Explain Traditional economy:
based off cultural beliefs, generational, old habits & customs
When a country has NO trade with another country
EMBARGO
What type of economy does Germany have?
MIXED
What body of water is being shown:
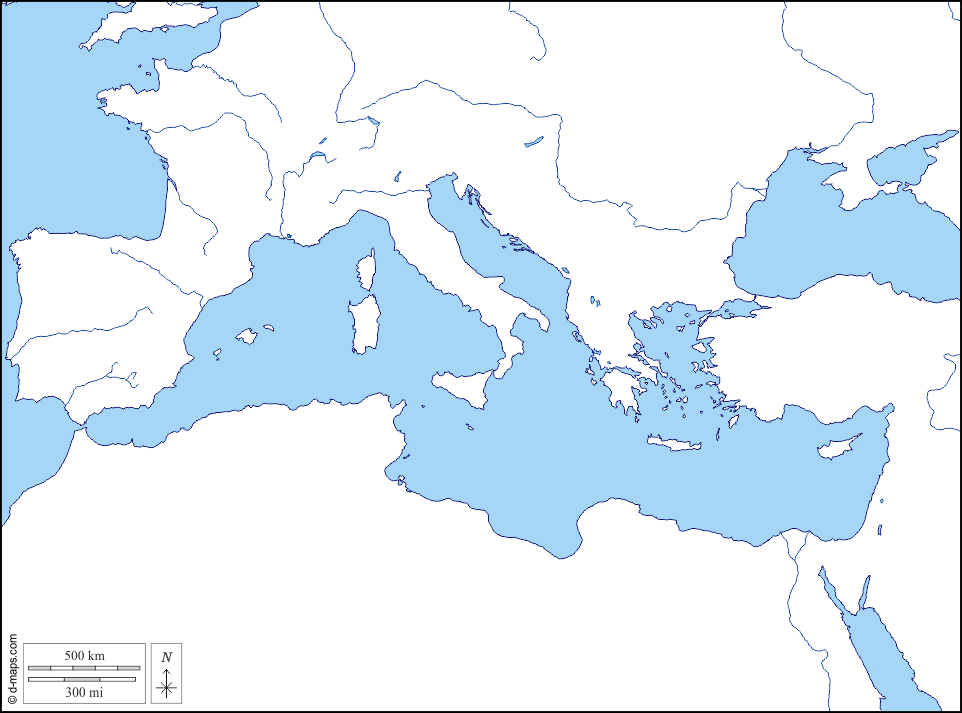
MEDITERRANEAN SEA
This type of trade barrier stops all trade between two countries, like the United States & Cuba.
EMBARGO
Explain how supply and demand influence what is produced in a market economy.
What is that businesses produce goods based on what consumers want and how much they’re willing to pay
This type of trade sets limits on the amount of items coming into the country
QUOTA
Most European economies have a mixed economies that lean closer to a pure ____ economy
MARKET
Which river is being shown:
RHINE RIVER
This trade barrier sets a limit on how many goods can be brought into a country
QUOTA
TRUE OR FALSE:
The United States has a Pure Market economy
FALSE: There's no such thing as "PURE" market or "PURE" command economy
A tax on trade:
TARIFF
Describe how the U.K.’s mixed economy combines elements of both market and command systems
What is that the U.K. has mostly market freedoms, but the government provides some services and regulates certain industries
Which mountain range is being shown?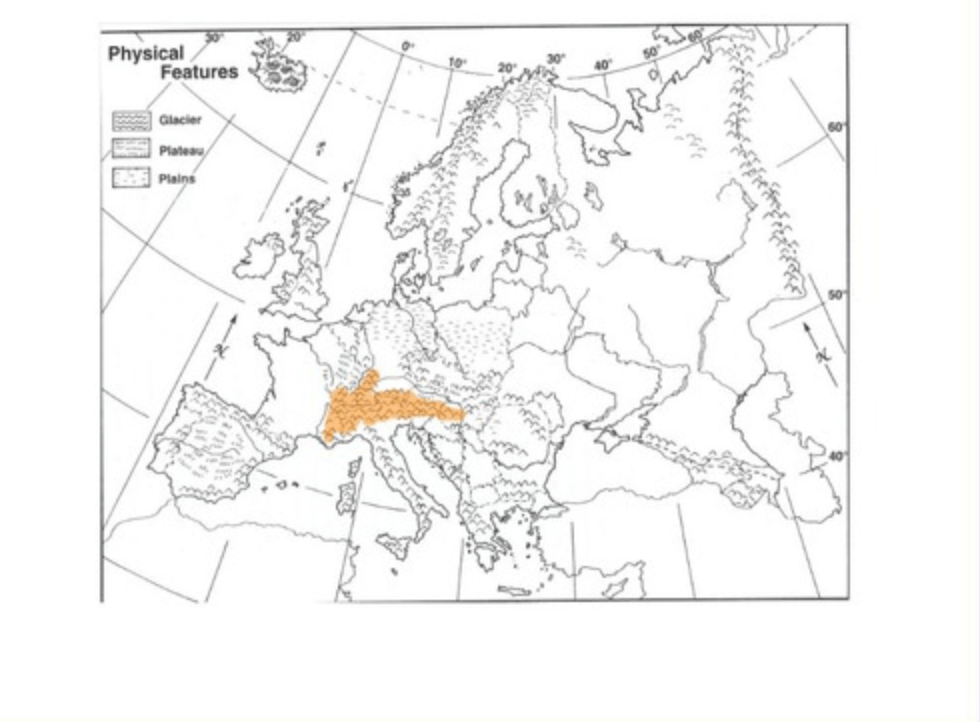
The Alps
