Products of the condensation reaction 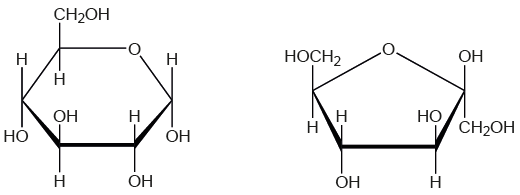
Water and sucrose
How facilitated diffusion in axons is similar to active transport
A. They both require the energy of ATP.
B. They both move substances against a concentration gradient.
C. They both use sodium–potassium pumps.
D. They are both carried out by proteins embedded in the axon membrane.
D! Use of proteins
Facilitated has channels, active transport has pumps
Graph that represents surface area to volume ratio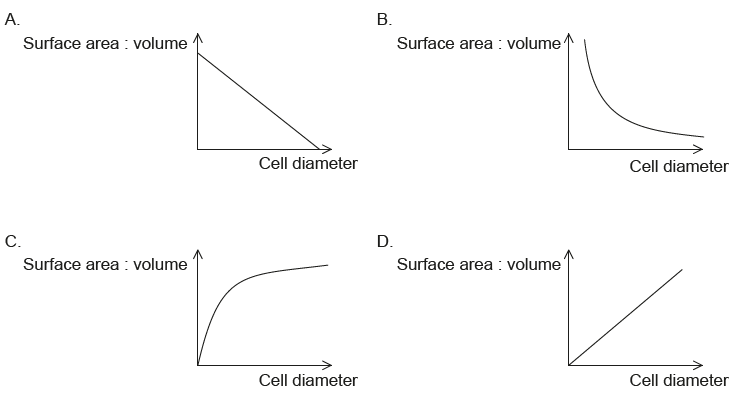
Graph B!
Reason large organisms need specialized gas exchange structures
A. They have a large surface area to volume ratio.
B. There is a short distance to the centre of their body
C. They have a relatively small surface in contact with the outside
D. Their skin is impermeable to respiratory gases.
C - Relatively small surface in contact with the outside
A. 18 and 7.8
B. 25 and 6.8
C. 18 and 6.8
D. 25 and 7.8
D! Warm and slightly basic
Properties of X & Y in the phospholipid
In regards to water and charge/polarity
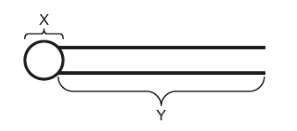
X = Hydrophilic
Y= non-polar
Distinguishes capillaries from other blood vessels
*Walls
Thin, permeable walls that allow exchange of materials between tissue and blood
Determines differences between two types of blood cells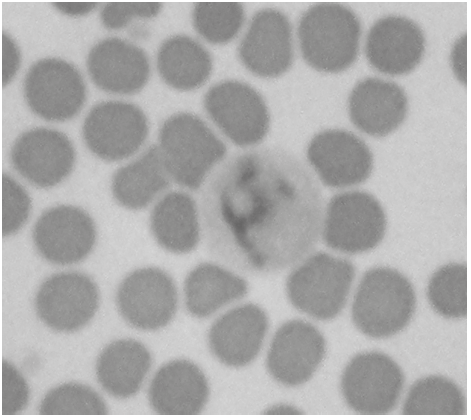
Different expression of some genes
Which occurs at gas exchange surfaces in lungs of mammals?
I. Gases diffuse across a moist surface.
II. Concentration gradients are maintained by ventilation.
III. Water is lost.
Gases diffuse across moist surface
Concentration gradients maintained by ventilation
Water is lost
Which organism would be classified as a saprotroph?
