This is how blood vessels and nerves pass through the hard matrix of bone.
What are canals?
Best suited for areas subjected to friction like the surface of the skin or in the mouth.
What is stratified squamous?
What is vascularized, no free surface, includes fibers, not named based on cell shape?
Characterized by striations, mononucleated, intercalated discs
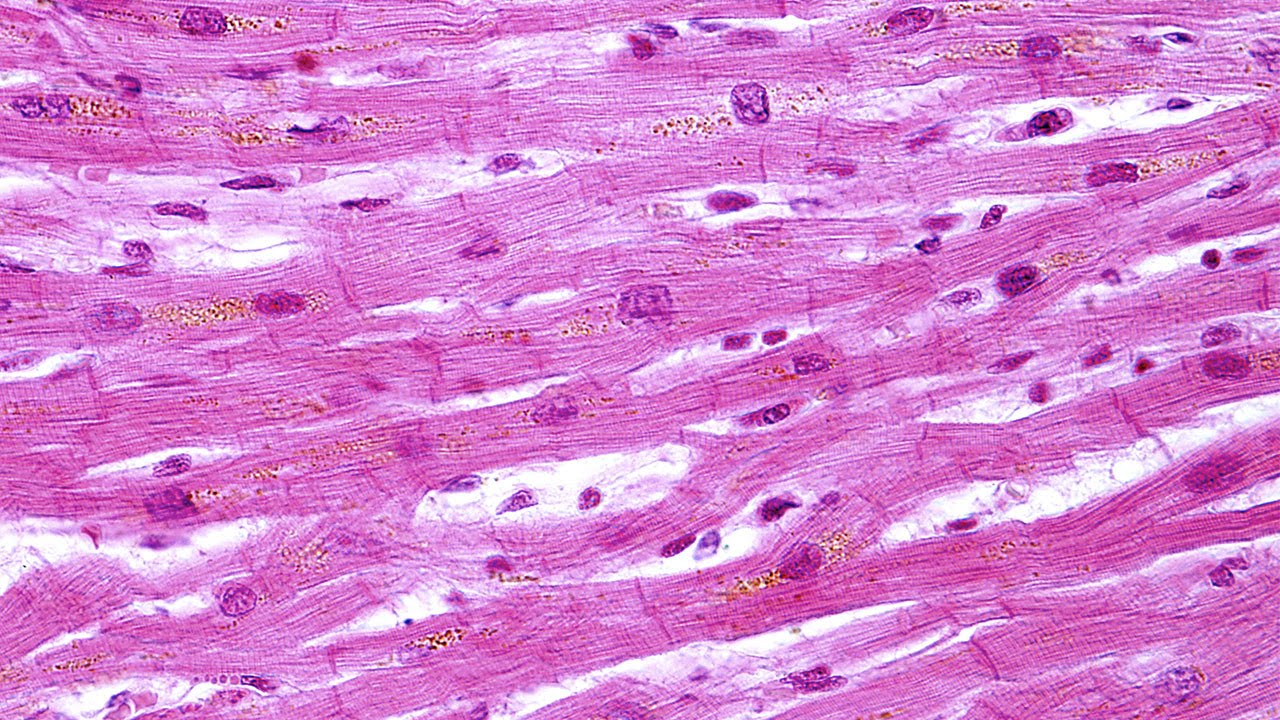
What is cardiac muscle?
The big cell in nervous tissue is this...
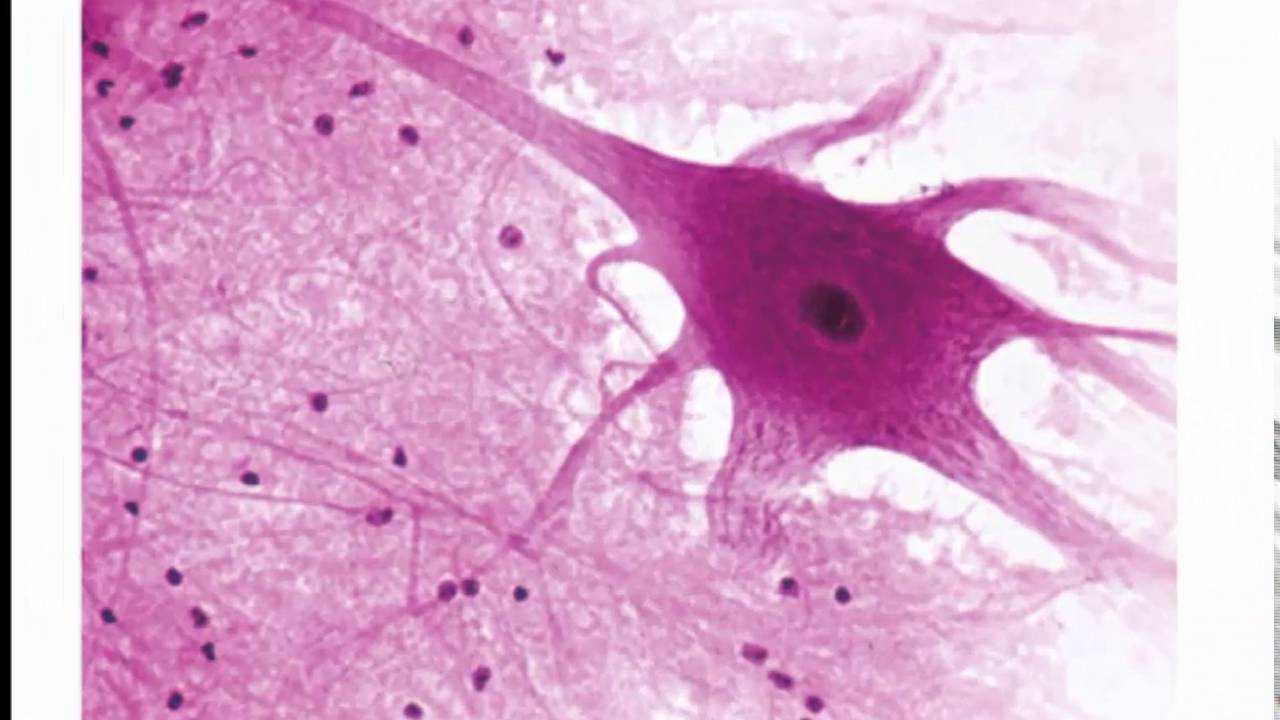
What is a neuron?
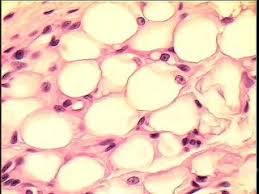
Connective Tissue stores energy and insulates the body against the cold. What type of connective tissue is in charge of these functions and describe key characteristics of this tissue)
What is adipose. Big cells filled with a fat droplet and nucleus pushed to the side so it looks empty.
 Moves substance across a mucous lined surface
Moves substance across a mucous lined surface
What is ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dense_connective_tissue-56a09aee3df78cafdaa32ca1.jpg) Characterized by collagen fibers arranged in parallel. Looks wavy.
Characterized by collagen fibers arranged in parallel. Looks wavy.
What is dense fibrous tissue?
Characterized by tapered cells with one nucleus and no striations
What is smooth muscle?
The smaller support cells in this tissue are these...

