Refers to hypertension that exists before pregnancy or is diagnosed before the 20 weeks of gestation.
What is Chronic HTN?
Cerebral or retinal endothelial dysfunction and vasospasm resulting in decreased perfusion, consistent with severe features of preeclampsia
What are Visual Disturbances?
cerebral endothelial dysfunction, vasospasm, and edema that impair oxygen and nutrient delivery to the brain, signaling worsening neurologic involvement
What is the altered LOC?
The reduction of environmental and sensory input in order to limit neurologic excitation.
What is Decrease Stimuli?
.35
What is PCR indicative of Preeclampsia?
10 grams IM;5 g IM in each buttock;
Use 50% solution; May use 1% lidocaine if available
What is emergency Magnesium Sulfate Therapy (after seizure)?
Occurs after 20 weeks of gestation in women who were previously normotensive. Characterized by elevated blood pressure w/o proteinuria or systemic signs.
What is Gestational Hypertension?
Hepatic sinusoidal endothelial injury with periportal fibrin deposition causing liver capsule distention (Glisson’s capsule)
Often, without warning, there is a generalized loss of neurologic control caused by acute cerebral endothelial dysfunction, vasospasm, and edema.
BP 176/110; 10 mg; No IV access; recheck BP in 20 minutes
What is Procardia IR?
A rapid shift of fluid out of the vascular space into the alveolar–capillary interface caused by endothelial injury, low oncotic pressure, and impaired fluid clearance in preeclampsia, leading to respiratory compromise.
What is Pulmonary Edema?
RR <12/min, absent reflexes, ↓ oxygen saturation, cardiac conduction changes, serum mag level >9–10 mg/dL, UO <30 mL/hr, renal failure/anuria, persistent hypotension, severe muscle weakness, altered mental status
What are the reasons to discontinue Magnesium Sulfate Therapy?
New-onset hypertension after 20 weeks of pregnancy, accompanied by signs of maternal organ dysfunction, with or without proteinuria
What is Preeclampsia?
New-onset hypertension is defined as systolic ≥140 mm Hg or diastolic ≥90 mm Hg after 20 weeks’ gestation, or severe-range pressures ≥160/110 mm Hg
What is Elevated Blood Pressure?
This may occur when cerebral endothelial dysfunction and vasospasm impair autoregulation and heighten neuronal excitability in preeclampsia. (Increases seizure risk awareness)
What is Hyperreflexia or Clonus?
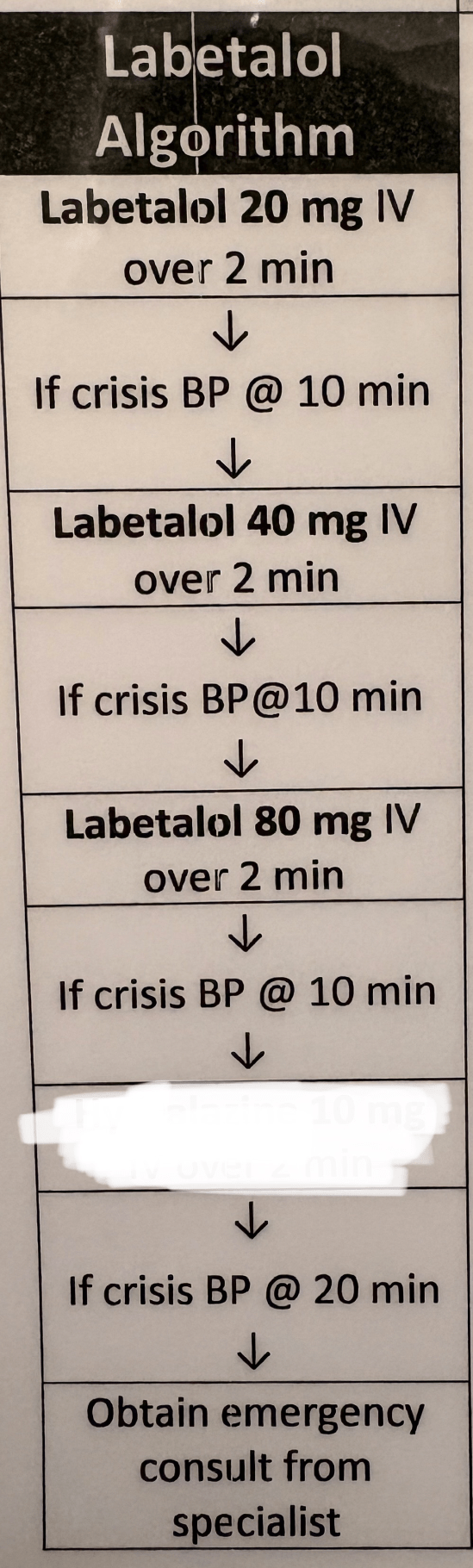
20mg, 40mg, 80 mg; IVP; BP checks every 10 minutes; commonly used for outpatient maintenance
What is Labetalol?
