A sample of DNA is analyzed and found to contain 24% A. One would expect to find _____ % C.
What is 26%
The enzyme represented by the gray oval in the image below:
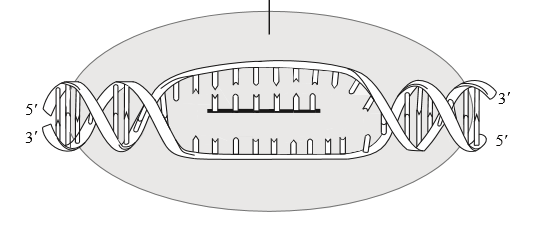
RNA Polymerase
Short segments of newly synthesized DNA complimentary bonded to the 5' to 3' parent strand
Okazaki fragments
The site(s) of amylase production.

What are the salivary glands and pancreas?
Involves a response that reinforces the change detected (it functions to amplify the change). The birth process is an example of this process.
- In the case of childbirth, fetal growth eventually causes stretching of the uterine walls, which is detected by stretch receptors
- This triggers the release of hormones (oxytocin) that induce uterine muscles to contract, further reducing space in the womb
- This causes more stretching and hence more contraction until the origin stimulus (the foetus) is removed (i.e. birth)
What is a positive feedback process?
Improves the speed of electrical transmission via saltatory conduction
What is myelination or the presence of the myelin sheath on axons?
What is Voldemort's middle name?
Marvolo
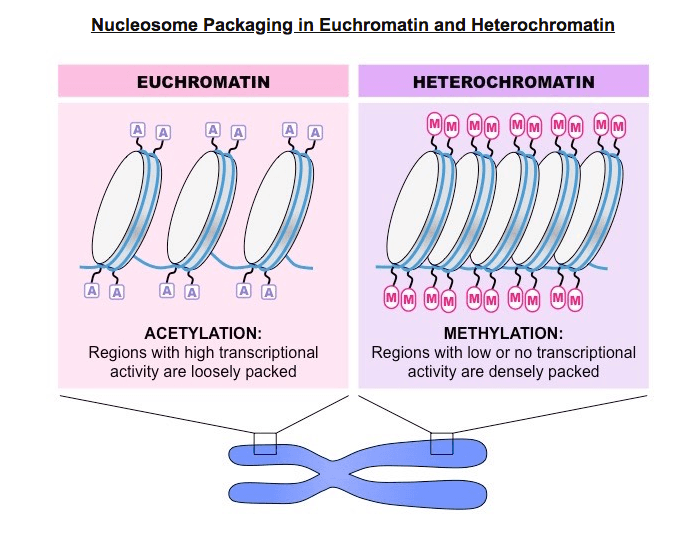
When DNA is supercoiled and not accessible for transcription
Heterochromatin
What is represented by "W" and "X" in the image below:
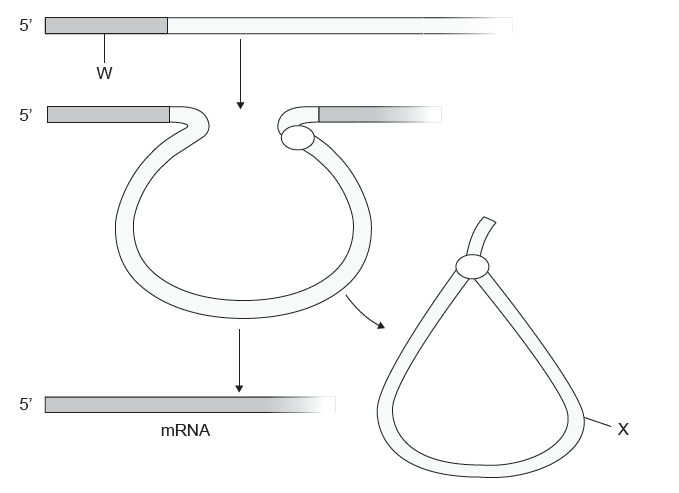
"W" = exon
"X" = intron
Indicate where in the image below a new DNA nucleotide would be attached.
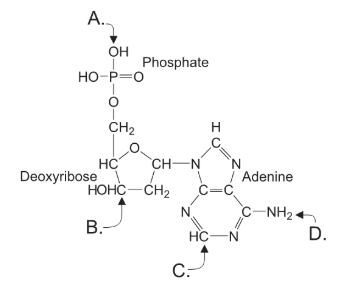
"B"
Hormone regulates the hours of sleep and wakefulness
What is melatonin?
Name the specific type of cell that is responsible for the differences in the speed and magnitude of the immune response after the second infection.
