A predator at the very top of its food web with no natural predators, like an orca or a lion.
Apex Predator
These natural disasters are examples of abiotic limiting factors. Name two.
wildfires, floods, volcanic eruptions, or hurricanes
This occurs when organisms, like the Red-Tailed Hawk and Barred Owl, struggle to survive using the same limited resources.
competition
This is the delicate balance between two populations, such as the lynx and the snowshoe hare.
Predator-prey
Carrying capacity is determined by all of these, both biotic and abiotic.
Limiting factors
The location in which an organism lives.
Habitat
These weather conditions are examples of abiotic limiting factors. Name two.
storms, drought, blizzards, or heat/cold
For a drastically increased deer population, this biotic factor would likely become limited.
food source (or food availability)
In the famous Yellowstone example, this animal was reintroduced, starting a trophic cascade.
Grey wolves
A population graph shows that after a period of rapid growth when carrying capacity is reached what will happen to the population?
It will level out or stop growing
A species, like the sea otter or the wolf, that has a huge impact on its ecosystem, and without it, the whole system changes.
Keystone species
This non-living factor is described as the available territory for nesting, hunting, and living.
limited space, space, available territory
This biotic factor, which can be caused by bacteria or viruses, can spread quickly and limit a dense population.
Disease
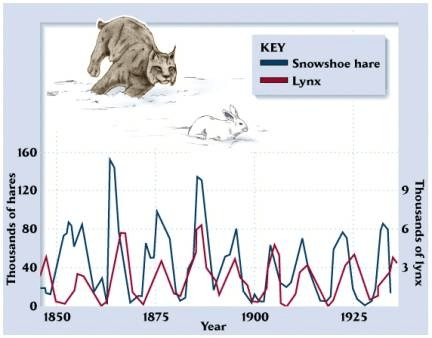 Which population causes the other population to increase or decrease
Which population causes the other population to increase or decrease
The predator population follows the prey population
As a population approaches its carrying capacity, this happens to its birth and death rates.
birth rates decrease and death rates increase
The maximum population size that an environment can support over a long period.
Carrying Capacity
In a dense forest, tall trees can block this, making it a limiting factor for plants on the forest floor.
Sunlight
How do human activities involving building homes, parking lots, and damming rivers impact the ecosystem acting as a limiting factor?
reduces available habitat.
The sea otter is a well-known keystone species in the Pacific kelp forest. Its main food source is the sea urchin, which in turn eats kelp (a type of large seaweed)
If the sea otter were removed from the food web what would happen to the population of the sea urchin?
It would increase
As an ecosystem approaches its carrying capacity what increases as resources become more limited?
Competition
This happens when a change at one level of the food chain, like removing a top predator, causes a ripple effect through the entire ecosystem.
Trophic cascade
A shrinking supply of this liquid is a critical abiotic limiting factor for many populations
Water
A lack of available prey, which are living organisms, will limit the population of their ___________. This is an example of a biotic limiting factor.
Predators
The sea otter is a well-known keystone species in the Pacific kelp forest. Its main food source is the sea urchin, which in turn eats kelp (a type of large seaweed)
If the sea otter were removed from the food web what would happen to the population of the kelp plant?
It would decrease because the sea urchin would eat it all.
 At what population number does it show the carrying capacity is reached
At what population number does it show the carrying capacity is reached
2000