bones apart of the axial skeleton
skull vertebrae ribs
Bones apart of the appendicular skeleton
Appendicular skeleton: along the sides of the body including pectoral girdle (shoulder), pelvic girdle (hips) and their attached limbs – arms and legs
What does ricer stand for
- Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation, Referral
- What are the two main types of causes of musculoskeletal injuries?
Intrinsic and Extrinsic
what do we call an injury caused by an external force like a collision?
direct injury
What is osteoarthritis and how does it affect joints?
A chronic degenerative joint disease where cartilage deteriorates causing pain and stiffness
- Name two physiological strategies used to prevent musculoskeletal injuries.
5 parts of the spine
Cervical:
Thoracic:
Lumbar –
Sacrum –
Coccyx –
Give an example of a ball and socket joint
Shoulder, hip
- How are ligament sprains graded?
- Grade 1 (mild), Grade 2 (moderate), Grade 3 (severe)
- What type of injury occurs suddenly, like a sprained ankle from landing awkwardly?
- B) Acute injury
- Name the two main ways musculoskeletal injuries can be classified based on how they occur.
- Direct injuries and indirect injuries
Give three examples of protective equipment used in sport.
- Helmets, mouthguards, padding, guards, footwear
- What does the RAMP warm-up protocol stand for?
- Raise, Activate, Mobilise, and Potentiate
What is a ligament
Join bone to bone
What type of bone is a vertebrae?
irregular
- Name two things to avoid in the early stages of injury according to the No HARM protocol.
- Heat and alcohol; running and massage
How they occur, when they occur, what they are
How = Intrinsic and extrinsic
When= Indirect and direct
What = Acute, chronic, overuse, fractire, sprain, strain, dislocation
- Give an example of an indirect injury.
ankle sprain
muscle strain
- What are three purposes of using taping during physical activity?
- Prevent injury, improve joint stability, reduce injury recurrence, correct biomechanics, enhance proprioception, relieve pain
- List two benefits of a cool-down after exercise.
- Aid recovery, prevent muscle stiffness, promote flexibility, reduce DOMS risk
What are antagonistic muscles?
pairs of muscles acting against each other to produce movement in opposite directions e.g. biceps & triceps
how many bones in the body
206
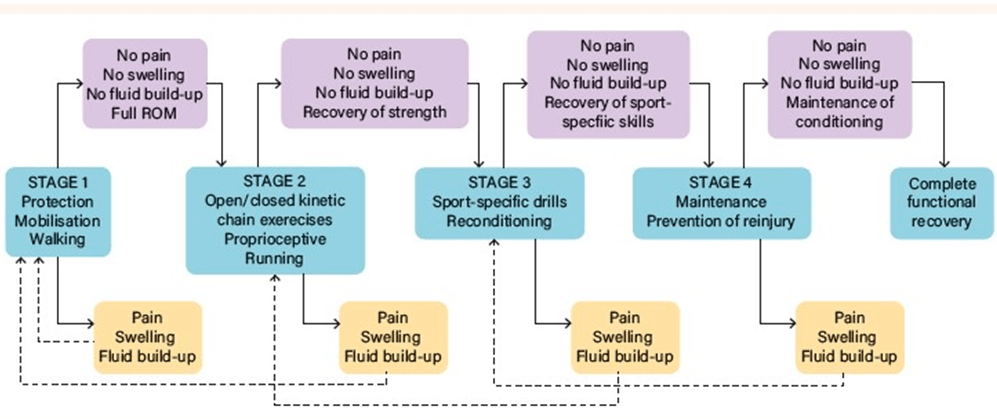
- What are two examples of rehabilitation strategies used to support recovery?
- What is the primary cause of overuse injuries?
Repetitive stress without adequate recovery
- How are chronic injuries mainly caused?
- Repeated overuse without adequate rest
What causes osteoporosis and what risk does it increase
- Decrease in bone mineral density, increasing fracture risk
- What causes Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness (DOMS)?
- Microscopic tears in muscle fibers caused by eccentric contractions
What do triceps do in the antagonist pairs do?
Triceps contracts to straighten the arm & this pulls the relaxed bicep muscle back to its original length
What is a tendon?
Join muscle to bone
- What is the main goal of rehabilitation after a musculoskeletal injury?
- To reduce the chance of reinjury and ensure safe progression
- Give an example of an intrinsic factor that affects injury risk.
- Individual’s strength, flexibility, age, or previous injury history
- What is the difference between a sprain and a strain?
- Sprains involve ligaments; strains involve muscles or tendons
- How do braces help support the musculoskeletal system?
- Immobilise or limit joint motion, reduce swelling, support alignment, minimise pain
- What are three key training principles to prevent injury?
- Intensity, frequency, and progression