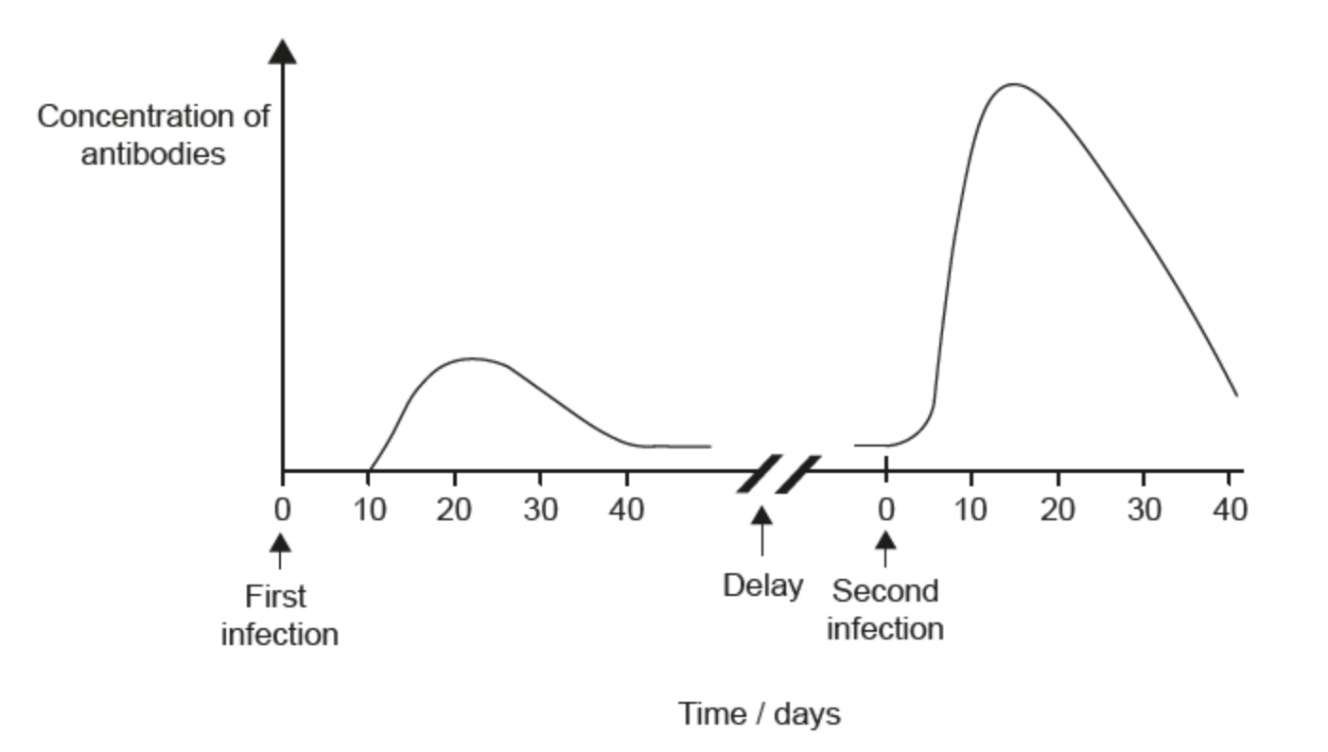
What are memory "B" cells?
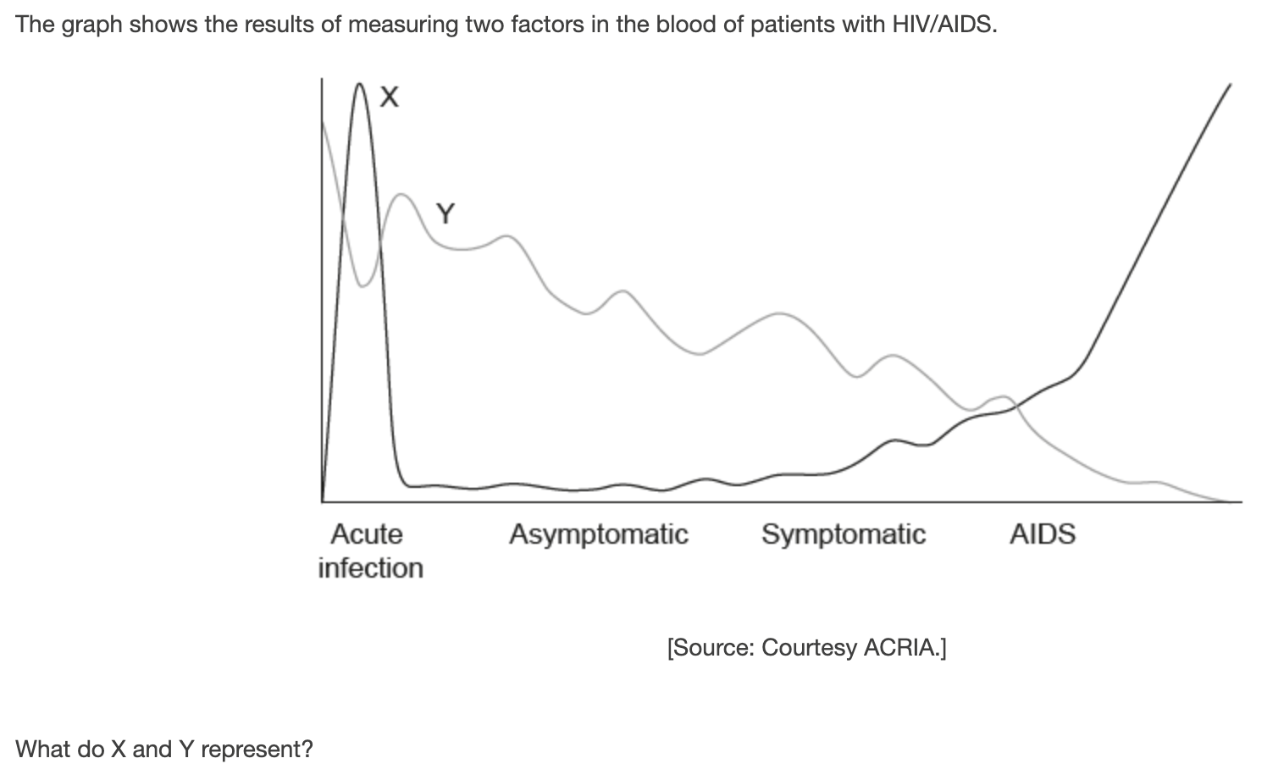
What are..
