This Greek philosopher is responsible for some of the earliest theories about the Moon including the fact that it is round and that it is located closer to the Earth than the Sun.
What are the light and dark regions on the lunar surface called?
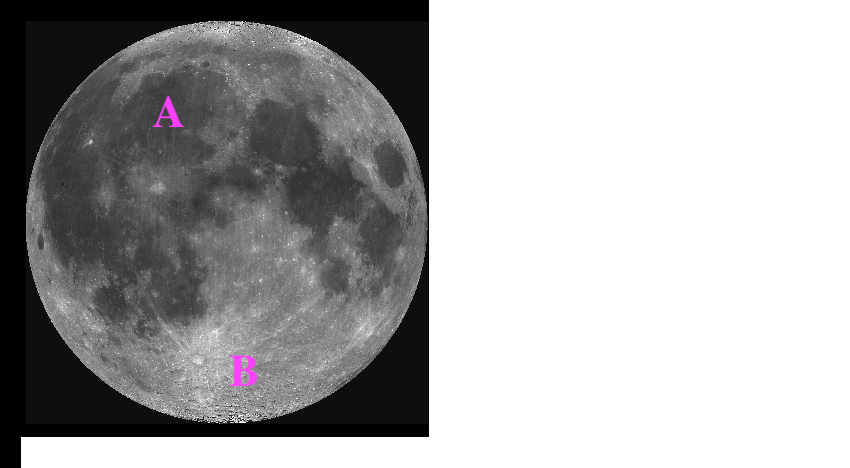
A - Mare
B - Highlands
You look out one night and see a full moon. Why?
The Moon is opposite the Sun as seen from Earth so the entire dayside is visible.
Describe the orientation of the Sun, Moon, and Earth during a lunar eclipse and during a solar eclipse.
Lunar: Sun - Earth - Moon
You see the same half of the moon in the sky every night (sometimes less depending on which phase the moon is currently in). Why?
The Moon is tidally locked with the Earth.
Galileo was responsible for which notable achievements with regard to the Moon?
1. Made the first telescopic observations of the moon.
2. Drew the first accurate pictures of the lunar surface.
How did mare form on the lunar surface?
Formed when lava flowed into impact basins and solidified between 4.2 and 1.2 billion years ago.
You look outside one night and see a Full Moon. Two nights later, you look outside and see the Moon pictured below. What phase is this?
Waning gibbous
What is the difference between a total solar eclipse and an annular solar eclipse?
In both eclipses the Moon is directly in between an observer on Earth and the Sun. In a total solar eclipse, the Moon is able to complete block out light from the sun. This happens when you are in the umbra shadow cast on Earth's surface, called the path of totality. In an annular solar eclipse, the moon is also directly between the Earth and the Sun but it appears too small and doesn't completely block out the sun.
Why is the Moon tidally locked with the Earth?
It takes the same amount of time for the Moon to rotate on its axis as it does for the Moon to make a complete orbit around the Earth (29.5 days).
The Earth has ___ times more gravity than the Moon.
6
What do we call the boundary between the sunlight and dark sides of the moon? How far does this boundary move each day?
Terminator
12o
What term is given to describe the variation in the apparent position of the moon each night (why does it appear to wobble in the night sky over time)?
Libration
Describe how the appearance of the Moon changes during a lunar eclipse. Be specific with your terminology.
Moon passes through the penumbra of the Earth’s shadow and darkens slightly
Moon enters the umbra of the Earth’s shadow and all direct sunlight is blocked
Longer wavelengths of light (red) are scattered around the Earth and the moon appears reddish/orange
Moon re-enters the penumbra and darkens again
Is the Earth tidally locked with the Moon?
No. Only the Moon is tidally locked with the Earth, meaning we only see one side of the moon. There is a "far side" that is not visible to us from Earth.
What is the Giant Impact Hypothesis?
Theorizes that a Mars-sized object called Theia collided with Earth 4.5 billion years ago and created a large ring of debris around Earth which eventually coalesced together to form the Moon.
How much of the lunar surface is illuminated by the Sun at all times?
1/2 of the Moon is illuminated by the Sun at any given point.
Describe the difference between a waxing and a waning phase.
The waxing phases occur when the Moon is transitioning from a New Moon to a Full Moon. The waning phases occur when the Moon is transitioning from a Full Moon back to a New Moon.
How often does any given point on Earth experience a total solar eclipse? In other words, if Charleston experienced a total solar eclipse in 2017, when will the next total solar eclipse occur in our city?
What would it mean if both the Earth and the Moon were tidally locked to one another?
The same sides of the Earth and Moon would always face one another. The same half of the Moon would be visible from Earth at all times but only half of the Earth would ever see that face.
Compare and contrast the capture and fission hypotheses.
Capture hypothesis- the Moon traveled by the Earth and got stuck in its gravitational pull
Fission hypothesis- rapidly spinning Earth expelled a piece of its mass shortly after the planet formed and the ejected piece stayed in orbit
When the moon is at its _____________, we see a "supermoon" that is bigger and brighter than it normally is.
Perigee
Describe where the Moon is located relative to the Earth and the Sun during a quarter moon and what it would look like at this phase.
The Moon would be perpendicular to the Earth and Sun. You see 1/2 of the illuminated side of the Moon in this phase so you're seeing 1/4 of the entire lunar surface.
How much farther from the Earth is the Sun than the Moon? What does this have to do with eclipses?
The Sun is 400 times farther away from the Earth than the moon and is also about 400 times larger than the Moon. This allows for a total solar eclipse to occur where the Moon completely blocks the Sun from view.
How do the near side and the far side of the moon differ in appearance?
The far side is covered in impact craters and basins. The near side has craters but is also covered in the mare.