The change in allele frequencies in a population over time
What is evolution?
He is known as the Father of Evolution
Who is Charles Darwin?
What is often referred to as "survival of the fittest?"
What is natural selection?
distantly related organisms evolve to become more similar
What is Convergent Evolution?
This type of speciation occurs when a physical barrier, such as a river or mountain, separates a population into two groups that evolve independently.
What is allopatric speciation?
Similar structures that evolved from a common ancestor such as bones humans, cats, bats, and whales have in common.
What are Homologous Structures?
Scientist who came after Darwin and cleared up how traits were passed down to offspring.
Who is Gregor Mendel?
Any inherited trait that increases an organism's chance of survival is known as this.
What is an adaptation?
Darwin was from the 1800's. What part of modern science did he lack knowledge of in order to better explain how traits were passed down from parent to offspring?
What is genetics?
A record of Earth changing over a long period of time
What is fossil record?
Preserved remains of ancient organisms
What are fossils?
This term refers to different traits and alleles within a population.
What is variation?
The concept that organisms who are the best suited to their environment will be the most successful
What is survival of the fittest?
The Hardy-Weinberg equation is p² + 2pq + q² = 1. What does 2pq represent?
Heterozygous dominant individuals
Unlike allopatric speciation, this type of speciation happens without a physical barrier, often due to genetic differences or behavioral changes.
What is sympatric speciation?
What characteristics did Darwin observe about the finches on the Galapagos Islands?
What are their beaks? They adapted to different food sources.
What is the function of Antibiotics?
What is to kill or slow the growth of bacteria?
This type of reproductive barrier prevents fertilization from occurring, such as temporal, behavioral, or mechanical isolation.
What is a prezygotic barrier?
This reproductive barrier occurs after fertilization and may result in hybrid inviability or sterility.
What is a postzygotic barrier?
This branch of biology focuses on the evolutionary history and relationships among species.
What is phylogeny?
Which term refers to the process by which individuals that are better suited to the environment survive and reproduce therefore passing down their genes to their offspring?
What is Natural Selection?
If a small number of tree frogs migrate to a mat of vegetation that is already home to an established population of tree frogs and introduce new alleles into the native population's gene pool, this change is referred to as what?
What is gene flow?
What is a group of organisms of one species that interbreed and live in the same place at the same time
What is population?
Conditions that limit an organisms ability to survive and controls the number in a population?
Selective pressure
collectively, all of the alleles of the population’s genes
What is a gene pool?
What has a stronger effect in small populations due to random sampling of alleles.
What is genetic drift?
when gene frequencies are changed by chance or random events in a isolated population
What is Genetic Drift?
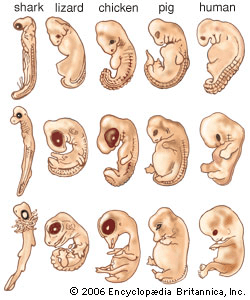
What are common ancestors?
Animals and plants can change as a ______________ but not as an individual.
species
A mistake or change that occurs in the DNA sequence is called a ______________________.
What is a mutation?
In the Hardy-Weinberg equation p2+2pq+q2=1p^2 + 2pq + q^2 = 1p2+2pq+q2=1, the term 2pq2pq2pq represents this group of individuals.
What are heterozygotes?
If the frequency of the recessive allele (q) in a population is 0.3, what is the frequency of the dominant allele (p)?
What is 0.7? (Since p+q=1p + q = 1p+q=1)
In a population of 1,000 cats, 160 have white fur, a recessive trait (ww). Assuming the population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium:
A. What is the frequency of the recessive allele (w)?
q (recessive allele frequency) = 0.4
In a population of 500 frogs, 250 are heterozygous (Bb). If the population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium:
A. What is the frequency of the heterozygous genotype?
Heterozygous frequency (2pq) = 0.5
A biologist observes that over several generations, a population’s allele frequencies are changing. Which of the Hardy-Weinberg conditions is being violated?
- Mutation (New alleles are introduced.)
- Genetic Drift (Random changes in a small population.)
- Gene Flow (Migration between populations.)
- Non-Random Mating (Selective breeding occurs.)
- Natural Selection (Certain traits provide survival advantages.)