X: HIV virus
Y: Lymphocytes (T Cells)?
Typo on the Liberty Bell
Pensylvania
Consists of a molecule of DNA wrapped around a core of eight histone proteins
Nucleosome
The DNA is complexed with eight histone proteins (an octamer) to form a complex called a nucleosome
Nucleosomes are linked by an additional histone protein (H1 histone) to form a string of chromatosomes
These then coil to form a solenoid structure (~6 chromatosomes per turn) which is condensed to form a 30 nm fibre
These fibres then form loops, which are compressed and folded around a protein scaffold to form chromatin
Chromatin will then supercoil during cell division to form chromosomes that are visible (when stained) under microscope
Two groups of proteins that mediate binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter and regulate transcriptional activity.
Transcription factors form a complex with RNA polymerase at the promoter
-physically can't transcribe without these
"X" in the image below:
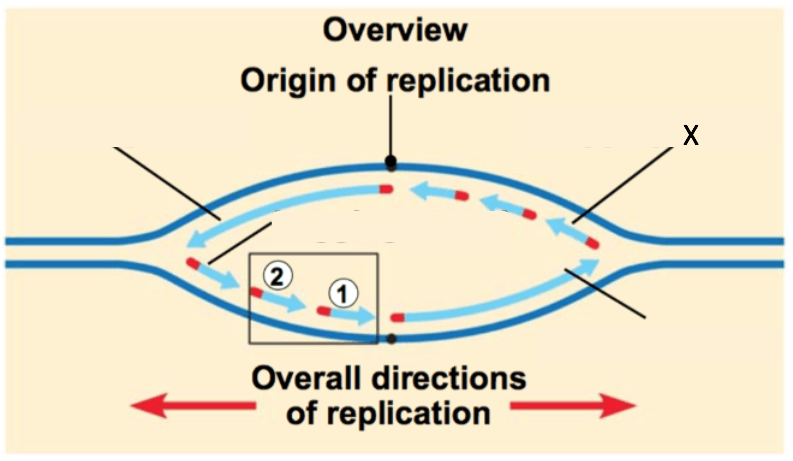
Okazaki Fragment
Location of the SA node. 
What is the right atrium?
A sudden change in neuron membrane potential – usually from a (relatively) negative to positive internal charge. Occurs in response to a signal initiated at a dendrite.
What is depolarization?
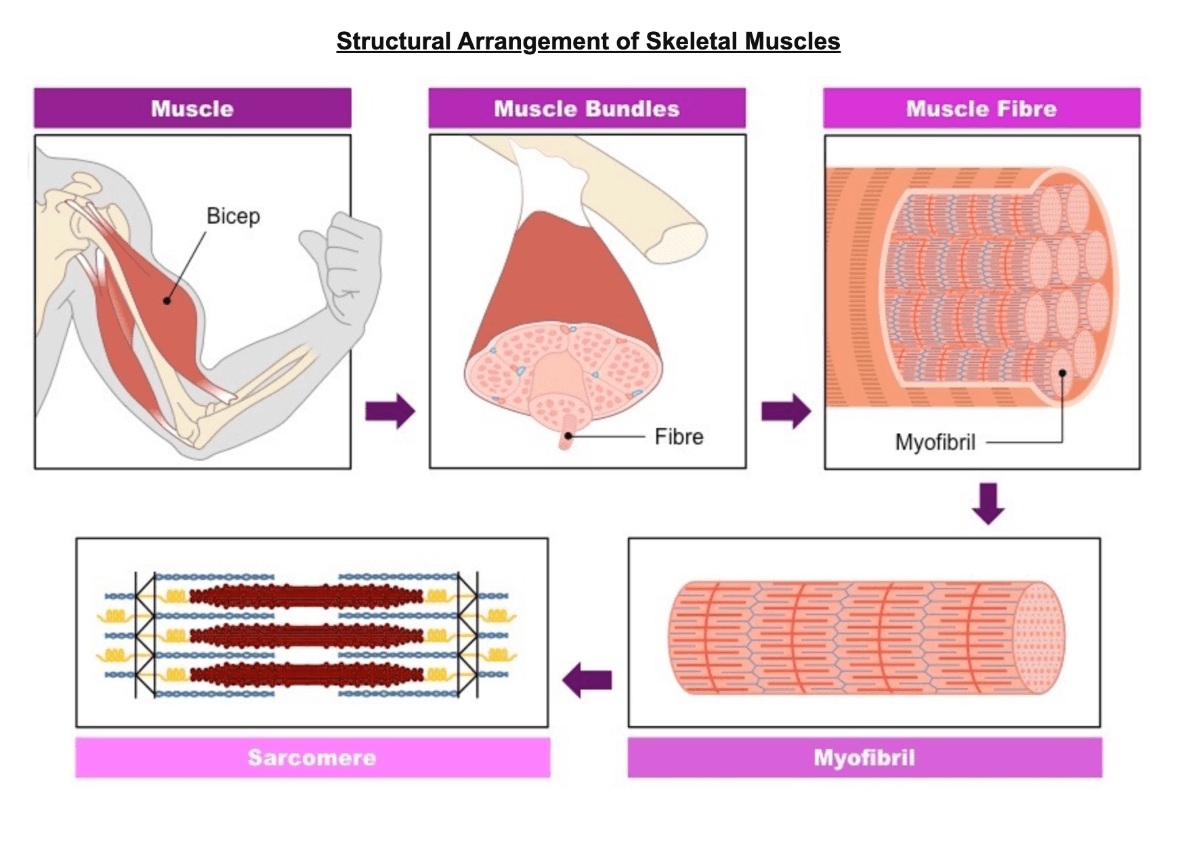
Muscle fibers (cells) contain tubular myofibrils that run the length of the cell and are responsible for muscular contraction. Myofibrils can be further divided into repeating contractile units called _______.
