Prior to the 14th century, what was the region of Western Europe called?
Christendom
After the ‘Fall of Rome’, who or what filled the power vacuum left from the collapse of the classical world in Western Europe?
The Medieval Catholic Church!
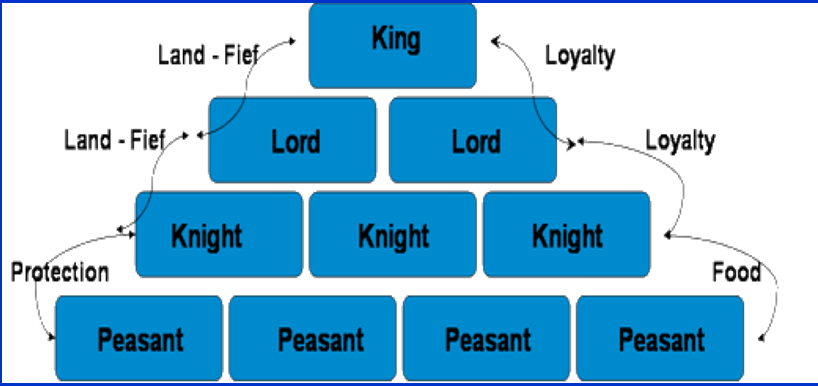
A political, economic and social system in the Middle Ages that was based on loyalty and military service
Feudalism
The forged document that gave popes a claim to rule Western Europe as a whole
The Donation of Constantine
This is an example of what type of architectural style?
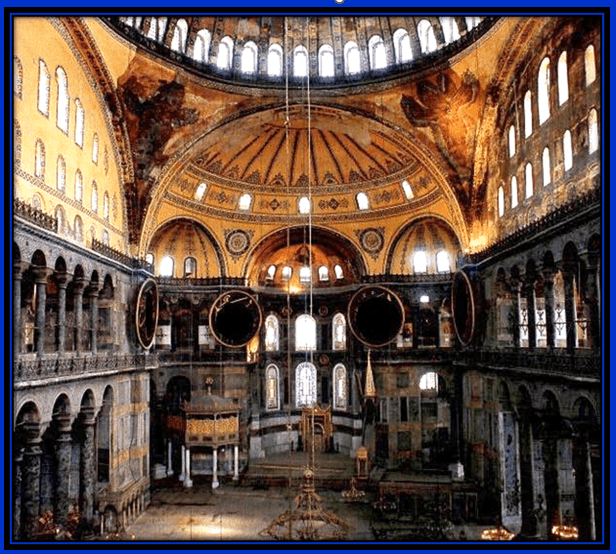

Byzantine Architecture
This empire has traditionally acted as a ‘buffer’ between East and West
Byzantine Empire
Explain 3 major factors in the religious break between the Eastern and Western Christian churches
The Great Schism: 1054
* Question of Doctrinal Authority & Papal Primacy
* Latin v. Greek?
* Iconoclastic controversy
* Disagreement over the Nicaean Creed
* Can priests marry?
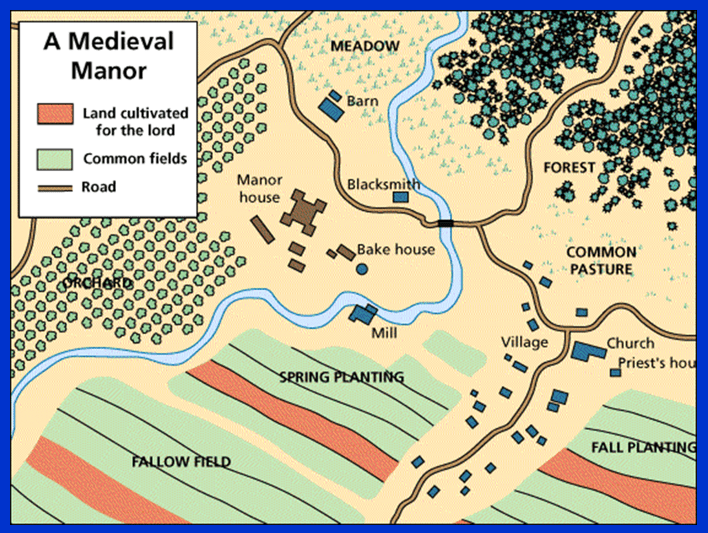
The agrarian economy of the Middle Ages was organized and controlled through these village farms:
Manors
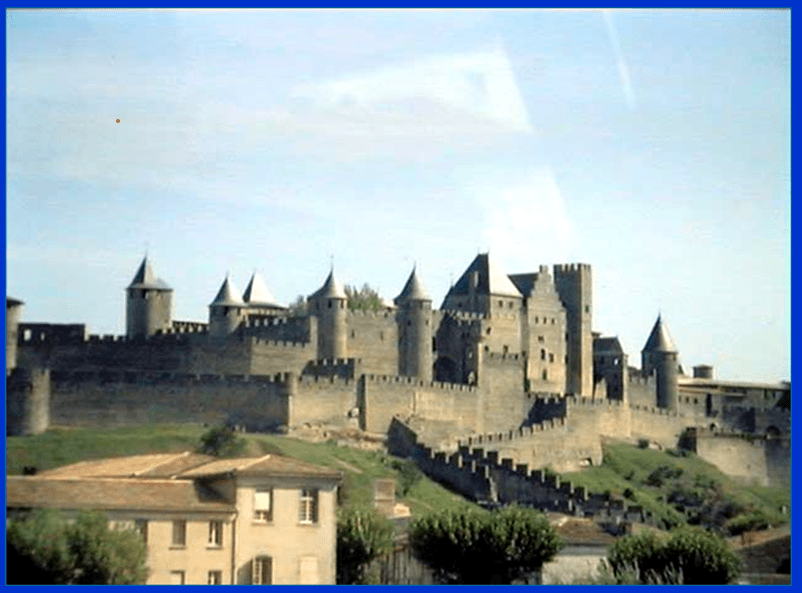
Life for nobles during the Middle Ages revolved around this place:
The Castle

