Look at the diagram of a roller coaster below. At what point on the track does the car have the greatest potential energy?
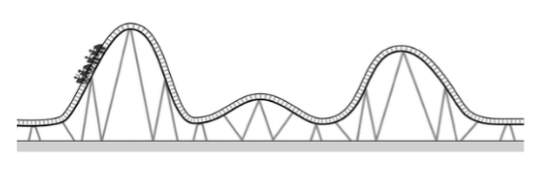
The highest point on the track
The motion of an object can be described by its:
A. position
B. direction
C. speed
D. all of the above
A sloth weighs 30 N and is hanging in a tree 4 m off the ground. What is its gravitational potential energy?
120 J
Heat energy is also known as?
Thermal energy
Jaime has a 20-N bird feeder on a 2-m pole in his yard. The gravitational potential energy (GPE) of the bird feeder is the result of:
A. its elasticity
B. its kinetic energy
C. gravitational pull of Earth
D. its speed and mass
C. gravitational pull of Earth
Look at the diagram of a roller coaster below. At what point on the track does the car have the greatest kinetic energy?
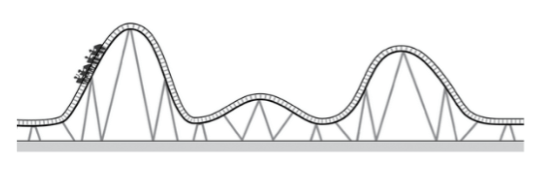
At the lowest point on the track
The rate at which work is done, and it equals the amount of work done on an object in a unit of time.
Power
A man riding his bike up a hill has a kinetic energy of 2 J and a potential energy of 1.5 J. What is his mechanical energy?
3.5 J
Sunlight enables plants to use water and carbon dioxide during photosynthesis to make and store sugar. Any animal that eats the plants can convert the sugar into the energy it needs to move from place to place. Which one type of energy is NOT involved in this example?
A. chemical
B. electromagnetic
C. kinetic
D. thermal
D. thermal
What are the two factors that affect kinetic energy?
Speed and mass
The following diagram of a pendulum shows the path it takes as it swings back and forth. As the pendulum moves from point 1 to point 3, what happens to its mechanical energy?
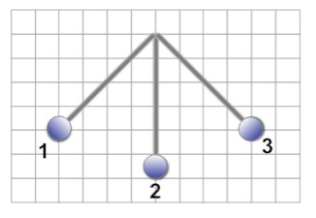
Potential energy is converted to kinetic energy and back again.
Kinetic and potential energy associated with the motion, shape or position of an object.
Mechanical Energy
(KE + PE!!!!)
Maria’s class has learned how to drop an egg without breaking it. After 0.2 s, the kinetic energy of the falling egg is 0.5 J. If its mechanical energy is 2.3 J, what is its potential energy?
1.8 J
A ball rolling down a hill is an example of what energy transformation?
Potential to kinetic
While Robert was helping his father in the garden, he pushed a shovel into the ground to dig a hole in the dirt. He picked up a shrub, carried it to the hole, and held it while he lowered it into the hole. During which parts of this process does Robert NOT do work?
He carried it to the hole.
Ali rolled a ball down a hill. The graph shows the kinetic and potential energy of the moving ball. According to the graph, what is the mechanical energy of the ball?
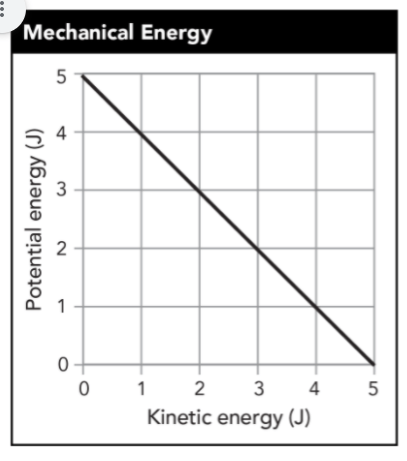
Mechanical Energy = 5 J
Any time a force is exerted on an object that causes it to change its motion in the SAME DIRECTION that the force was exerted in.
Work
The Kentucky Derby is one of the most exciting horse races run every year. In 1973, the horse Secretariat set a record that still stands. This 500-kg horse ran the 2000-m track in 120 s. What was Secretariat’s average kinetic energy? (1 kJ = 1000 J)
69.0 kJ
Marcus is hanging a porch swing on his front porch. The first thing he has to do is attach two springs to the ceiling. Then, he fastens the swing to the springs so that they can stretch and support the weight of the swing. Which two types of potential energy do the springs have?
Elastic and gravitational
What is the difference between transfer and transformation?
Transfer - the same form of energy is moved to a different object
Transformation - one form of energy changes into another form
In the graph, the ball is still moving down the hill. Explain how the graph would change if it showed the ball reaching the bottom of the hill and stopping. Then, explain how coming to a stop affects the mechanical energy of the ball.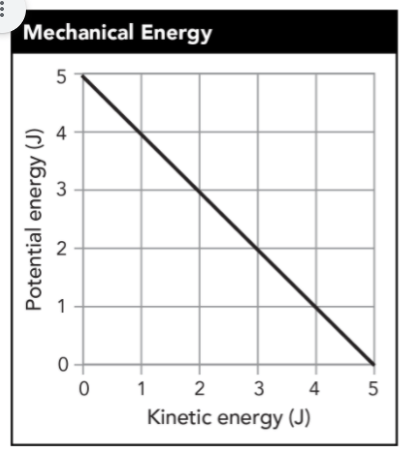
The line would be opposite of what is shown - It would start at (5,5) which is the most kinetic and potential energy at the same time. It would end at (0,0) which is the bottom of the hill - 0 KE and 0 PE.
Coming to a stop reduces the mechanical energy of the ball because there is no kinetic energy without motion.
Energy cannot be created or destroyed. It is ALWAYS conserved.
Jordan wants to know the difference between using a 60-W and 100-W light bulb in her lamp. She calculates the energy it would take to use each bulb for 30 days by using this equation:
Power = Energy transferred (J)/time (s)
What is the difference in the amount of energy transferred by the two bulbs during this time?
1200 J
Chloe is training for her first half-marathon, which requires her to run 21.1 km. Before she runs, she carefully chooses the foods that will give her the energy her body requires for the race. She stands still at the starting line, then she starts running, her body warming up as she runs. Which three energy transformations take place in this example?
A. chemical energy to kinetic energy
B. chemical energy to electrical energy
C. chemical energy to thermal energy
D. potential energy to kinetic energy
A, C, and D
The relationship between energy and motion involves:
Forces