What are Sarcomeres?
Current age of Harry Potter (the character, not the actor that played Harry Potter)
Any Potterhead worth their wand will know Harry Potter's birthday is July 31 and that he was born in 1980. That means that The Boy Who Lived is now a 41-year-old man who is set to celebrate his 42nd birthday in the summer of 2022
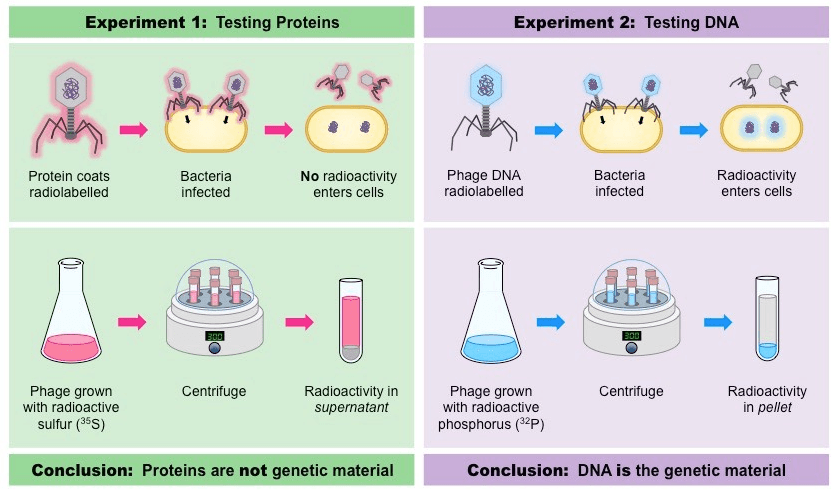
Scientist(s) who proved that DNA, not protein, was the primary genetic material.
Who were Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase.
The mRNA transcribed from the following DNA:
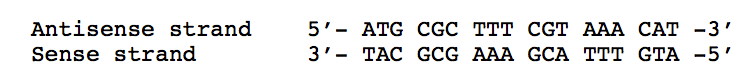
5’-AUG UUU ACG AAA GCG CAU-3’
Removes the RNA primers from the lagging strand and replaces them with DNA nucleotides
DNA Polymerase I
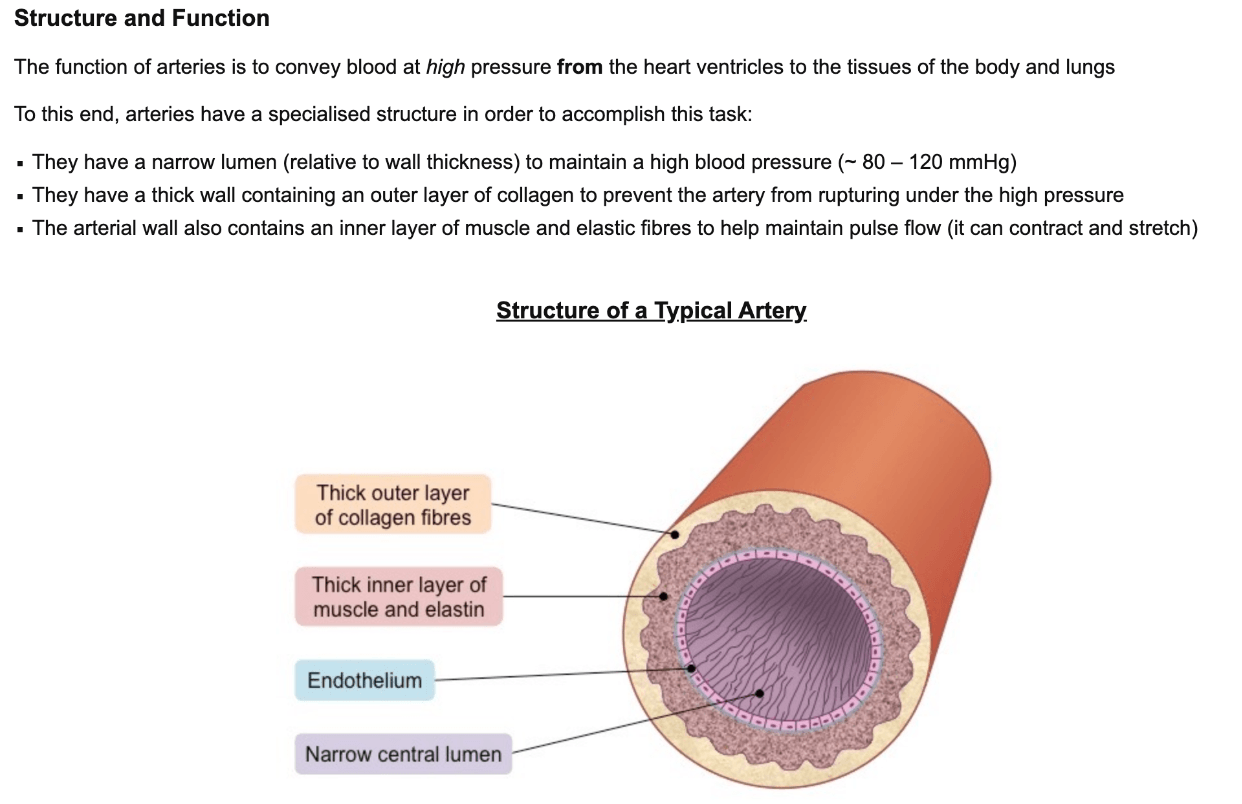
Narrow lumen (relative to wall thickness) to maintain a high blood pressure as well as thick wall containing an outer layer of collagen to prevent from rupturing under the high pressure
What are arteries?