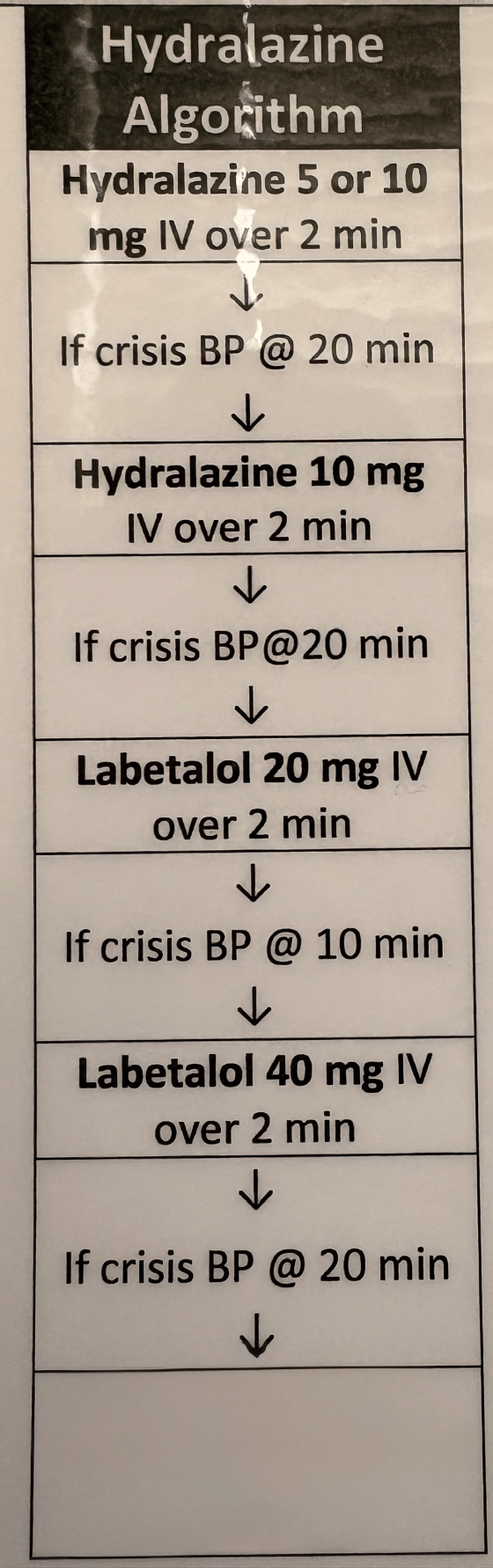
What is 10mg Hydralazine IV over 2 min?
BP, Respirations, DTR, Neuro, I&O, Breath Sounds
What are Hourly Mag Checks?
New, unexplained seizures in a pregnant or postpartum patient with preeclampsia.
What is Eclampsia?
Loss of cerebral autoregulation causes increased cerebral perfusion pressure, vasogenic edema, and meningeal stretch
What is a Headache?
Worsening endothelial injury causes hepatic ischemia, hemoconcentration, platelet consumption, and rising protein loss over time
What is HELLP Syndrome?
5 or 10 mg IV; BP check after 20 mins
What is Hydralazine?
AST: 92; ALT: 88;LDH:640;PCR:0.48; Hgb&Hct: 16 & 48;Plts: 96,000
What are abnormal labs indicative of Preeclampsia?
Restores membrane excitability at neuromuscular and cardiac sites, reversing depressant effects on respiration, reflexes, and cardiac conduction.
What is Calcium Gluconate?
Worsening blood pressure after 20 weeks in a patient with preexisting hypertension, accompanied by new-onset proteinuria or signs of maternal organ dysfunction
What is CHTN w/SI Precclampsia?
Loss of selective permeability of the filtration interface allows macromolecules to cross into the excretory pathway.
What is Proteinuria?
A consumptive coagulopathy caused by severe endothelial injury in preeclampsia, resulting in clotting factor depletion and bleeding risk
What is DIC?
A calcium channel blocker used in pregnancy to lower blood pressure by relaxing vascular smooth muscle and reducing systemic vasoconstriction, providing steady 24-hour control
What is Procardia XR?
What is Obtain emergency consult from specialist?
A monitoring strategy used to detect decreased filtration and impaired free-water excretion from glomerular endotheliosis in preeclampsia, helping prevent oliguria, fluid overload, and pulmonary edema.