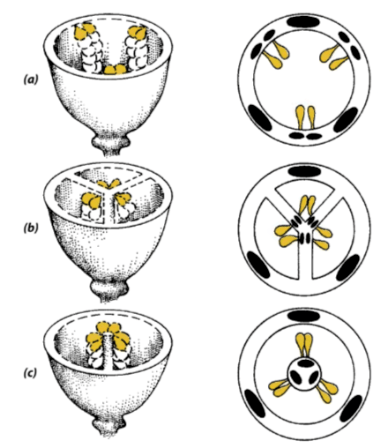
Although algae live in aquatic habitats and benefit from wave action, some of their gametes have this structure to swim.
What are flagella?
The portion of the lifecycle that is dominant
What is the gametophyte?
This is still required for reproduction in seedless vascular plants.
What is water?
The dominant mode of pollination in gymnosperms.
What is wind?
The dominant mode of pollination in Angiosperms.
What is animal or mobile?
Algae exhibit three lifecycle types.
What are: sporic, gametic, zygotic?
This chemically inert polymer, which protects spores and pollen in all land plants, first evolved in bryophytes.
What is sporopollenin?
In ferns, this portion of the lifecycle is reduced but free-living
What is the gametophyte?
What are fascicles?
Flowers are generally made up of these four whorls.
What are sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils.
Some algae exhibit two gametes that differ in that one gamete is larger and the other is smaller and flagellated.
What is oogamous?
Prior to the evolution of Bryophytes these protective cells in the antheridia did not exist.
What is the sterile jacket?
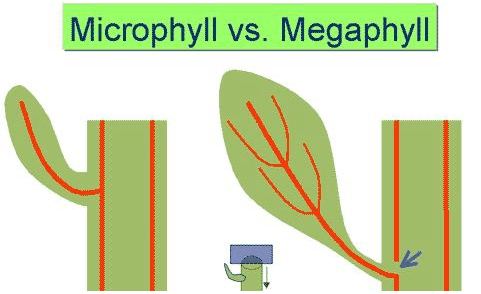
These two types of leaves, which first evolved in the seedless vascular plants, are defined by their venation how they attach to the stele.
What are microphylls and megaphylls?
The transition to this type of -spory (spore morphology) was an important precursor to the evolution of the seed
What is heterospory?
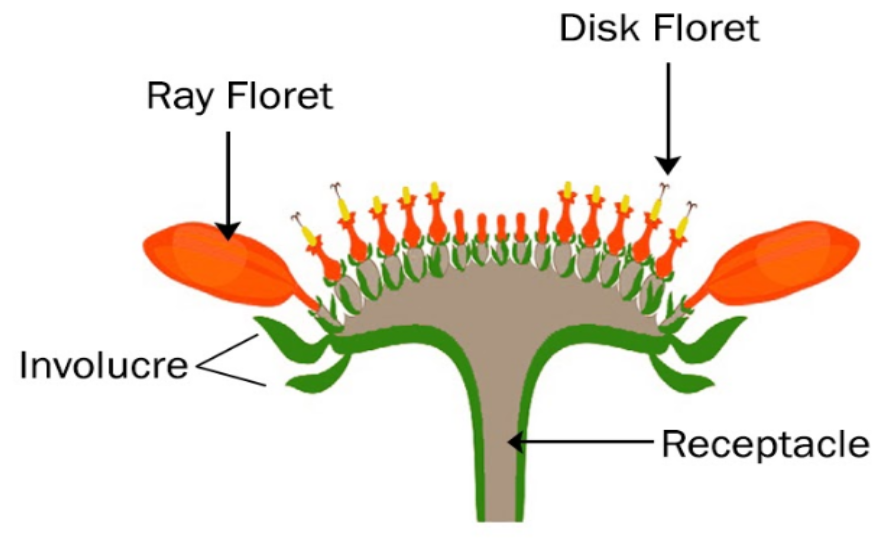
The evolution of this structure is a major reason for the global dominance of the sunflower family (Asteraceae).
What is the capitulum?
What is the term for the phenomenon in algae where the two alternating generations, the sporophyte and the gametophyte, have similar or nearly identical appearances?
What is isomorphic generations?
This phylum of bryophytes is the only group of land plants that does not have true stomata.
What is Marchantiophyta (Liverworts)?
Heterospory is a synapomorphy for these two groups.
What are Isoetes and Selaginella?
This structure, which first evolved in gymnosperms, is a highly reduced microgametophyte made up of only a few cells.
What is pollen?
This unique process results in a triploid (3n) endosperm and a diploid (2n) zygote.
What is double fertilization?

This type of algal reproduction strategy is independent of water and movement of gametes.
What is asexual reproduction?
These water- and nutrient- conducting cells, found in true mosses, lack lignin found in the vascular tissues of angiosperms and gymnosperms.
What are hydroids and leptoids (hadrom and leptom)?
Derived from multiple surface initials, the resulting sporangium walls are >2cells thick, and protect the spores from damage while retaining moisture.
What is eusporangia?
This divides to produce the archegonia and nutritive tissue for the eventual embryo.
What is the megagametophyte?
In botany, the term "placentation" describes the orientation of these structures, which house the megagametophytes, within the ovary.
What are ovules?