In the initial phase of the menstraul cycle, this hormone is secreted from the anterior pituitary and stimulates growth of ovarian follicles.
What is FSH (follicle stimulating hormone)?
This hormone functions to maintain the endometrium (which is nourishing the embryo) and thicken the cervix during pregnancy.
What is progesterone?
lemniscate (mathematical term/concept)
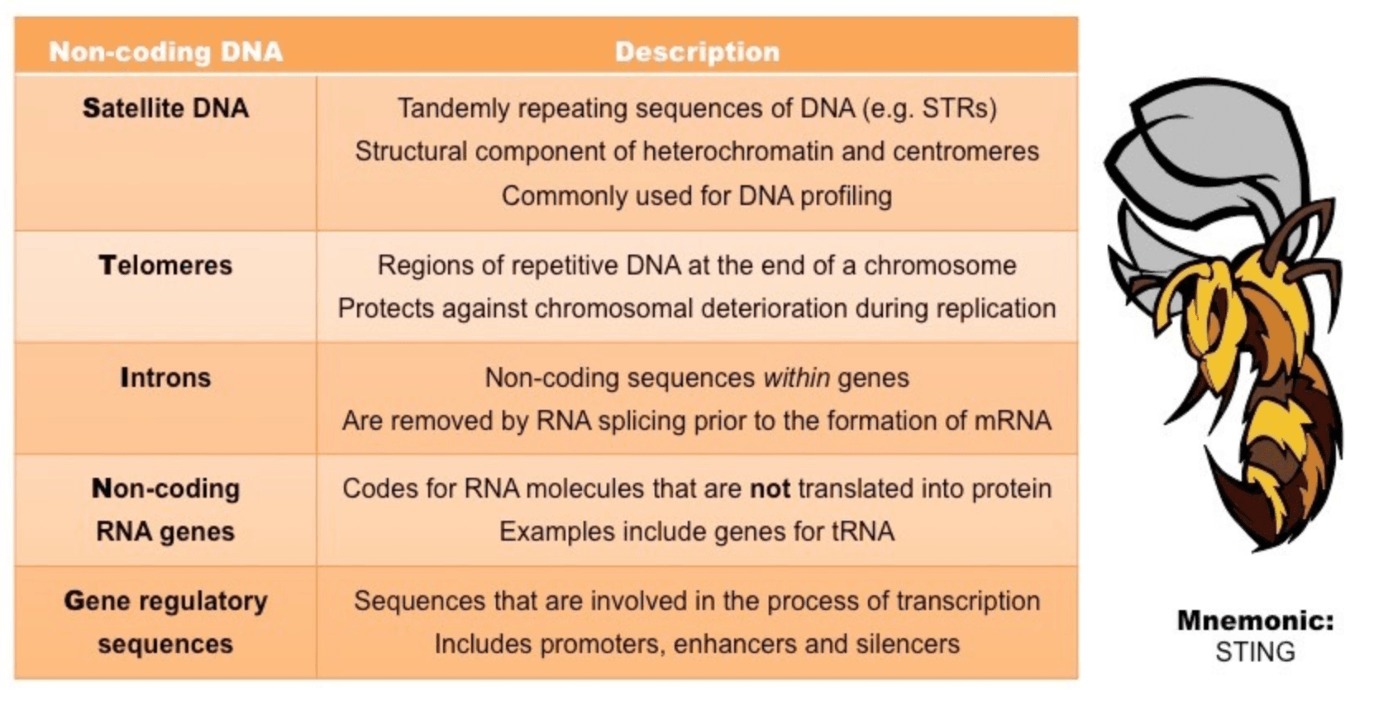
Regions of repetitive DNA located at each end of a chromatid and function to prevent chromosomal deterioration
Telomeres
Segment of DNA to which a repressor protein binds (inhibits transcription by obstructing RNA polymerase)
Operator
Recall:
There are three basic components to an operon
- Promoter – Upstream sequence to which RNA polymerase binds
- Operator – Segment of DNA to which a repressor protein binds (inhibits transcription by obstructing RNA polymerase)
- Structural genes – Genes that are collectively regulated by the operon

3’-end of the primer and covalently joins the free nucleotides together in a 5’ → 3’ direction
DNA Polymerase III
Major function of type 1 and type 2 pneumocytes, respectively.