What are neuroglia?

What is bone tissue?
Epithelial tissue does not have this characteristic.
What is vascularized (has blood vessels to supply nutrients)?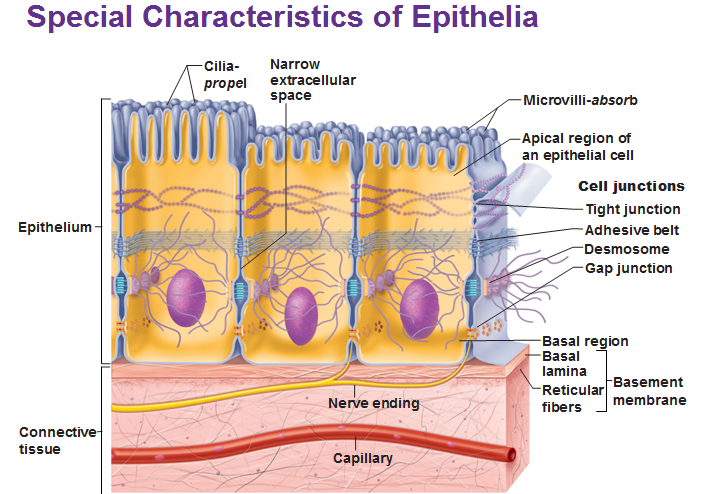
All three types of cartilage tissue have this in common.
This the difference between elastic and hyaline cartilage.
What are chondrocytes?(cartilage cells)
Hyaline is smooth and "glossy, or glassy" between chondrocytes, elastic is "hairy" (elastic fibers) between chondrocyt es.
es.
This muscle can also be characterized by a branching pattern.
What is cardiac muscle?
A=? C=? E=? G=? H=? F=?

A=Dendrites
C=Nucleus
E=Myelin sheath
G=Axon
F=Schwann cell
H=Axon terminal/synapse

What is hyaline cartilage?
This is why simple squamous is found in the alveoli (air sacs) of the lungs.
What is it allows diffusion easily because it is very thin (on one cell thick) and flat cells?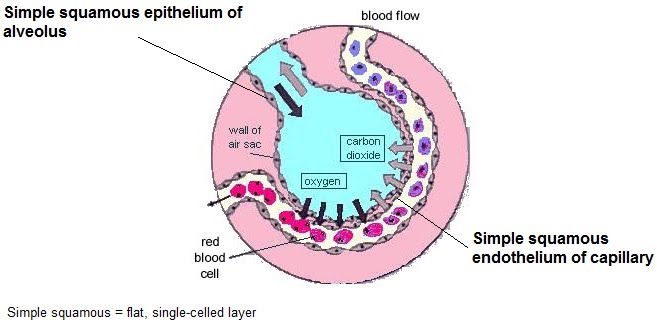
Connective tissue below your skin that provides strength and resistance to multidirectional stretching.
What is loose connective tissue (or areolar tissue)
A scientist observes a sample under the microscope.
It contains long cylindrical cells with striation, and many nuclei located along the edges of each cell.
What is Skeletal Muscle?
This the function of nervous tissue.
What is transmit electrochemical impulses?
Identify the tissue below. what is d,b, and c (1 thing), what is A, what is e?

Blood tissue
WBC
RBC
Plasma
Characterized by stacked cuboidal cells that can slide over one another which allows it do do this.
What is transitional tissue, distend (stretch)?
These cells make fibers
These cells make cartilage
The cells work in immune and inflammatory response
These cells "eat up" foreign invaders and junk
What are fibroblasts, chondrocytes, mast cells, macrophages?
A muscle cramp is a sudden and involuntary contraction of one or more of your muscles.
If I have a cramp in my calf muscle it is this type of muscle.
What is skeletal muscle?
Nervous tissue can be found in these locations.
What is brain, spinal cord, nerves?