8; Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune
The movement of warmer air/fluids rising and cooler air/fluids sinking is called what?
Convection
What are the three layers of the Earth?
The crust, mantle and core
__________________ are any evidence of past life, including bones, teeth and shells.
Fossils
This type of scientist studies the stars, planets, galaxies and other celestial bodies.
Astronomers
Earth is found in a region of the solar system referred to as the ___________________.
Goldilocks zone OR Habitable zone
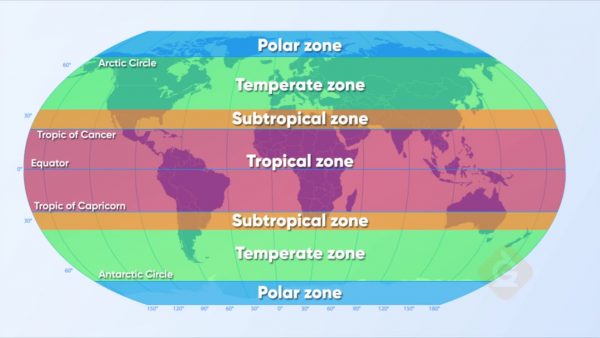 The Earth is broken into different climate zones. In which zone is the equator located?
The Earth is broken into different climate zones. In which zone is the equator located?
The tropical zone
What are the three types of rock?
Igneous, Metamorphic, and Sedimentary
The image shows the skull of a sabertooth cat. This type of fossil is an example of a __________ fossil, because it can provide evidence of what the animal ate (as evidence from its sharp pointed fangs).

Trace fossil
These type of scientists study the Earth and its structure, materials, and history.
Geologists
How do the planets stay in orbit around the Sun?
The planets stay in orbit around the Sun because of the Sun's gravitational pull. Since the Sun makes up 99.8% of the mass in our solar system, it pulls the planet into orbit around it. Each of the planets also have their own gravitational fields which cause moons and other smaller objects to orbit around them.

Between which lines of latitude is the Temperate zone in the Northern Hemisphere found?
Between the Tropic of Cancer (Above the subtropical zone) and the Artic Circle
Scientists track Earth's 4.6 billion year history using the ______________________.
Geologic time scale
The image shows two types of fossils for the same organism. The one on the left has been filled in with rock, and the one on the right is a hollow imprint of the organism. Which fossil is a cast fossil and which is a mold fossil?

The left is a cast fossil, the right is a mold fossil
This is the study of weather.
Why was Pluto reclassified as a dwarf planet?
Pluto is not big enough to clear other objects out of its orbit.
__________________ are winds that blow in one direction and move air masses around; they are caused by the uneven heating of air.
Prevailing winds
List and describe the three types of plate boundaries.
Transform boundaries - two plates slide past each other
Convergent boundaries - two plates crash into one another
Divergent boundaries - two plates slide apart from one another
 This "landfish" fossil is an example of a ______________ fossil, because it is provides evidence that animals moved from living in water to living on dry land.
This "landfish" fossil is an example of a ______________ fossil, because it is provides evidence that animals moved from living in water to living on dry land.
Transitional fossil
These scientists study evidence of past life in order to understand extinct species.
Paleontologists
Describe the difference between a solar eclipse and a lunar eclipse.
A solar eclipse occurs when the Sun, Earth and Moon are in alignement and the Moon covers the Sun. A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon moves into Earth's shadow.
This effect describes why air currents "bend" to the right or east in the Northern Hemisphere and is caused by the rotation of the Earth and the speed at which it does so at different latitudes.
The Coriolis Effect
List the 7 major tectonic plates. What types of natural disasters are common at the boundaries of these tectonic plates?
Pacific Plate, North American Plate, South American Plate, African Plate, Eurasian Plate, Indo-Australian Plate, Pacific Plate
Earthquakes and Volcanoes
The _______________________ provides evidence that organisms that are extinct today once existed. It also gives a chronological history for how organisms have evolved in water and on land.
Fossil Record
A ________________ studies volcanoes and volcanic phenomena. They may need to be familiar with plate tectonics in order t o understand their field fully.
Volcanologist