Type I pneumocytes are involved in the process of gas exchange between the alveoli and the capillaries
- They are squamous (flattened) in shape and extremely thin (~ 0.15µm) – minimising diffusion distance for respiratory gases
- Type I pneumocytes are connected by occluding junctions, which prevents the leakage of tissue fluid into the alveolar air space
- Type I pneumocytes are amitotic and unable to replicate, however type II cells can differentiate into type I cells if required
Type II pneumocytes are responsible for the secretion of pulmonary surfactant, which reduces surface tension in the alveoli
- They are cuboidal in shape and possess many granules (for storing surfactant components)
- Type II pneumocytes only comprise a fraction of the alveolar surface (~5%) but are relatively numerous (~60% of total cells)
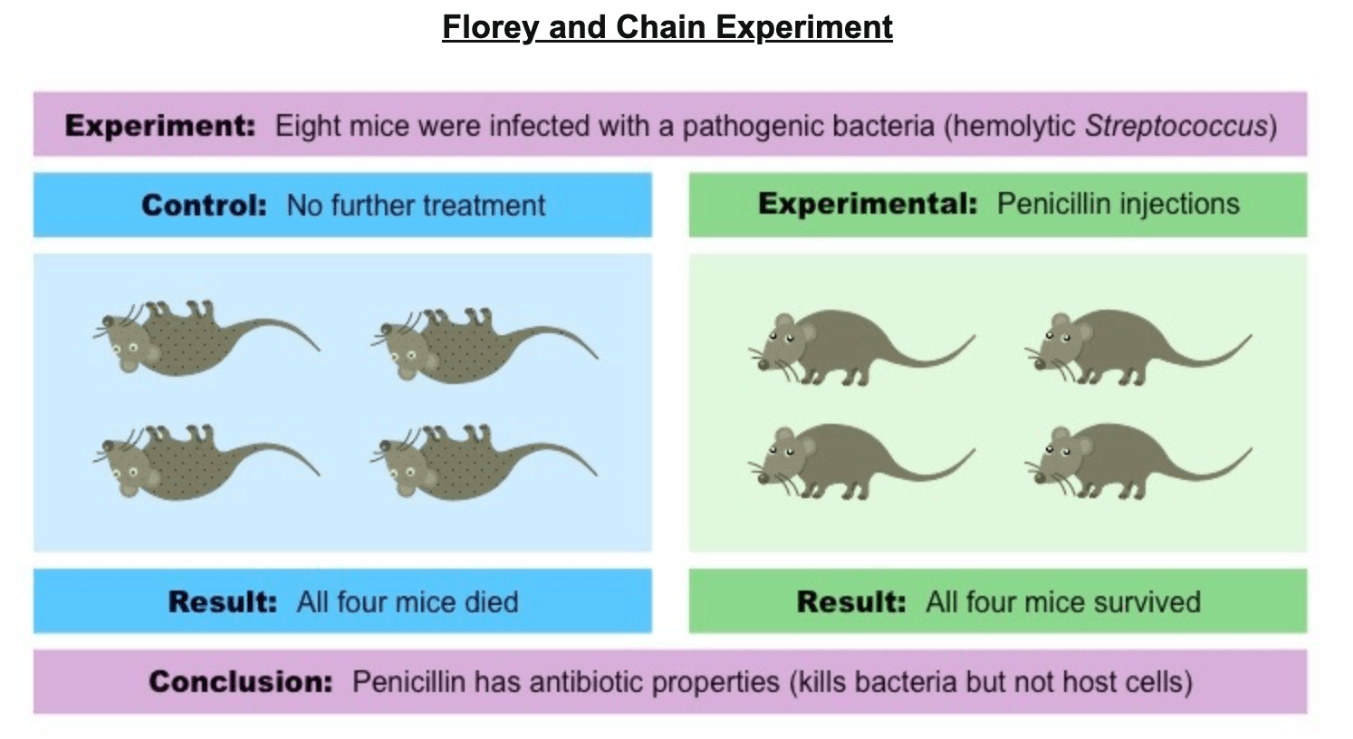
The significance of the Florey Chain experiment.
What is proving that penicillin had antibiotic medicinal properties?