A. A single-celled eukaryote that obtains its carbon compounds by photosynthesis and ingestion of other single-celled organisms
B. A jellyfish that uses the stinging cells in its tentacles to paralyse its prey, which is passed to an internal gastric cavity through a single opening
C. A fungus that feeds by secretion of digestive enzymes onto its food and absorption of digested material
D. A dung beetle that feeds on the fecal material left behind by other animals
C - fungus that feed by secretion of digestive enzymes into its food and absorption of digested material
The part of the amino acid leucine that distinguishes it from other amino acids
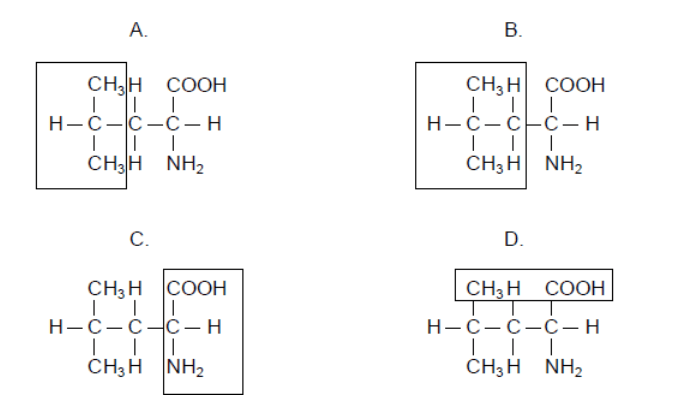
B - Find the NCC and go from there
Feature of phloem sieve tubes
A. Numerous chloroplasts
B. No nucleus
C. Lignified walls
D. No cytoplasm
No nucleus
Description of stem cells
A. Cells found only in the early embryo.
B. Multipotent embryonic cells that can differentiate into all cell types.
C. Totipotent stem cells that are found in specific niches in adults.
D. Pluripotent stem cells that may differentiate into blood cells.
D - Pluripotent that may differentiate into blood cells
Consequence of the evaporation of water from mesophyll cells in leaves of a healthy plant
A. Plasmolysis occurs in mesophyll cells.
B. Photosynthesis stops.
C. Stomata close to reduce transpiration.
D. Water moves up the stem in the xylem.
The pie chart shows the modes of nutrition of fungi in Huahu Lake wetland in China. Most common mode of nutrition of fungi in this wetland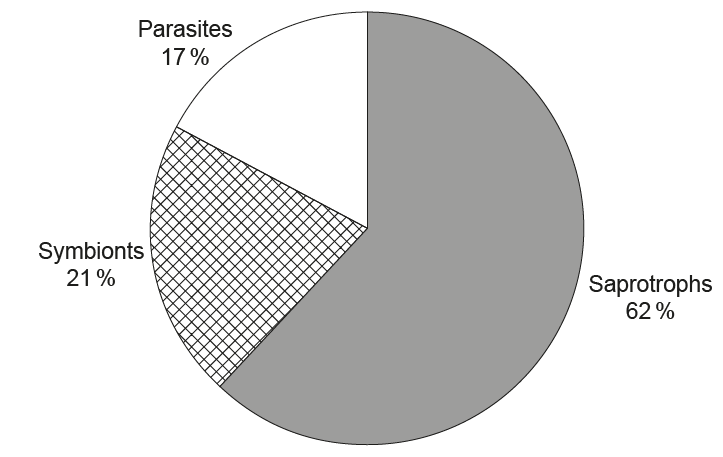
A. Heterotrophic fungi that feed on living organisms by ingestion
B. Autotrophic fungi that obtain organic nutrients from detritus by internal digestion
C. Fungi that have either an autotrophic or heterotrophic method of nutrition
D. Heterotrophic fungi obtaining nutrients from dead organisms by external digestion
😅😅😅😅
D - Heterotrophic obtaining nutrients from dead organisms by external digestion
Type of fatty acid 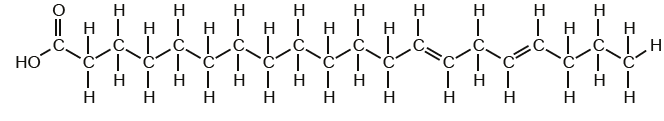
Trans unsaturated
Hydrophilic regions of the fluid mosaic model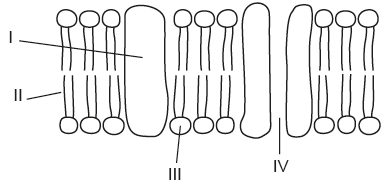
III and IV
What accounts for undifferentiated cells to become specialized to perform specific functions in a multicellular organism.