Explain how SPECIALIZATION can help countries like the U.K., Germany, and Russia increase trade with other nations.
Specialization helps countries focus on producing goods they make best or most efficiently. By focusing on their strengths, these countries can trade with others for the goods they don't produce
What are the 3 basic economic questions?
2. How to produce
3. For whom to produce for
Explain how a tariff on imported goods can affect the price of those goods for consumers.
tariffs make imported goods more expensive for consumers
A local bakery decides to make more chocolate cupcakes because customers have been buying them faster than other flavors. The bakery lowers the price of vanilla cupcakes to encourage sales. Which type of economy is being described, and why do businesses make these kinds of decisions?
What is a market economy, where businesses respond to supply & demand, and consumer choices to decide what and how much to produce
Which mountain range is shown:
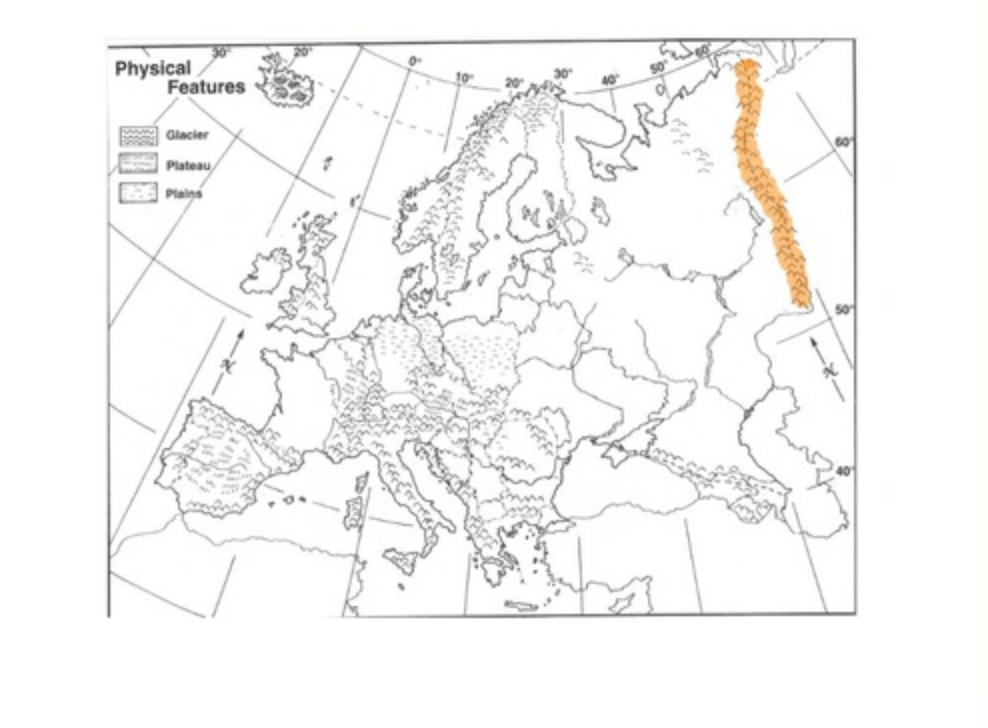
The Ural Mountains
Describe how investing in CAPITAL GOODS, like machines and factories, can help economies grow
It helps economies grow because it makes production faster and more efficient. When businesses can produce more goods in less time, they can sell more products
Compare how decisions about what to produce are made in a command economy versus a market economy.
