This is a positively charged particle in the nucleus of an atom
Proton
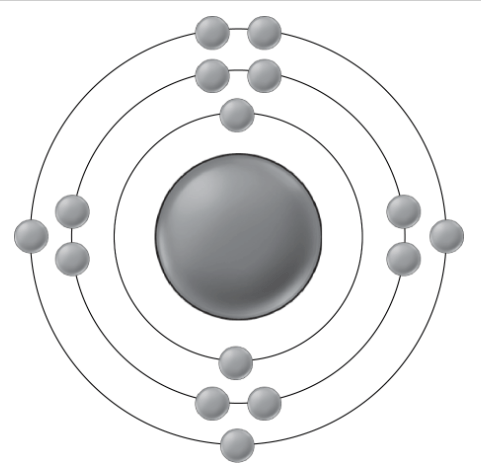 What is this way of representing elements known as?
What is this way of representing elements known as?
It is a Bohr's Model
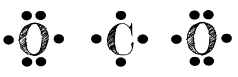 What is this way of representing elements known as?
What is this way of representing elements known as?
They are dot diagrams.
In this kind of bonding, metals bond with non-metals, giving away electrons to the non-metals to help complete their valence. This results in positive and negative charges. The structures are crystal shaped.
This is ionic bonding
This type of compound is corrosive to metals, taste sour, and reacts with carbonates.
Acid
This is a neutral (no charge) particle in the nucleus of an atom.
A Neutron
Dalton, Rutherford, Bohr, Thomson, and Schrodinger all contributed different ideas about matter. Together these ideas make up the way we understand atoms. This understanding is called:
Modern Atomic Theory
The tall columns (also known as groups) are together because they have this in common:
They all have the same # of valence electrons.
In this kind of bonding, non-metals bond with other non-metals to form molecules. This arrangement involves sharing electrons, rather than giving them away. This structure forms molecules.
These are covalent bonds.
This type of compound feels slippery, tastes bitter, and if found in many household cleaning products.
Base
This is a negatively charged particle orbiting around the nucleus of an atom.
An electron.
The combination of the number of neutrons and protons in a nucleus (added to together)
Atomic Mass
Elements will bond with one another in order to get a full valence. How many electrons make a full valence in the first layer?
How many electrons make a full valence in every layer after the first layer?
Two
Eight
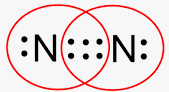 Is this a picture of an ionic bond or a covalent bond? How can you tell?
Is this a picture of an ionic bond or a covalent bond? How can you tell?
It's covalent because electrons are being shared
The result of mixing an acid and a base is usually the production of _________.
A salt
This is an electron in the outermost layer
A valence electron
Why is the Periodic Table of Elements called "periodic"
It follows a repeating pattern
These elements have 4-8 valence Electrons, are usually dull, brittle, terrible conductors of heat and electricity
These are non-metals.
 Is this covalent bond polar or no polar? How can you tell?
Is this covalent bond polar or no polar? How can you tell?
It is polar because Chlorine (bonding from it's 3rd layer) is pulling way hard than Hydrogen (bonding from it's first layer)
Mixing an acid and a base together will produce this kind of reaction
A neutralization reaction
a type of element that has the same number or protons and electrons, but a different number of neutrons
(Ex: Carbon-12, Carbon-13, Carbon-14)
An isotope
Why are neutrons more difficult to observe than other particles?
1) They are in the nucleus.
2) They have no charge.
These elements are very reactive, have 1-3 valence electrons, are shiny, malleable, and good conductors of heat and electricity.
These are metals.
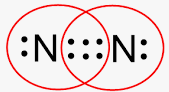 This is a non-polar, covalent bond. Is it considered a single, double, or triple bond? How can you tell?
This is a non-polar, covalent bond. Is it considered a single, double, or triple bond? How can you tell?
It is a triple bond because each Nitrogen atom is sharing three electrons.
Which is most likely to be damaged by an acid?
a. a glass jar
b. a plastic bottle
c. a gold bracelet
d. an aluminum can
D. An aluminum can