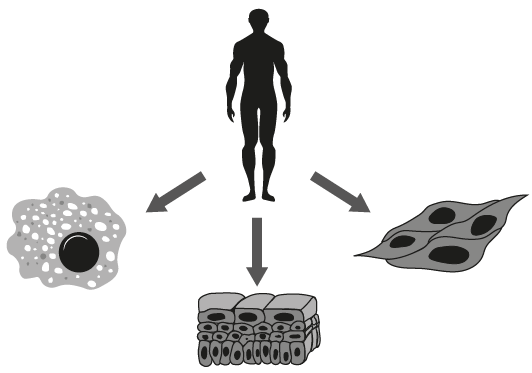
A. Their chromosome number differs.
B. Their proteomes are different.
C. They have slightly different genomes.
D. They express different chromosomes.
B - PROTEOMES ARE DIFFERENT
Proteome - complete set of proteins produced or modified by an organism
What can be seen in a plan diagram of a leaf
A. Spongy cells and surface of the upper epidermis
B. Chloroplasts in palisade cells and position of waxy cuticle
C. Vascular bundles and thickness of palisade mesophyll
D. Guard cells and distribution of air spaces
NO INDIVIDUAL CELLS
C - Vascular bundles and thickness
Mode of nutrition for this species...
Mycena interrupta lives in small colonies on moist, rotting dead wood in rainforests. It feeds on this plant material by breaking it down with enzymes before ingestion.
Saprotroph
Which are true facts on the structure of proteins?
I. Proteins are made from amino acids linked together by peptide bonds.
II. The sequence of amino acids in all proteins is the same.
III. A protein may consist of more than one polypeptide.
I. & III.
Made from amino acids linked by peptide bonds
May consist of more than one polypeptide
Modes of transport in the diagram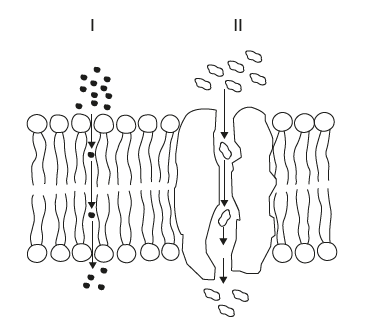
I - Simple diffusion
II - Facilitated diffusion
Organelles l, ll & lll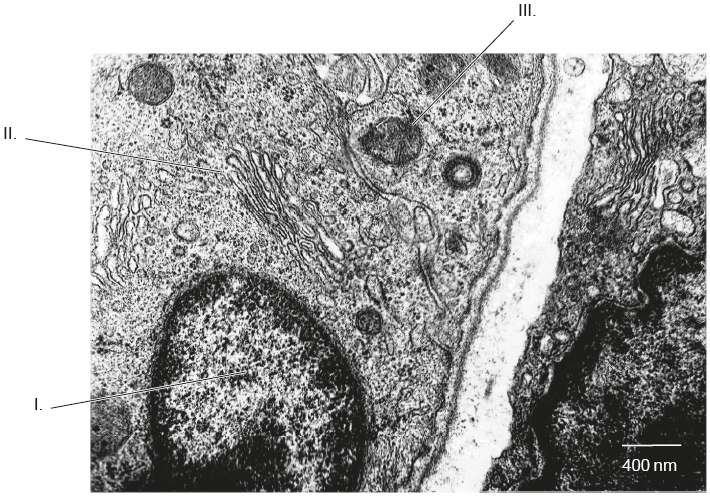
ll. Golgi apparatus/body
lll. Mitochondrion
Causes the expansion of the thorax during inspiration
2 things....
Contraction of diaphragm and external intercostal muscles
Correct row that describes a type of nutrition 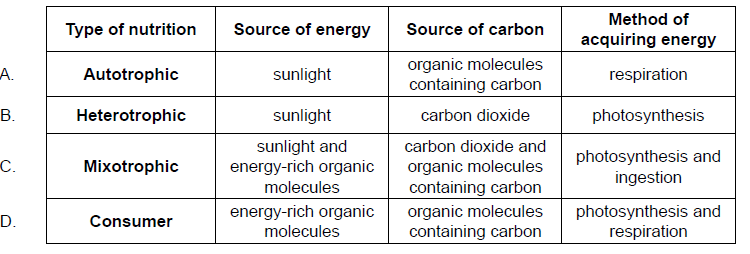
C - We need to go over this.....😅😅😅