A group of cells with similar structure and function.
A tissue
Epithelial tissues are found on surfaces as either _____ (outer surfaces) or ______ (inner surfaces).
Coverings or linings
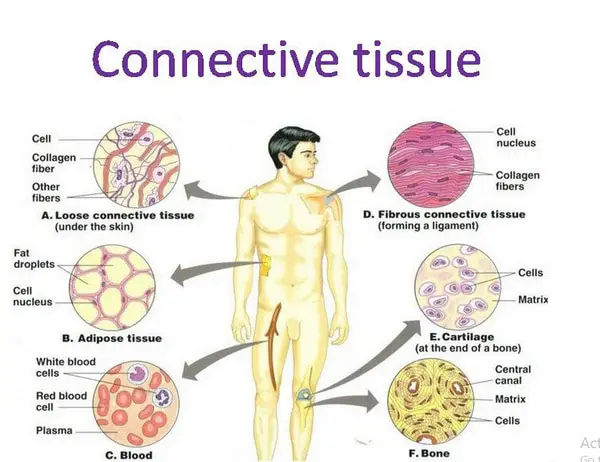
Name the 7 types of connective tissue. (hint-Table 4-2)
A characteristic that all connective tissues have in common is the presence of a matrix (not the one starring Keanu Reeves) in addition to cells. What is a matrix?
Areolar, Adipose, Fibrous, Elastic tissues, as well as Blood, Bone, and Cartilage.
A matrix is a structural network or solution (meaning it can be liquid) of non-living intercellular material- specific to its type of connective tissue.
Muscle tissue is specialized for contraction. Muscles cells or muscle fibers are also called _____. There are three types of muscle tissue. Name them.
Myocytes
Skeletal, Smooth, and Cardiac
Membranes are sheets of tissue that cover or line surfaces or separate organs or lobes of organs. Many produce secretions with special functions. The two major categories of membranes are ____ & _____.
Epithelial and connective
Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, and Nerve Tissue
What type of Epithelial Tissue is being described?
1. A single layer of flat cells, thin and smooth- to allow for the efficient exchange of gases and/or other material. The smooth surface they provide inside small vessels aids in preventing blood clots. (alveoli and capillaries)
2. Many layers of flat cells with rounded cells on the bottom layer that undergo mitosis constantly to replace cells worn off the surface. Acts as a barrier to microorgansims. (Epidermis, Lining of oral cavity, esophagus, and vagina)
1. Simple Squamous Epithelium
2. Stratified Squamous Epithelium
My matrix is made of plasma. My cells are made from stem cells in the red bone marrow. My cell's functions are to transport materials, carry oxygen, destroy pathogens and prevent the loss of me through injuries.
Blood
Also called striated or voluntary muscle. Cells are cylindrical and have several nuclei each and appear striped due to protein arrangement within them. This type makes up muscles that are attached to bones and are supplied with motor nerves and moves the skeleton (except the diaphragm with is NOT attached to a bone) Each muscle cell has its own motor nerve ending. Even though it may not have to be consciously done, all the impulses that move these muscles originate in the cerebrum. So we have to "think" about it to make it happen.
Skeletal Muscle
There are two types of epithelial membranes. They both secrete a fluid. What are they and very simply, where are they located?
Serous Membrane- sheets of simple squamous epithelium that line some closed body cavities and cover the organs in these cavities.
Mucous Membranes- Line the body tracts (systems) that have openings to the environment. (respiratory, digestive, urinary, and reproductive tracts)
What is the term for a sheet of tissue that has a specific location and function?
A Membrane
These surface cells change shape from round to squamous (flat). The urinary bladder is lined with this type of epithelium- the cells are round when the bladder is empty, but flatten out as it fills, enabling the bladder to expand and stretch without tearing the lining.
Transitional Epithelium
1. My function is to support the body and attach muscles, protect internal organs from mechanical injury, store extra calcium, and contain and protect marrow. I have Osteocytes in my matrix along with calcium salts and collagen.
2. Instead of Osteocytes, I have chondrocytes in a flexible matrix and I do NOT have calcium salt. I help hold your trachea open with my rings and prevent friction between bones. I support and give shape to the tip of your nose and outer ear. I also absorb a lot of shock and provide cushions for your vertebrae so you can move around.
1. Bone
2. Cartilage

Cardiac muscle cells are branched and have one nucleus each with faint striations. The cell membrane at the end of them is extensively folded and interlock with folds of the next one. What are these folds called?
Cardiac muscle as a whole is called what?
Cardiac muscle contraction- where does the impulse come from that makes it happen?
Intercalated discs
The myocardium
Cardiac muscles cells have the ability to contact by themselves-maintaining their own beat-a a drum with its own beat, so to speak. Nerve impulses only increase or slow the rate, situationally.
Mucous membranes line body tracts that have openings to the environment. What is the importance of the mucus secreted by these membranes? What are some examples of things it does for us?
