What is the main function of epithelial tissue?
Protection (also absorption and secretion)
What is the main function of nervous tissue?
Coordination/Communication
What is the main function of muscle tissue?
Movement
What is the main function of connective tissue?
Support/Structure (also transport and defense)
What is the function of microscopes?
Magnification of specimens too small to see with the naked eye
This type of epithelial tissue makes up the skin 
Stratified squamous epithelium
Where in the body is nervous tissue found?
Brain, spinal cord, nerves
This type of muscle tissue is attached to bones and tendons 
Skeletal muscle tissue
This type of connective tissue carries oxygen throughout your body :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cml-under-microscope-5b85803346e0fb005093fb84.jpg)
Blood
What are the two knobs used to focus the microscope?
Coarse and fine focus
This type of tissue is found in the kidney for secretion
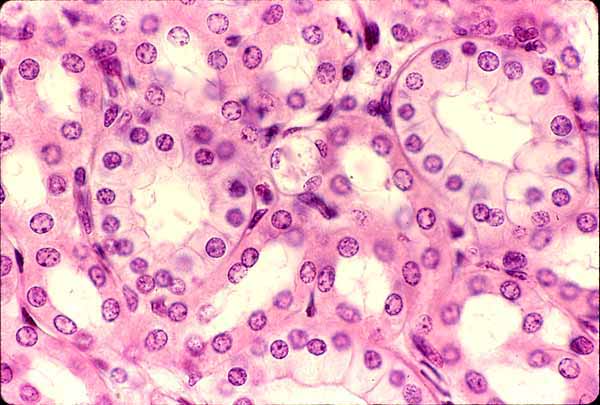
Simple cubodial epithelium
What type of cell is this? 
Neuron
This type of tissue is found in the walls of organs
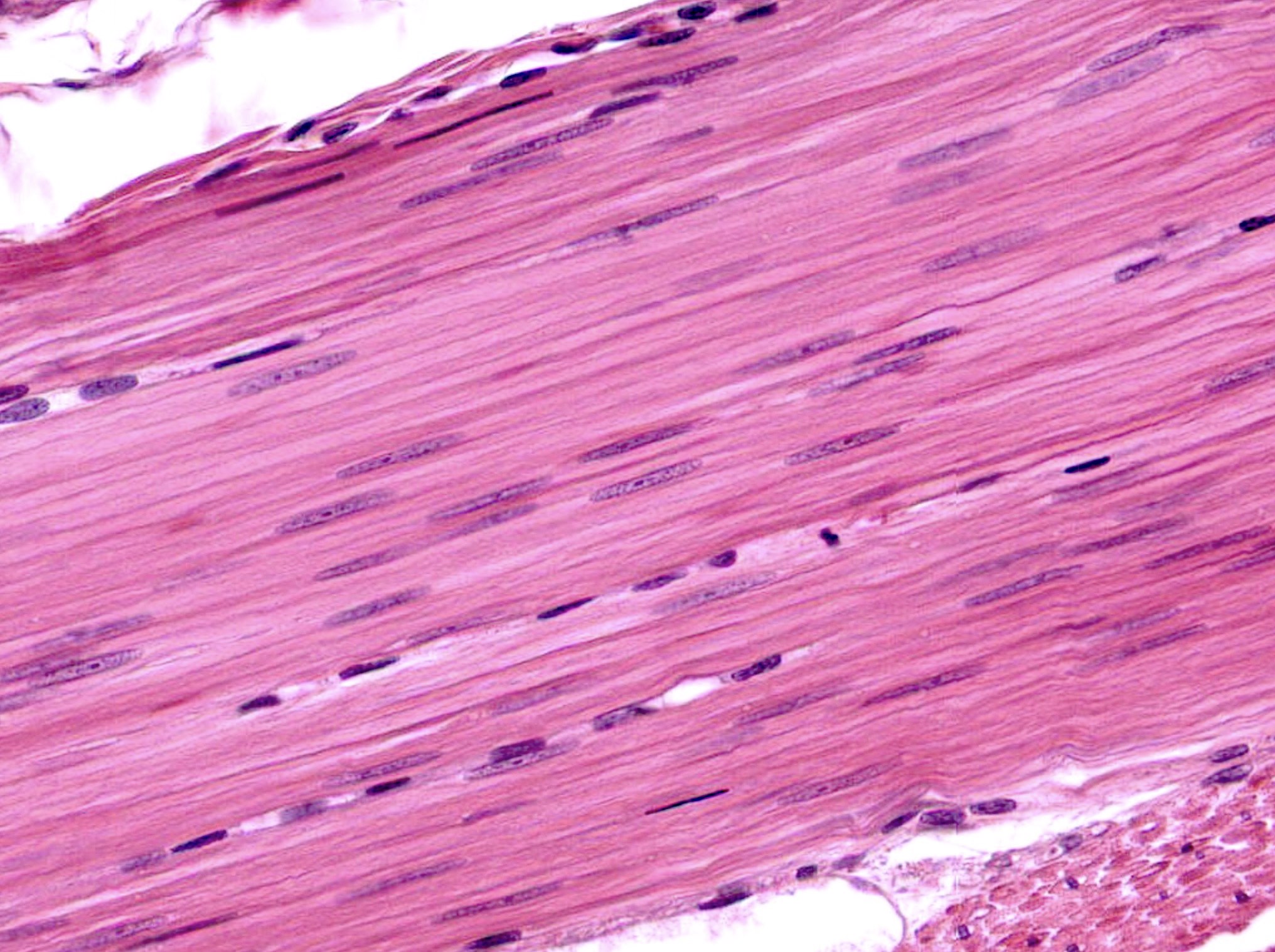
Smooth muscle tissue
This type of connective tissue makes bones strong 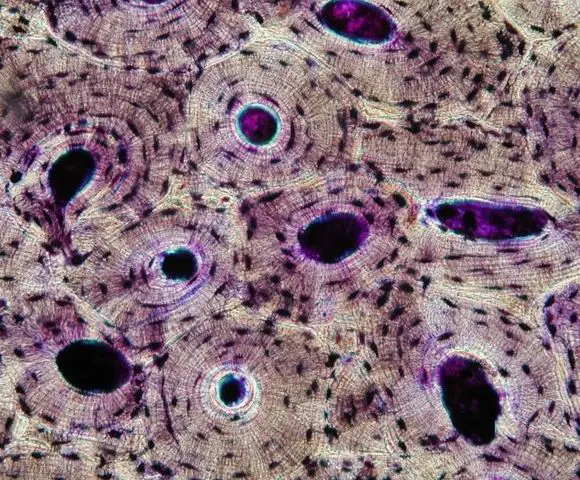
Compact bone
What are the two different lenses on a compound light microscope?
Eyepiece (ocular lens) and objective lens
This type of tissue is found in the stomach for secretion

Simple columnar epithelium
The small dots are cells that protect and support neurons. What are they called? 
