John placed a cup of ice on the counter to sit. After 5 minutes it starts to ______.
Melts
Heat moving through fluids like air or water.
Convection
The diagram below shows the arrangement of _____.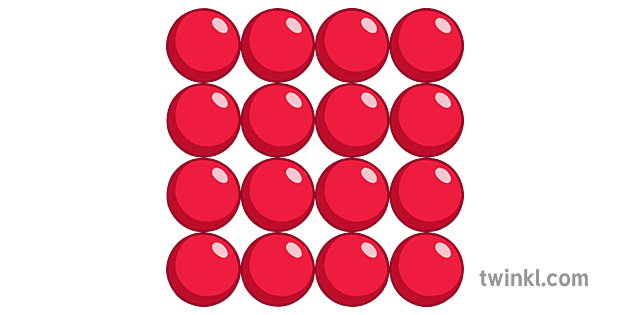
Solid
The instrument used to measure temperature
Thermometer
The measure of how much matter is in an object.
Mass
Dry ice ________. It changes from solid directly to gas.
Sublimes
Heat moving through direct contact.
Conduction
Particles in this state of matter has a lot of kinetic energy.
Gas
Heat always flows from this to this.
Hot to cold
The amount of space matter takes up.
Volume
This phase change turns liquid into gas at the surface.
Evaporation
Heat transfer that makes soup swirl in a pot.
Convection
The particles in this state of matter vibrates.
Solid
Sarah was in her little pool outside playing. Sarah mom then added some ice to the pool, the ice then started melting. Where did the heat traveled from?
from the warmer water in the pool to the ice
A block of ice is left outside on a hot summer day. After a while, you notice water droplets forming around the ice and then a small puddle underneath.
Explain what phase changes are happening as heat is added to the ice.
The ice is melting and changing to liquid as it is absorbing heat from its environment
Gas cooling down to become liquid.
Condensation
Heat transfer when you touch a hot pan.
Conduction
The basic building block of matter.
Atoms
The average kinetic energy of particles in matter.
Thermal Energy
A student leaves a full water bottle in the freezer overnight. The next morning, the bottle has bulged out and the water inside is solid.
Explain what happened when heat was removed. Why did the bottle bulge?
Removing heat made the liquid water freeze into ice. Water expands when it freezes, so the solid ice took up more space, causing the bottle to bulge.
The opposite of melting, liquid to solid.
Freezing
Heat moving through empty space as waves.
Radiation
State with definite volume but no definite shape.
Liquid
This type of heat transfer does not need matter to travel and can even move through the vacuum of space.
Radiation
In a pot of soup heating on the stove, small bits of vegetables rise to the top while others sink back down. The soup is constantly moving in circles.
Explain why the vegetables and soup move this way. How does convection help cook the soup evenly?
The soup at the bottom gets hot, becomes less dense, and rises. Cooler soup sinks to the bottom, creating a circular current (convection). This motion spreads heat evenly, cooking the soup throughout.