In a command economy the government makes the decisions, but in a market economy individuals and businesses decide
In a traditional economy, people often follow the same jobs and roles as their parents and grandparents. Explain how this way of life can both help and limit a community’s ability to adapt to change
it helps keep traditions and skills alive, but makes it hard to adopt new technology or respond to outside changes
In a small village, families grow the same crops their parents grew, make their own clothes by hand, and trade goods with neighbors instead of using money. They rarely change how they do things, even when new technology arrives. What type of economy is being described?
Traditional economy
What is this physical feature and how has this body of water influenced trade and travel?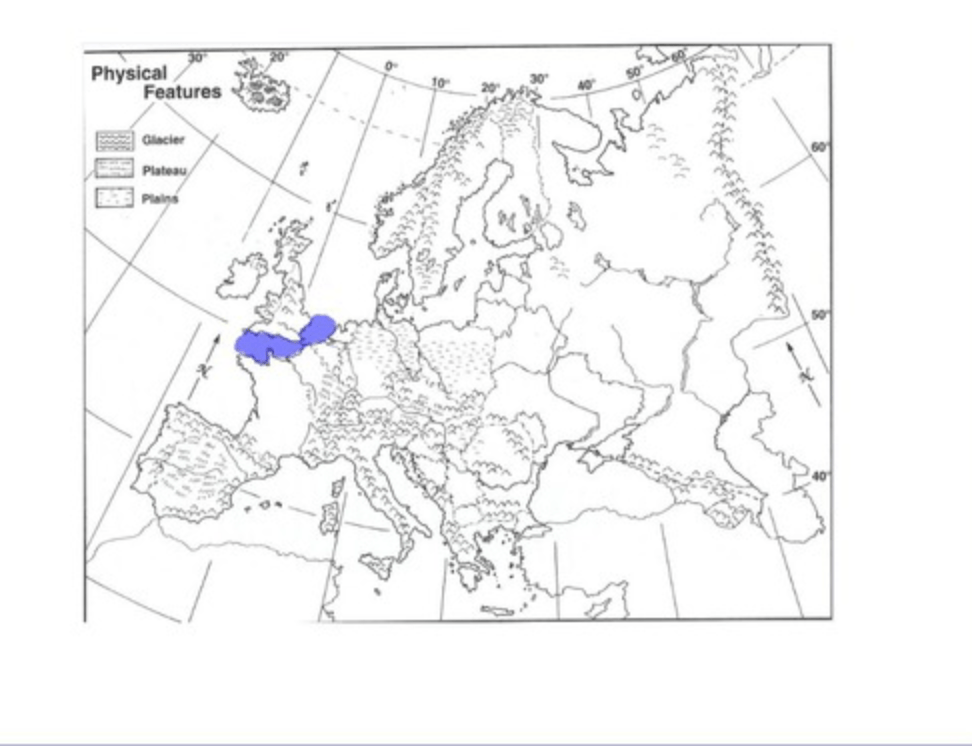
English Channel; natural trade barrier effecting shipping and traveling from U.K. to mainland Europe. Allows items to be shipped quickly and travel made easier
Explain how investing in HUMAN CAPITAL, such as education and training, can improve a country's GDP (Gross Domestic Product)
Investing in human capital through education and training helps workers gain skills and knowledge. Skilled workers can do their jobs and produce higher-quality goods and services, which improves a nations GDP.