This is an example of an _____.

Icon
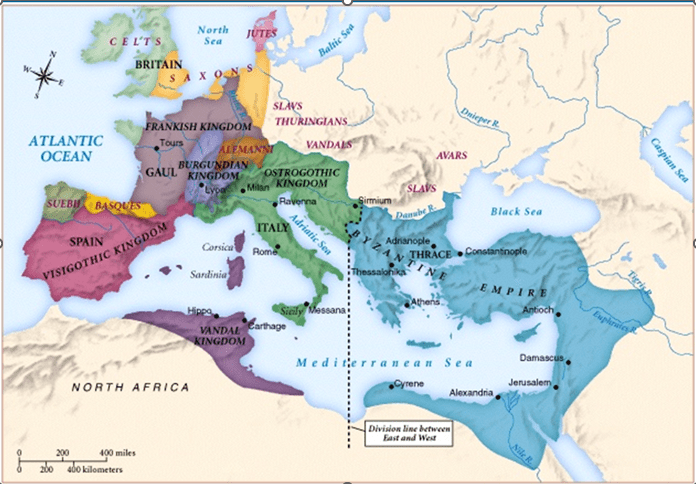
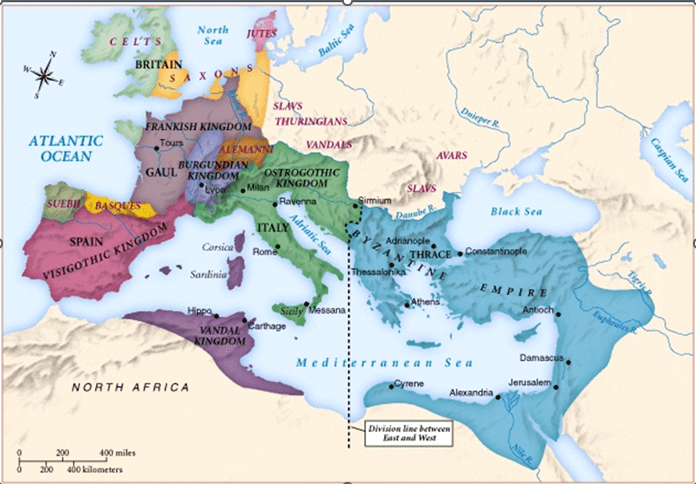
Germanic tribes invaded Western Europe, eventually leading to the Fall of Rome in 476. Name 3 of these ‘Gothic’ tribes and where they settled in the West.
Gothic Tribes:
The Franks in Gaul, the Anglo-Saxons in Britain, the Visigoths in Spain, Vandals in N. Africa, Lombards in Italy
What was the significance of Charlemagne being crowned ‘Holy Roman Emperor’ in 800?