Glial cells
This type of tissue is found in the heart
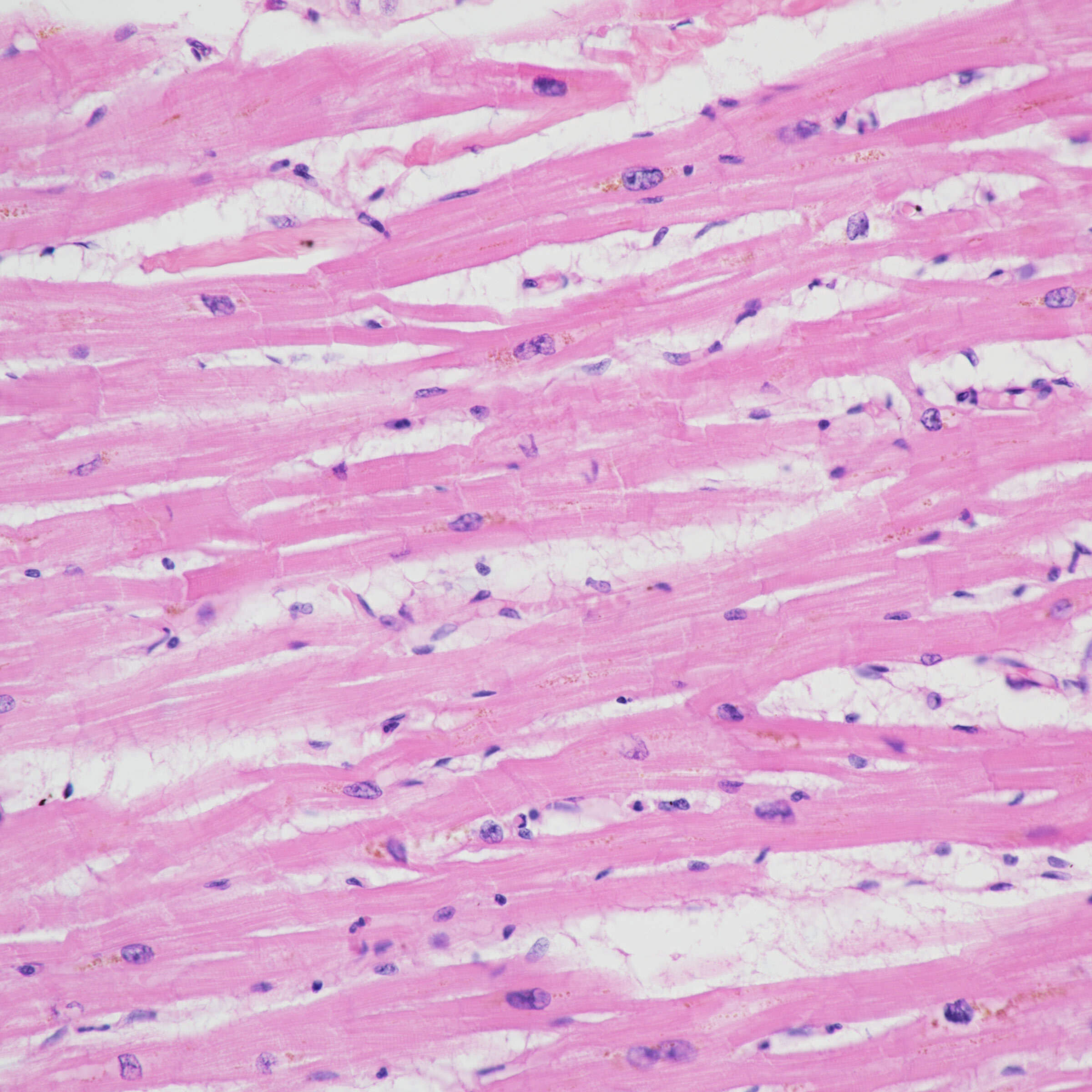
Cardiac muscle tissue
This type of connective tissue makes up ligaments and tendons
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dense_connective_tissue-56a09aee3df78cafdaa32ca1.jpg)
Dense connective tissue (regular in this photo)
Which magnification should be used when first focusing the microscope?
The lowest magnification (x4)
This type of tissue is found in the trachea 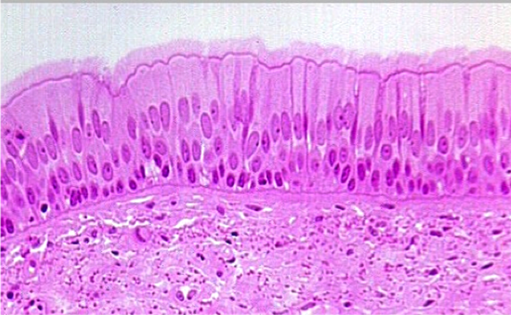
Pseudostratified epithelium
The name of the long tail that transmits signals from the neuron 
Axon
Which types of muscle tissues are involuntary?
Smooth and cardiac
This type of tissue cushions organs

Loose connective tissue
What is the magnification if the eyepiece is 10x and the objective lens is 40x?
400x