Which sentence below describes cultural diffusion?
A. Warships and armies from Japan attacked Korea.
B. Practices and beliefs spread from Korea to Japan.
C. Written languages developed separately in Japan and Korea.
D. Korea and Japan grew different crops because of different climates.
Practices and beliefs spread from Korea to Japan.
How did gagaku, a form of Chinese court music, influence music in Japan?
A. The Japanese hired Chinese musicians.
B. Japanese chants became more popular.
C. New musical instruments were used.
D. The Japanese sang only Chinese songs.
C. New musical instruments were used.
In Buddhist teachings, how does meditation help lead to wisdom?
A. by teaching the steps to a moral life
B. by emptying the mind of distracting thoughts
C. by providing a time to regret one's sins
D. by encouraging the study of books by enlightened teachers
B. by emptying the mind of distracting thoughts
Before the time of Prince Shotoku, Japanese government
A. ruled over Korea and China.
B. depended on local leaders.
C. had a bureaucracy of officials.
D. filled jobs based on examinations.
B. depended on local leaders.
What does Buddhism's moral code focus on?
A. expressed respect
B. acting correctly
C. using meditation
D. all of the above
D. all of the above
Emperor Tenmu and Empress Jito made changes in land ownership to strengthen imperial power. Who would have been most upset by these changes?
A. merchants
B. clan leaders
C. peasants
D. military leaders
B. clan leaders
The design of a Shinto temple would most likely draw attention to
A. a code of moral rules.
B. worship of foreign gods.
C. the cycle of pain and suffering.
D. respect for the beauty of nature.
D. respect for the beauty of nature.
After they learned about Chinese writing, the Japanese
A. changed their grammar to be more like Chinese.
B. began speaking Chinese in everyday conversation.
C. invented a new set of characters based on objects in Japan.
D. used simplified Chinese characters for sounds in Japanese words.
D. used simplified Chinese characters for sounds in Japanese words.
Which of the following city features did Nara and Chang'an NOT share?
A. checkerboard pattern streets
B. Buddhist temples
C. protective wall
D. imperial palace
C. protective wall
What kind of architectural design did the Japanese adopt when Buddhism arrived in Japan?
A. the stupas design
B. the tanka design
C. the kanji design
D. the pagoda design
D. the pagoda design
What Indian architectural feature inspired pagodas?
A. kanjis
B. tankas
C. stupas
D. arches
C. stupas
In the late 7th century, Japanese land was taken from the clans and given to the emperor who
A. redistributed it to free men and women.
B. divided it into various different regions.
C. gave it to wealthy government officials.
D. sold it to other countries at high prices.
A. redistributed it to free men and women.
When Korean workers settled in Japan, how did they change the lives of the Japanese?
A. They set up a new government over the country.
B. They advised the emperor on government policy.
C. They brought knowledge and skills from the mainland.
D. They became the customers who bought Japanese crafts.
C. They brought knowledge and skills from the mainland.
How can one tell whether a Japanese poem is a tanka?
A. by counting the syllables in each line
B. by identifying the social class described
C. by analyzing the symbols described
D. by checking whether pairs of lines rhyme
A. by counting the syllables in each line
If a visitor compared the Chinese capital Chang’an and the Japanese capital Nara, what difference might the visitor notice?
A. Nara lacked a wall for protection.
B. Nara lacked an imperial palace.
C. Nara lacked religious temples and monasteries.
D. Nara lacked an orderly street pattern.
A. Nara lacked a wall for protection.
How many syllables does a tanka poem have?
A. 5
B. 10
C. 17
D. 31
D. 31
As a result of foreign influence, the Japanese began creating sculptures of
A. Shinto kami.
B. emperors.
C. the Buddha.
D. armored warriors.
C. the Buddha.
A Japanese sho (which came from a Chinese sheng) sounds like
A. cither.
B. a phoenix.
C. an owl.
D. a panda.
B. a phoenix.
The form of Chinese court music that arrived to Japan in the 6th century is called
A. sheng.
B. gagaku.
C. phoenix.
D. pagoda.
B. gagaku.
What is one important way in which Prince Shotoku changed Japan?
A. He turned it into an agricultural society.
B. He divided power among the chiefs of clans.
C. He increased contact with neighboring cultures.
D. He introduced the craft of bronze and iron smithing.
C. He increased contact with neighboring cultures.
A central teaching of Mahayana, the form of Buddhism that reached Japan, was that
A. life on Earth is the only life.
B. all people can reach nirvana.
C. all buddhas hold false beliefs.
D. only the material world is real.
B. all people can reach nirvana.
Prince Shotoku’s creating ranks for government officials was based on
A. Shinto ideas.
B. Muslim ideas.
C. Buddhist ideas.
D. Confucian ideas.
D. Confucian ideas.
Which of the following is true of Japan during Empress Suiko and Prince Shotoku's reign?
A. Japan's power was divided among chiefs.
B. Japan had a rural agricultural society.
C. Women had a relatively high status.
D. all of the above
D. all of the above
The dots on the timeline show about when Buddhism arrived in four different countries: India, Korea, China,
and Japan. Based on the timeline and your knowledge, where did Buddhism arrive between 1 and 500 C.E.?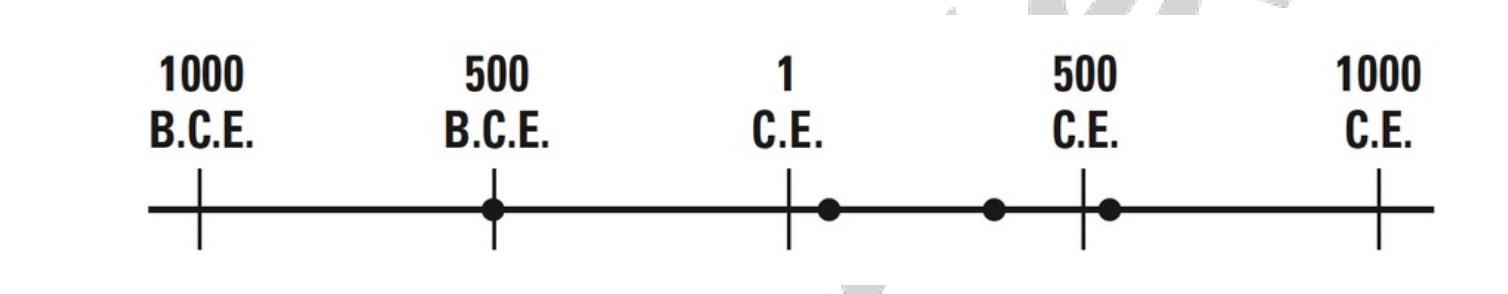
A. India and Japan
B. India and China
C. Korea and Japan
D. China and Korea
D. China and Korea
Which architectural style did Japanese Buddhists adopt for their temples?
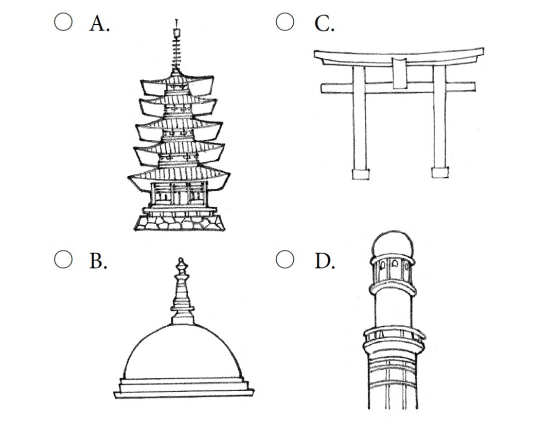
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
A