Legacy of Charlemagne:
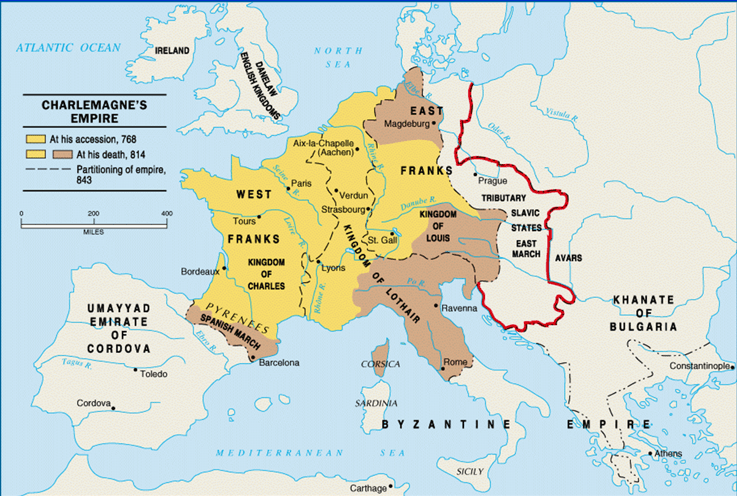
In both Western Europe and Byzantium, the majority of the population was made up of ______________.
Dependent farmers
In Medieval Europe, these became the centers of learning:
The Monastery

Describe three classes you might have taken at a medieval university

A Medieval University Curriculum:
* Logic
* Philosophy
* Greek
* Law
* Medicine
The last gasp of unity between East/West Europe came under Emperor Justinian (527-565). How did he try to hold the empire together?
(1) Corpus Juris Civilis: common law code in >1500 cities: (provides the foundation for most subsequent European law down to the 19th C!)
(2) Imposed Orthodox Christianity
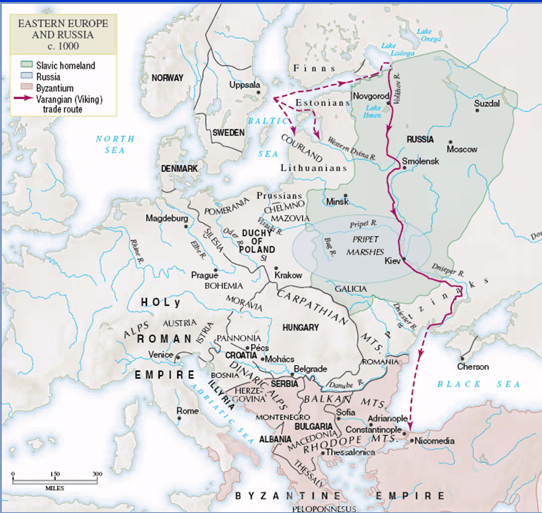
When the Eastern European state of Kievan Rus began to interact with the larger world, Prince Vladimir of Kiev chose this religion to unite his diverse population
Eastern Orthodoxy
The language of commerce in the East
Greek
This language remained the hallmark of educated people in the West well into the 20th Century
Latin
Name this architectural style:
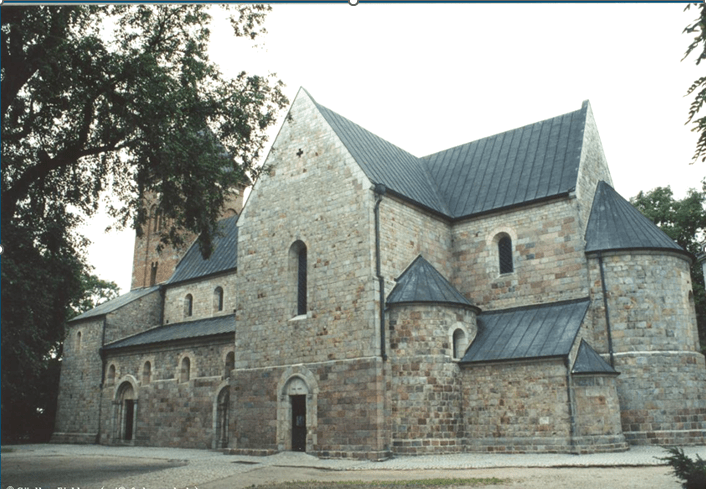

Romanesque Architectural Style:
•Rounded Arches.
• Barrel vaults.
• Thick walls.
• Darker, simpler interiors.
• Small windows, usually at the top of the wall.
Following the Germanic tribes’ westward march, the dominant people of Eastern Europe (the Slavs) migrated from this region all the way to the Peloponnesus in Greece.
Kievan Rus (Russia)
What were 3 consequences of the Crusades?
Consequences:
* Church and papacy lost prestige
* Weakened the Byzantine Empire, accelerated its fall
* Thousands of children sold into slavery
* Reopened trade routes
* Revival of cities, monied economy in the West
The term for a decline in the number of inhabited cities
Ruralization
This Germanic Kingdom became the dominant power in Western Christendom
The Franks
To whom does Western society “owe” for introducing scientific achievements such as astronomy, mathematics and irrigation techniques, and making this knowledge available during the Renaissance of the 1400s?
The Arab Islamic World