The mucus secreted by these membranes keeps the lining epithelial cells wet. They are living cells, so if they dry out, they die. Mucus in the digestive tract lubricates the surface to permit smooth passage of food. It traps dust and bacteria in the respiratory tract- which is then swept to the pharynx by ciliated epithelium. In all of its locations it serves as a barrier to microorganisms- again- as these mucous membranes line all the body tracts with an opening to the outside.
What do you call a cooperation of tissues (2 or more) with similar structure and function?
An Organ
These are cells or organs that secrete something- producing a substance that has a function at that site or a distant site.
Unicellular means "one cell" like a goblet cell. Multicellular means they are made of many similar cells with their individual secretions making a collective secretion. Multicellular type is divided into 2 major groups. Name them and give an example of each. Do you remember from your chapter reading what is so special about the pancreas?
Glands.
Exocrine Glands- have ducts that take secretions away from the gland to the site of its function. Ex. Salivary glands, sweat glands, gastric glands.
Endocrine Glands- ductless glands. Secretes hormones that enter capillaries and circulate throughout the body to bring about specific effects in their targeted organs. Ex. thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pituitary gland.
Remember the Pancreas acts as both- exocrine part secretes digestive enzymes that travel through ducts to the duodenum. The endocrine part has islets cells that secrete the hormones insulin and glucagon.
Adipose tissue- White- more abundant and the amount varies depending on the person. Brown- thermogenic and less abundant in adults. Infants have more to help regulate body temp until they learn to shiver. Exercise can turn white fat cells into brown ones.
Smooth muscle or visceral muscle is also called ______ muscle because although nerve impulses do cause their contraction, we do not normally have control over it.
The functions of smooth muscle are actually functions of the _____ in which the muscle is found.
Smooth muscle contracts in each of these places to do or control what? Stomach/Small Intestine? Wall of arteries and veins? Iris of the eye?
Involuntary
Organs
Waves of peristalsis propel food through the digestive system, Constricts or dilates vessels to maintain normal blood pressure, two sets of smooth muscle constrict or dilate the pupil to regulate the amount of light striking the retina.
The _____ membranes are the serous membranes of the thoracic cavity. The Parietal pleura lines the _____ and the visceral pleura covers the ____.
The heart has its own set of serous membranes. The parietal ________ lines the fibrous pericardium and the visceral pericardium or _______ is on the surface of the heart muscle.
The peritoneum is the serous membrane that lines which cavity? The mesentery or visceral peritoneum is folded and covers the organs here.
Serous fluid between all these membranes and organs does what?
Pleural membranes, lines the chest wall, covers the lungs.
Pericardium, epicardium
Abdominal Cavity
Prevent friction between organs and/or other membranes. (lungs expanding, heart beating, as stomach and intestines contract and move against other organs.

What are the 3 distinctive shapes of the cells that make up and help classify epithelial tissues?
Define the difference between layers of cells called Simple and those called Stratified.
Squamous, Cuboidal, and Columnar
Simple is the term used to describe a single layer of cells, while Stratified means that many layers of cells are present.
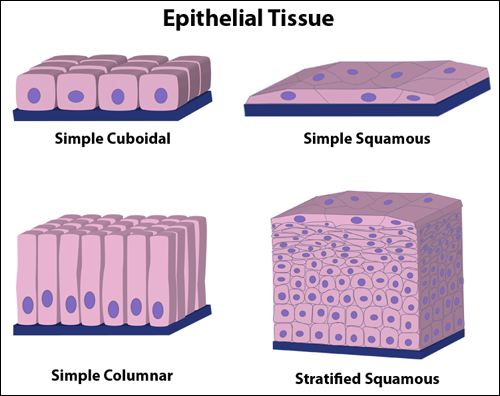
Briefly describe Simple Cuboidal Epithelium, Simple Columnar Epithelium, and Ciliated Epithelium.
Simple Cuboidal- Single layer of cubed shape cells. Makes up functional units of thyroid and salivary glands- here they act as glandular epithelium and secrete hormones or saliva depending on location. Also, present in kidney tubules to reabsorb material into the blood.
Simple Columnar-Taller than they are wide. Specialized for secretion and absorption. Line the stomach and secret gastric juice, Line the small intestines (these have microvilli) and secret digestive enzymes, and absorb end products of digestion. Also includes the specialized cell- a unicellular gland- that secrets mucus in the lining of the intestines and respiratory tract.
Ciliated- columnar cells that are covered in motile cilia on their free surface that sweep materials across the cell surface. Lines nasal cavities, larynx, trachea, large bronchial tubes, and lining fallopian tubes.
Briefly describe Areolar, Fibrous, and Elastic connective tissues.
