The molecule released in the synaptic cleft.
What is a neurotransmitter?
Contains the brain and spinal cord.
What is the central nervous system?
Measures brain waves.
Readily images bones in 2D.
What is xray?
Condition caused by multiple unprovoked seizures.
What is epilepsy?
The mechanism of electric impulse propagation.
What is the action potential?
"Fight or flight"
What is the sympathetic nervous system?
Treatment for hydrocephalus.
What is a shunt?
"3D xray"
What is CT.
Direction of afferent neuron.
Towards the spinal code/brain.
The longest nerve in the human body.
What is the sciatic nerve?
The act of thinking.
What is cognition?
Deep brain stimulation is often used for patients with this neurologic condition caused by lewey bodies.
Solution injected to provide opacity in soft tissues.
What is contrast?
The movement of ions is called.
What is a current?
The insulation around the axon.
What is the myelin sheath?
The brain regulates homeostasis along with this body system.
What is the endocrine system?
Common condition in diabetic patients related to nerves.
What is neuropathy?
Uses radioactive isotopes to measure activity of tissues.
What is PET?
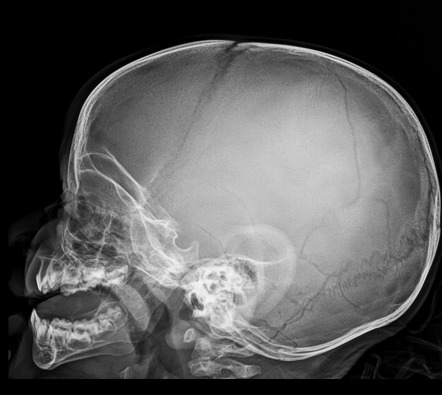
What is a skull fracture?
The resting membrane potential (mV).
What is -65 mV?
The branch of the nervous system that includes the somatic nervous system.
What is the peripheral nervous system?
What is responsive neurostimulation?
Uses gadolinium.
What is MRI?
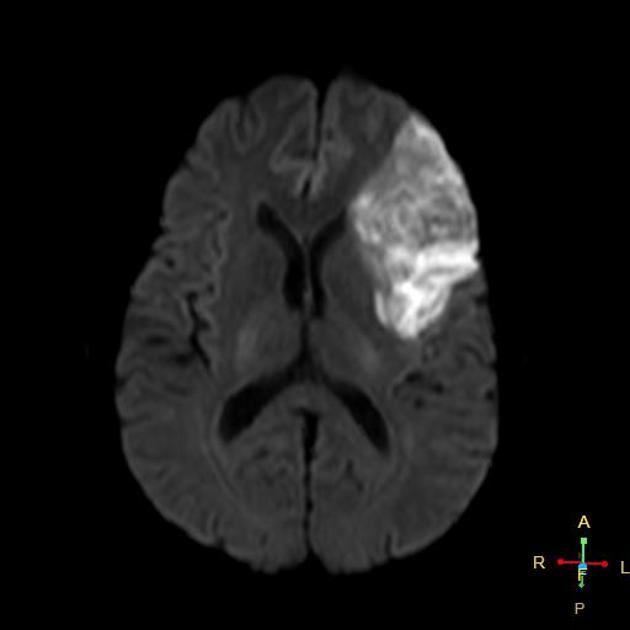
What is a stroke?