The study of life.
What is biology?
Classify the following genotypes.
Gg
Hh
Tt
Aa
What is heterozygous?
These scientists discovered the structure of DNA.
Who were Watson and Crick?
This scientist proposed the theory of natural selection.
Who was Darwin?
Put the following terms in order from MOST SPECIFIC to MOST BROAD.
community, ecosystem, species, biome, biosphere, individual
individual, species, community, ecosystem, biome, biosphere
Describe 2 difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
Eukaryotes: linear DNA, DNA in nucleus, have a nucleus
Prokaryotes: circular DNA, DNA in cytoplasm, nucleus absent
Classify BOTH of the following genotypes.
Row 1: AA, GG, TT, HH
Row 2: aa, gg, tt, hh
Row 1: homozygous DOMINANT
Row 2: homozygous RECESSIVE
Describe the difference between transcription and translation.
Transcription produces RNA from DNA. Occurs in nucleus.
Translation produces protein (sequence of amino acids) from RNA. Occurs in ribosomes/cytoplasm.
Darwin first discovered _______ in _______.
Describe the difference between autotrophs and heterotrophs and give an example of each.
autotroph - makes its own food (ex. plants)
heterotroph - gets energy / food from another source (ex. lion, human, bear, squirrel)
Describe the difference between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction.
Sexual produces genetic diversity.
Asexual makes copies / no genetic diversity.
A purple daisy and white daisy produce some offspring that are purple only and some that are white only. Classify this type of inheritance pattern.
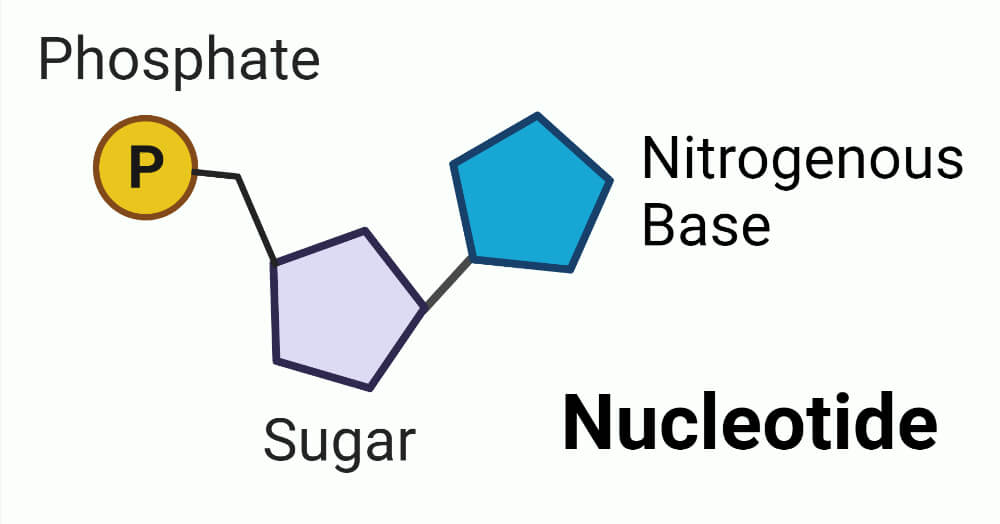
Draw a nucleotide. Label all 3 parts.
Describe and give an example of natural selection.
An organism adapting over time to their environment that increases chances of survival and successful reproduction.
Example: birds acquiring webbed feet in an environment after a flood
giraffe necks becoming longer over time
peppered moth wing color changing due to pollution
Describe a keystone species and give an example.
A species that plays a vital role in an ecosystem to maintain balance and control of populations of other organisms
ex. wolves of Yellowstone Park
Describe the difference between unicellular and multicellular.
Unicellular - single cell
Multicellular - more than one cell
A white daisy and purple daisy produce pink offspring. Classify this type of inheritance pattern.
What is incomplete dominance OR blended inheritance?
Answer 1: These are spliced together to make the final RNA product.
Answer 2: These are spliced out / removed from the final RNA product.
1: exons
2: introns
Describe the difference between analogous and homologous structures.
analogous - organisms that evolved along different paths that have structures with similar function but different appearance / structure
homologous - organisms that evolved along similar paths that have structures with different functions but similar appearance / structure
These limiting factors include but are not limited to disease, predation, space, and resources.
What are density-dependent limiting factors?
Name 3 characteristics of living things.
-need energy to carry out processes
-can reproduce
-can grow
-respond to stimuli
-dependent on environment
In a species of mice, black fur is recessive and white fur is dominant.
Complete a cross between a male mouse with black fur and a female mouse heterozygous for white fur. Include genotypic and phenotypic ratio for the offspring.
Punnett square to be drawn on board.
White - 50% Black 50%
Bb - 50%
bb - 50%
This enzyme unwinds the DNA double helix for replication to begin.
What is helicase?
This scientist developed the naming system for organisms.
Who was Linneaus?
Name the 3 symbiotic relationships, describe what they are, and give an example of each.
mutualism - both organisms benefit (clownfish and sea anemone)
commensalism - one benefits, the other is unaffected (manta ray and small aquatic organisms)
parasitism - one benefits the other is harmed (tick on a human or dog)