Areolar- "loose" connective tissue. Cells are called fibroblasts that produce protein fibers. The most abundant being collagen and elastin. Matrix is made of Collagen, Elastin, tissue fluid, and contains mast cells. Found beneath the dermis of the skin and epithelial tissue of all body systems with openings to the environment. Strategically placed to intercept pathogens before they get into the blood and circulate.
Fibrous- Matrix is mostly parallel collagen fibers with a few fibroblasts. Strong yet flexible. Located where there is a need for this flexible strength. Outer walls of arteries because the vessels contain high-pressure blood flow. Also, tendons and ligaments because they need to move when the skeleton does and withstand great mechanical force. Has a poor blood supply- so the repair process is slow. The dermis has an irregular version (crisscrossed collage fibers) that has a good blood supply
Elastic- Matrix is made primarily of elastin fibers with a few fibroblasts. Stabilizing fibers of the protein fibrillin are important. Found in the walls of large arteries like the Aorta and its branches because these vessels stretch when the heart beats and then snap back when the heart relaxes. It is also found in the alveoli of the lungs where it stretches with inhalation and then goes back on exhalation to squeeze out all the air.
Nerve Tissue consists of nerve cells called ____.
2 divisions of the nervous system are?
Label the Nerve Cell:
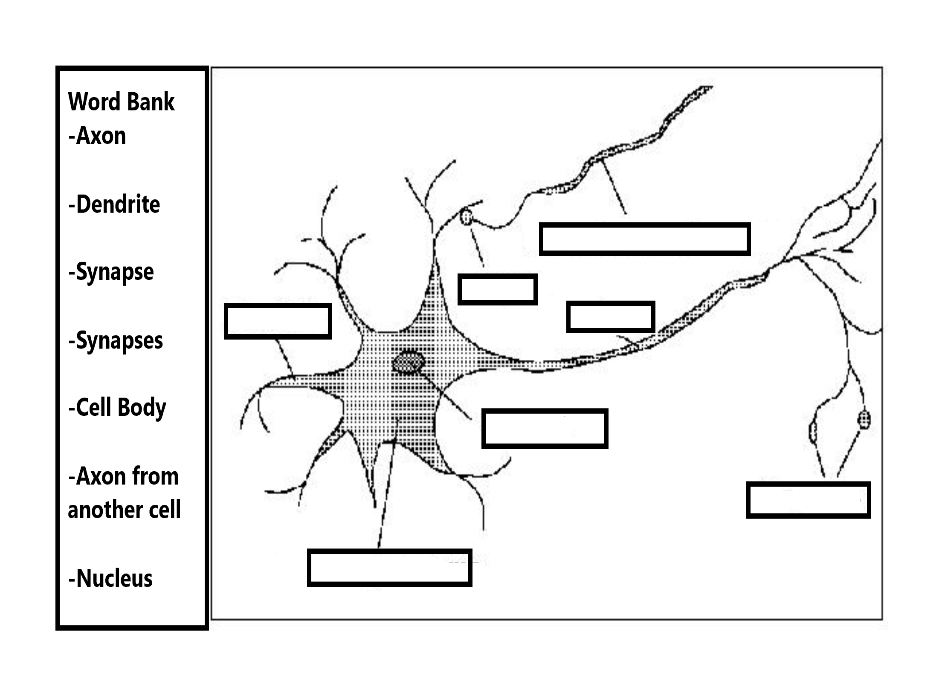
Neurons
Central Nervous System (CNS-Brain and Spinal cord) & Peripheral Nervous System (PNS-all nerves that emerge from CNS and supply the rest of the body)
Cell body- contains the nucleus and regulates the functioning of the neuron.
Axon is a cellular process that carries electrical impulses away from the cell body.
Dendrites are cellular processes that carry electrical impulses toward the cell body.
Synapse(s)- Space between the axon of one neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the next neuron. Transmits the impulses from one neuron to the others with the assist of chemicals. (known as neurotransmitters that are released by axons to help the impulses across the synapse.)

Connective Tissue membranes are made of connective tissue. Remember that Line and Cover have very precise meanings as they describe the location. Of the 7 of these summarized in your book- name the location and function of each. 1. Superficial fascia 2. Periosteum 3. Perichondrium 4. Synovial 5. Meninges 7. Fibrous pericardium
1. Superficial fascia- between skin and muscle. Adipose tissue stores fat, WBCs destroy pathogens entering breaks in skin.
2. Periosteum- Covers each bone, contains blood vessels that enter bone, anchors tendons from muscles, and ligaments from other bones.
3. Perichondrium- Covers cartilage, contains capillaries so its the only blood supply for cartilage.
4. Synovial- Lines joint cavities, secretes synovial fluid to prevent friction with joint movement.
5. Deep fascia- Covers each skeletal muscle, anchors tendons.
6. Meninges- Cover the brain and spinal cord, lines the cranial and spinal cavities, contains cerebrospinal fluid.
7. Fibrous pericardium- Forms a sac around the heart, lined by the serous parietal pericardium.