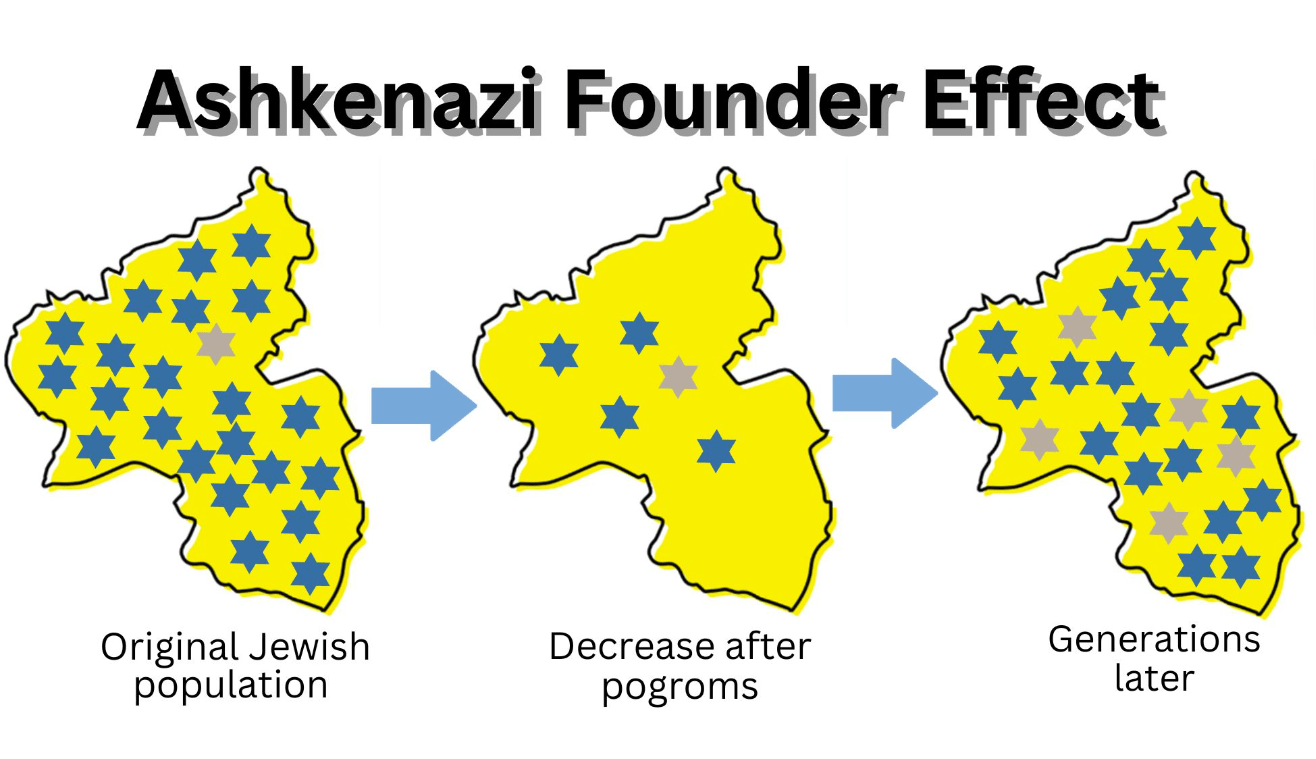
What are founder mutations?
Founder mutations begin when persons with a rare mutation in an isolated community survives by chance when the size of community is dramatically reduced. Then subsequent intermarriage within the isolated group results in a larger fraction of the community descendants having the mutation.
What does the term kosher refer to? Give a few examples.
Kosher refers to laws about what you are allowed to eat. Eating meat from pigs and shellfish are not allowed. Also, you can't eat a mixture of meat and dairy together.
What does GINA stand for?
Genetic Information Non-discrimination Act
Who are the kids in this picture?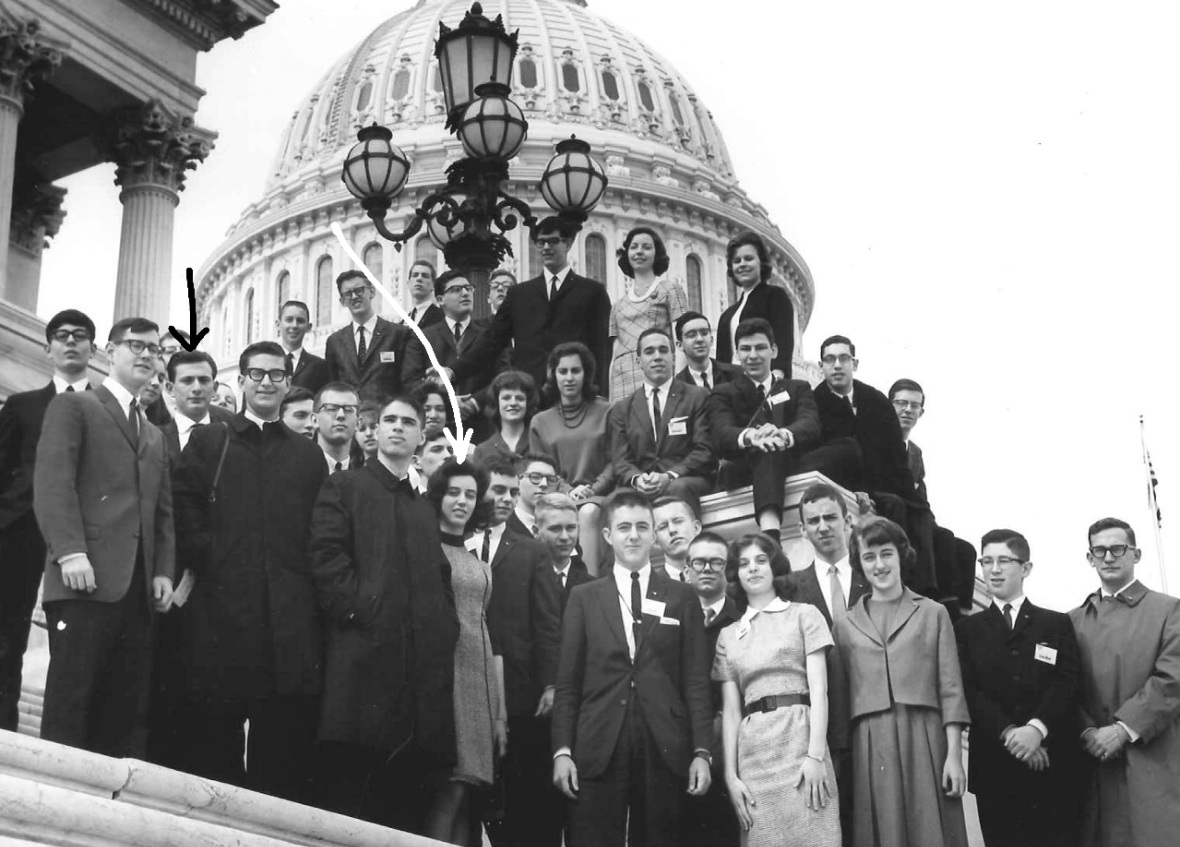 
1964 Westinghouse Science Talent search finalists on the capitol steps in Washington DC.