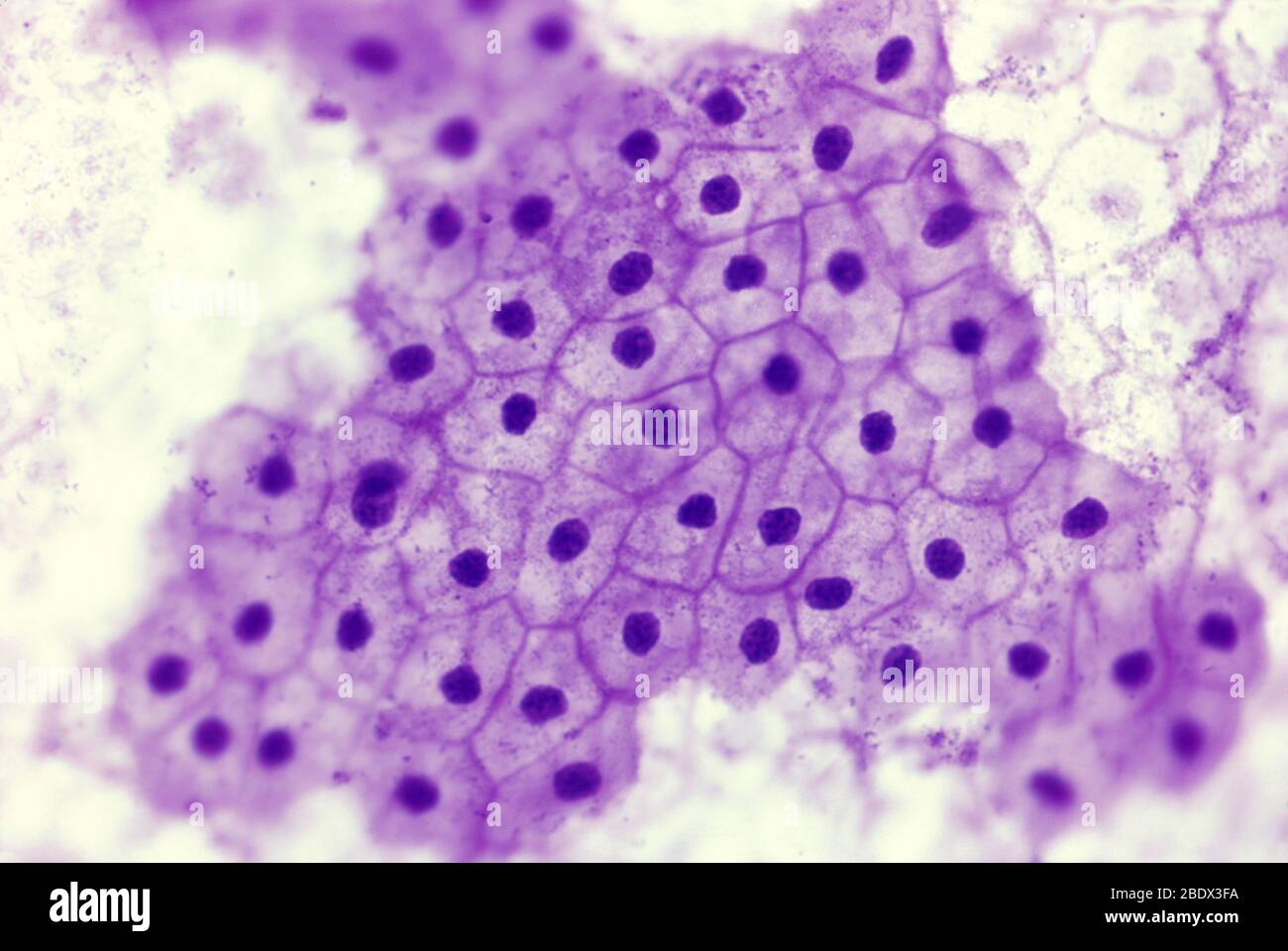
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Simple Squamous Epithelium Function
allows for rapid diffusion and filtration; secretion in serous membranes
- forms the lining of the air sacs of the lung bc it allows for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the blood and inhaled air
Simple Squamous Epithelium Location
Air sacs in the lungs (alveoli)
lining of lumen of blood vessels and lymph vessels (endothelium)
serous membranes (mesothelium)
Simple Squamous Epithelium Stucture
Subtypes of muscle tissue
Skeletal
Cardiac
Smooth
elastic cartilage connective tissue
Ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium function
- Secretion of mucin and movement of mucus along apical surface of epithelium by cilia
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Location
Surface of ovary
Regions and ducts of most exocrine glands
Location of Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
epidermis of skin
Subtypes of the nervous tissue
none

Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Maintains shape while permitting extensive flexibility
Elastic Cartilage
Location: Intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, menisci of knee joints
Fibrocartilage
Fibroblasts squeezed between densely packed, parallel arrays of collagen fibers; scarce ground substance, limited blood vessels
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
What are the subtypes of epithelial tissue?
Simple Epithelium (simple squamous, simple cuboidal, simple columnar), Stratified Epithelium (stratified squamous, stratified cuboidal, stratified columnar, transitional)

Function: Protection and secretion
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Location: Lining of urinary bladder, ureters, and part of urethra
Transitional Epithelium
Structure: stellate or spindle-shaped; ground substance is a viscous fluid with some immature protein fibers
Mesenchyme Embryonic Connective Tissue
What are the subtypes of Connective Tissue?
Connective Tissue Proper Loose (areolar, adipose, reticular)
Dense (regular, irregular, elastic)
Supporting CT Cartilage (hyaline, elastic fibrocartilage)
Bone Fluid (blood, lymph)
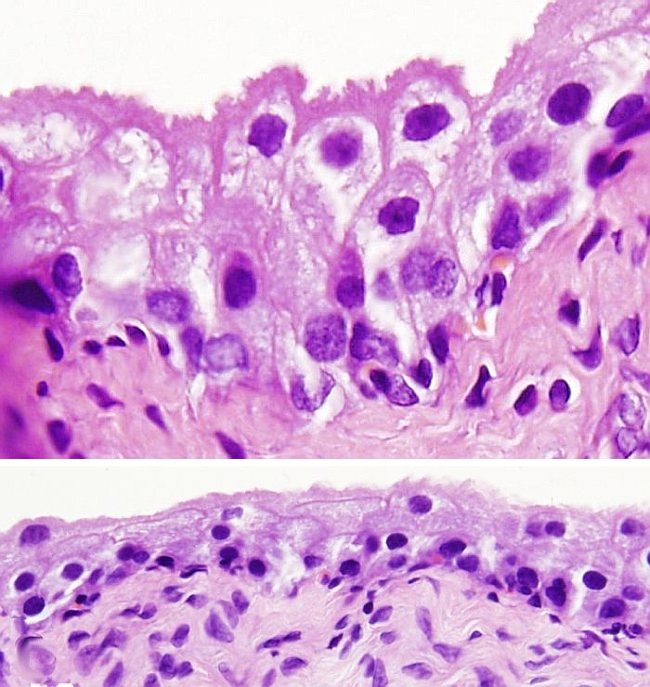
Transitional Epithelium
Function: Protection of underlying tissue from abrasion
Keratinized and Nonkeratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Lining of the larger bronchioles of the lungs and the uterine tubes
Ciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium
Structure: two or more layers of cells, cells at the apical surface are taller than they are wide
Included within simple epithelium
simple squamous
simple cuboidal
simple columnar
