Fat that sits just below the skin
Subcutaneous Fat
Padding between different organs
Visceral Fat
White adipose tissue
Less associated with disease risk, however when increased with cases of obesity can be indicative of a higher risk
Subcutaneous Fat
White adipose tissue
External cushioning, insulation, energy storage, passageway for nerves and vessels
Subcutaneous fat
Subcutaneous fat
Increase of this type of fat in obesity is strongly linked to an increase in chronic disease risk (eg. T2D, CVD)
Visceral Fat
Fat located inside the abdominal cavity
Visceral fat
Main storage mechanism - Fatty acids can be released and transported when energy required
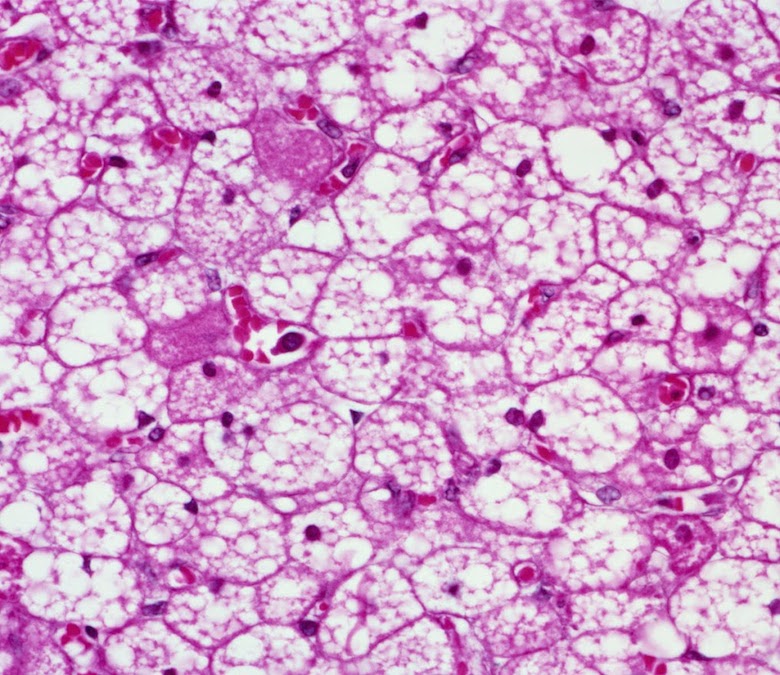
Brown Adipose tissue
Potential for using this tissue to increase the basal energy usage to treat obesity
Brown Adipose tissue
Fat with lots of mitochondria and UCP1 enzyme to alter ETC function
Brown adipose tissue
Uses fatty acids (and some glucose) for heat production
Brown (and beige) adipose tissue

Visceral fat
Seen as an adaption in elite athletes, or those exposed to prolonged cold - potentially effecting basal metabolic rate and heat
Beige adipose tissue
Fat with increased mitochondria and UCP1 enzymes but occurs within white adipose tissue
Beige adipose tissue

Beige adipose tissue