What did the Proclamation of 1763 tell colonists about settling land?
No settlement west of the Appalachian Mountains.
Which Boston lawyer defended the soldiers from the Boston Massacre?
John Adams
What do we call refusing to buy goods to make a political point?
boycott
What was a goal of the First Continental Congress?
A) To declare war on Great Britain
B) To find a solution to the conflicts with Great Britain
C) To create taxes acceptable to the Americans
D) To bring British and American representatives together
To find a solution to the conflicts with Great Britain
In 1774, how did most colonists primarily view themselves?
A) United Americans
B) Dependent on the king
C) Citizens of their individual colonies
D) United under the British government
C) Citizens of their individual colonies
What did the Stamp Act (1765) require colonists to buy for newspapers, wills, and playing cards?
Stamps on printed paper items.
How did many of the Loyalists view the Patriots?
as ungrateful rebels
What protest did colonists use to oppose the Townshend Acts, leading to repeal of most duties?
Boycotts of British goods.
After the Boston Tea Party (342 chests dumped in Boston Harbor), which British response punished Massachusetts with closed ports, new controls on government, and more troops?
The Intolerable Acts
What short phrase sums up the colonists’ belief that they shouldn’t be taxed by a legislature where they had no vote?
“No taxation without representation.”
Why did Parliament pass the Townshend Acts (1767)?
To help pay for troops/defense in America and assert Parliament’s authority.
What new idea did Patrick Henry bring to the First Continental Congress about identity?
Think of themselves as Americans united, not just Virginians, etc.
The colonists boycotted British goods to protest the Townshend Acts. How did women play a part in the boycott?
They created American-made items so that colonists did not have to buy British-made items that were taxed
Which group benefited from the Proclamation of 1763?
--The colonists
--American Indians
--French soldiers
American Indians
What word means the cruel or unjust use of government power?
Tyranny
What did the Quartering Act (1765) require local assemblies to provide to British troops?
Housing and supplies (quarters, candles, bedding, fuel, etc.).
Before 1760, in most colonies, which local group made laws and collected taxes?
Colonial Assemblies
In the 1760s–1770s, how did Great Britain increase its control over the American colonies?
by requiring colonists to pay taxes
What territories were gained by the British after the French and Indian War?
Canada and last west of the Appalachian Mountains
Colonists branded the March 5, 1770 confrontation “the Boston Massacre.” What was the main goal of using this dramatic label?
to create anti-British sentiment (feelings/opinions)
Name two parts of the Intolerable Acts (1774) that punished Massachusetts.
Any two: closed Boston Harbor; put MA government under tighter British control; trials for soldiers moved to Britain; more troops sent to Boston.
Which group formed the Sons of Liberty?
Patriots
From the first shots in April 1775 at Lexington and Concord, it became unmistakable that colonists were prepared to do this to defend self-government.
The colonists were willing to fight for the right to govern themselves.
What was one positive outcome for the British after the French Indian War?
What was one negative outcome for the British after the end of the French Indian War?
The British defeated France
The British gained all of Canada and land west of the Appalachian Mountains
The British spent and borrowed a lot of money for this war and went into great debt.
To which of the following events are the two Paul Revere engravings referring?
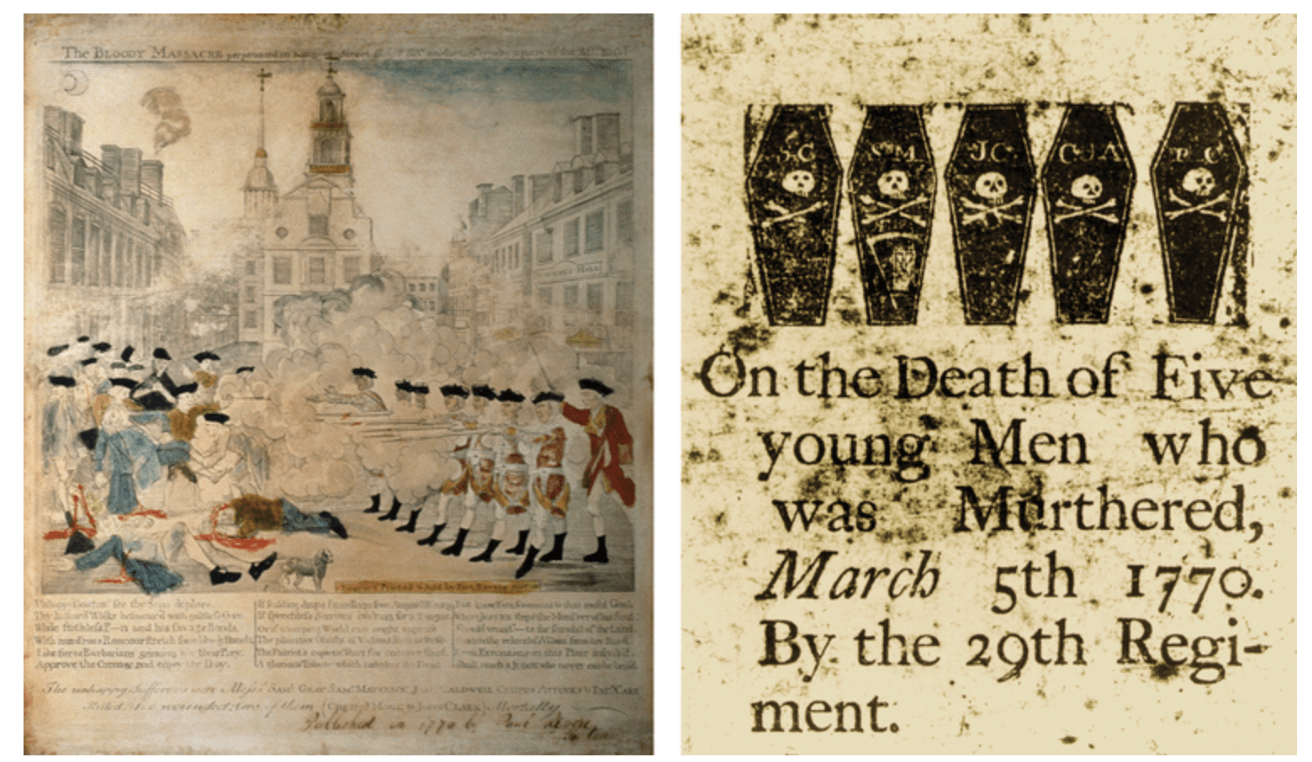
Boston Massacre
Who said, “I am not a Virginian, but an American,” and at what gathering was it said?
Patrick Henry, at the First Continental Congress (Philadelphia, 1774).