Though possibly not a unanimously accepted abbreviation, within the context of this topic what does OLV stand for?
One lung ventilation
 A and B are, respectively
A and B are, respectively
A. Right DLT
B. Left DLT
The bronchial cuff of double-lumen endotracheal tube rarely needs greater than ____ amount of ____ (this necessary component)
2 mL of air
When the patient is awake and spontaneously breathing you expect no change in ventilation to perfusion but once anesthetized this results
Increased V/Q mismatch
 What is this little "BB"?
What is this little "BB"?
Bronchial blocker
For a right thoracotomy, the patient should be positioned in the ______ position so that the ______ lung is (classically referred to as) dependent.
Left lateral decubitus, left.
Right-to-left shunt with one lung ventilation
increases 20-30%
In the lateral position the dependent lung receives around 60% of pulmonary blood flow; this is due to
Gravity
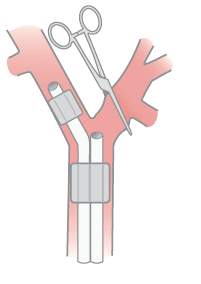 Name the operative lung and the type of airway device
Name the operative lung and the type of airway device
Right lung surgery, left double lumen tube
An anesthetized patient has a decrease in his SpO2 from 100% to 91% after being moved into the lateral decubitus position. His lungs are being mechanically ventilated with isoflurane 1% in oxygen; SpO2 remains at 91% for several minutes. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the desaturation?
A. Atelectasis
B. Endobronchial intubation
C. Hypoventilation with inadequate minute ventilation
D. Isoflurane inhibition of hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction
Endobronchial intubation
A 70-kg, 65-year-old man with COPD has severe pain after undergoing thoracotomy for excision of a tumor in the lung. Which of the following methods is most effective for decreasing pain while improving ventilation?
A. Application of thoracic TENS
B. Continuous lumbar epidural infusion of fentanyl
C. Continuous thoracic epidural infusion of morphine and bupivacaine
D. IV PCA with morphine
Continuous thoracic epidural infusion of morphine and bupivacaine
A 56-year-old man is anesthetized for pneumonectomy. After initiation of one-lung ventilation, SpO2 rapidly decreases to 69%. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management
A. Apply continuous positive airway pressure to the nonventilated lung
B. Increase respiratory rate and decrease tidal volume
C. Occlude the pulmonary artery supplying the nonventilated lung
D. Resume bilateral lung ventilation
Resume bilateral lung ventilation
As the famous quote goes, "Assume nothing, ..."
Trust no one
Maximum peak airway pressure for OLV
35 cm H2O