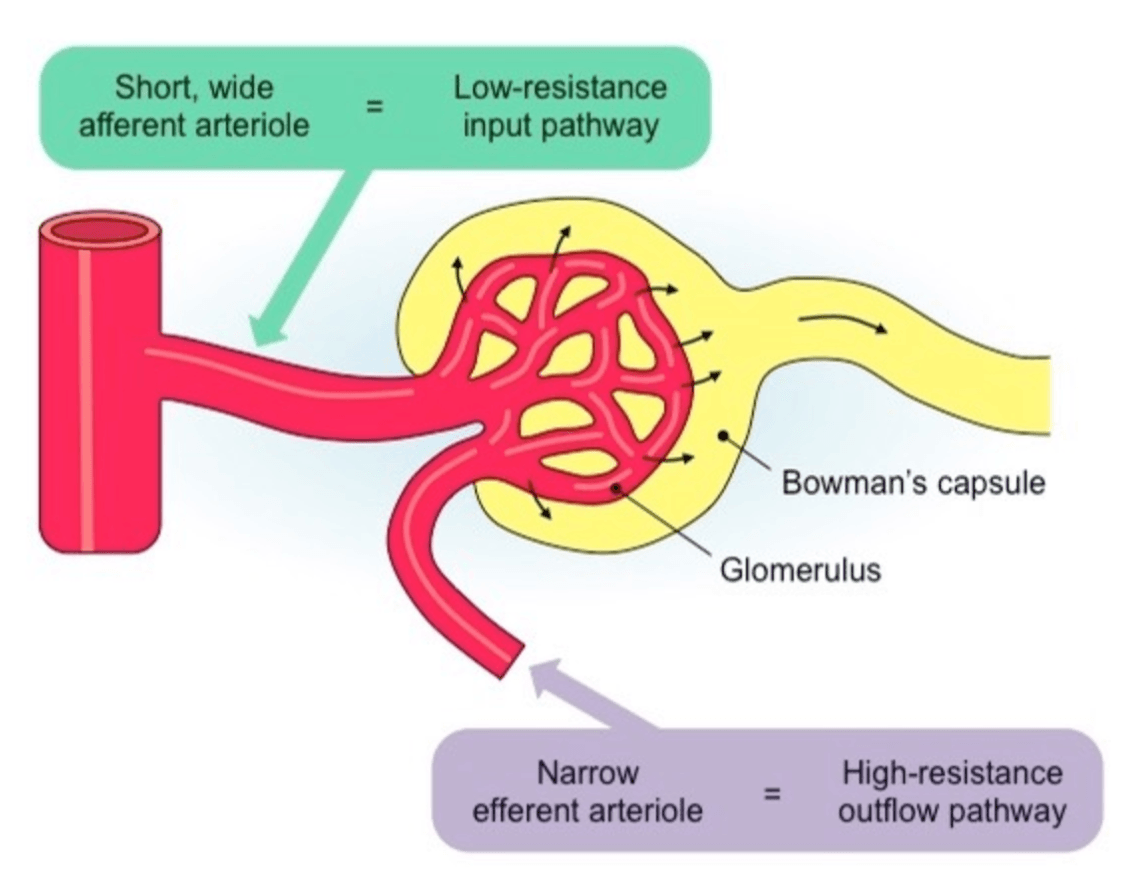
Ultrafiltration involves blood being forced at high pressure against the basement membrane, optimising filtration in the kidney. This is the cause of the high hydrostatic pressure in the kidney's glomerulus.
What is having a wide afferent (incoming) arteriole and a narrow efferent (outgoing) arteriole?
The Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer, considered by many to be the first electronic computer, was made at which University?
UPENN
Example of non-coding DNA
Decreases gene expression (by preventing the binding of transcription factors)
DNA Methylation
Lack the 3’-hydroxyl group necessary for forming a phosphodiester bond and can therefore be used in DNA sequencing
Dideoxynucleotides
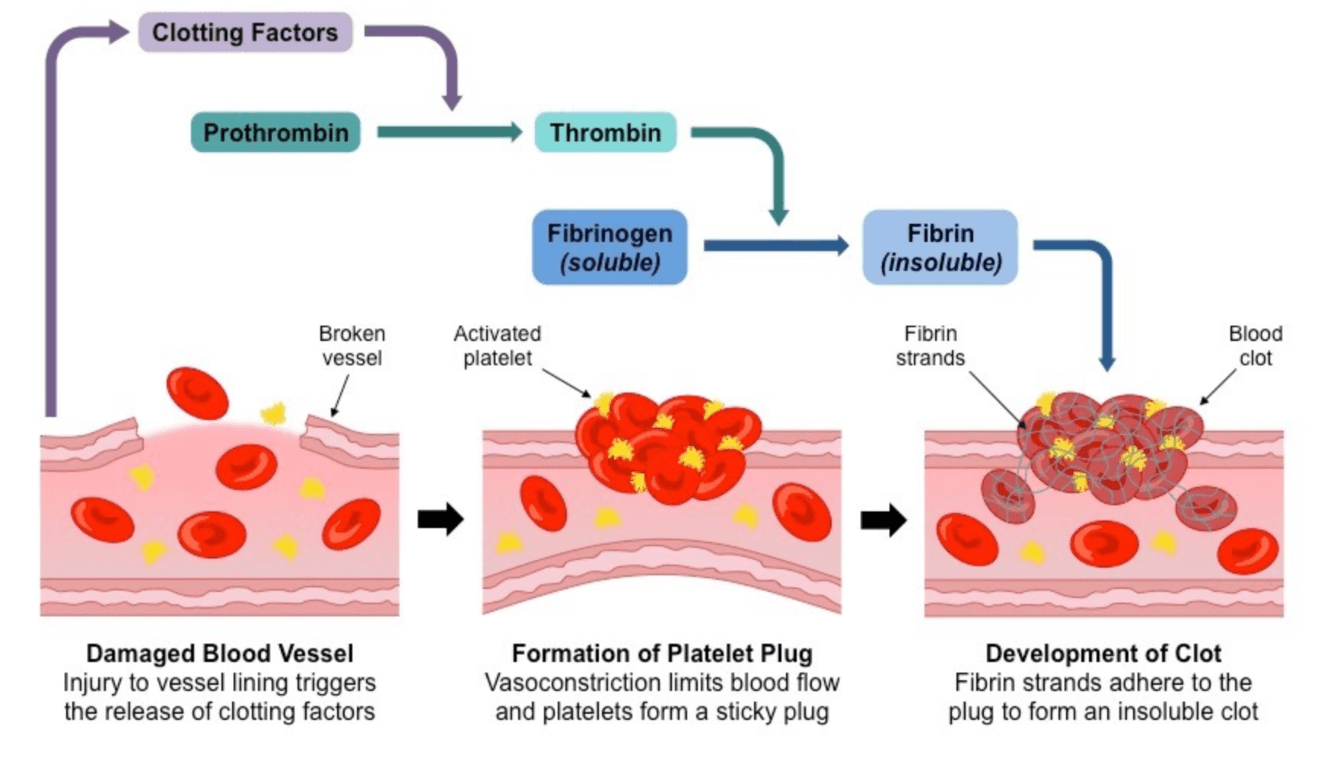
Explain the blood clotting cascade.
Clotting factors cause platelets to become sticky and adhere to the damaged region to form a solid plug
These factors also initiate localized vasoconstriction to reduce blood flow through the damaged region
Clotting factors trigger the conversion of the inactive prothrombin into the activated enzyme thrombin
Thrombin in turn catalyses the conversion of the soluble plasma protein fibrinogen into an insoluble fibrous form called fibrin
The fibrin strands form a mesh of fibres around the platelet plug and traps blood cells to form a temporary clot
In muscle contraction, calcium ions bind to this structure and reconfigure the complex, exposing the binding sites for the myosin heads
What is troponin?
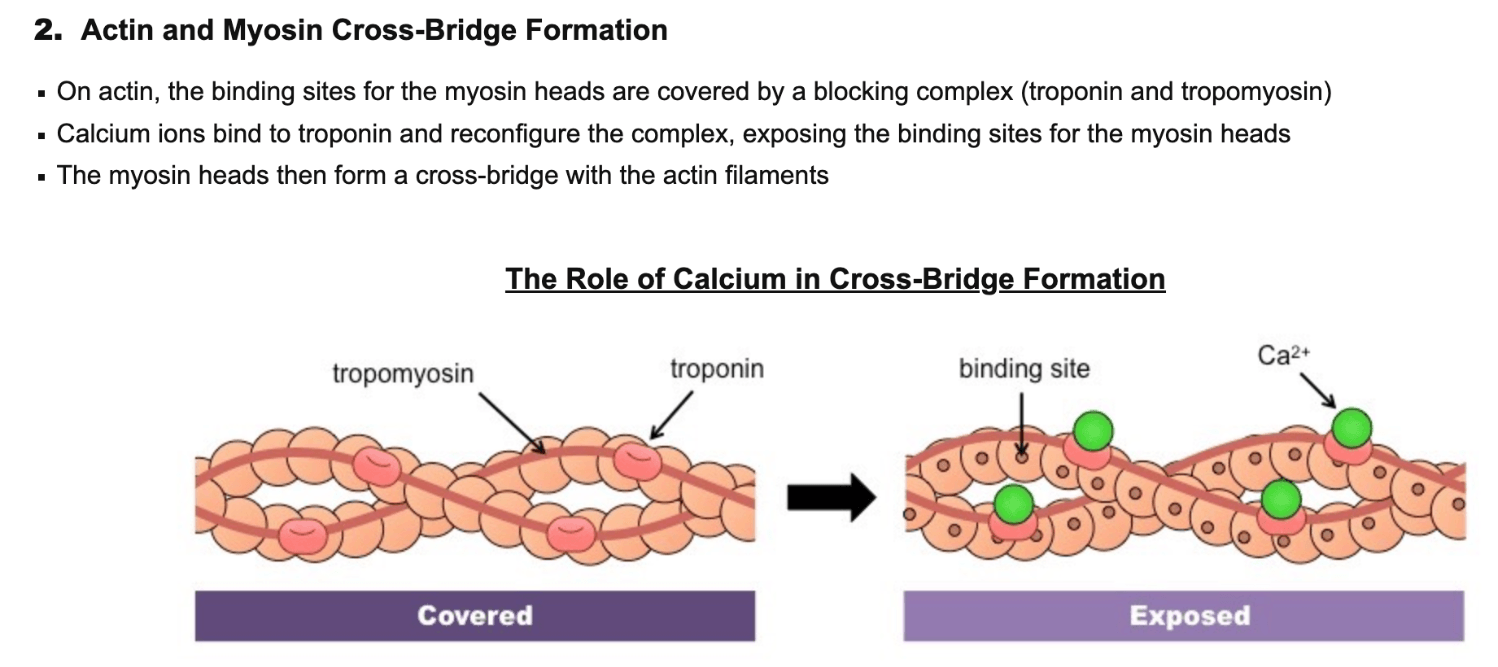
Summarize Muscle Contractions
Summary of Muscle Contractions
- Action potential in a motor neuron triggers the release of Ca2+ ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
- Calcium ions bind to troponin (on actin) and cause tropomyosin to move, exposing binding sites for the myosin heads
- The actin filaments and myosin heads form a cross-bridge that is broken by ATP
- ATP hydrolysis causes the myosin heads to swivel and change orientation
- Swiveled myosin heads bind to the actin filament before returning to their original conformation (releasing ADP + Pi)
- The repositioning of the myosin heads move the actin filaments towards the centre of the sarcomere
- The sliding of actin along myosin therefore shortens the sarcomere, causing muscle contraction
Name the President/Vice President combo where neither were elected to those positions in the general election.
Ford/Rockefellar