What are the types of igneous rocks?
What is Igneous rocks are classified as intrusive igneous rock and extrusive igneous rock.
Which one of the following is a biochemical sedimentary rock?
A.sand sized material
B.coal
C.shale
D.conglomerate
B.coal
Define metamorphic rock
Metamorphic rocks started out as some other type of rock, but have been substantially changed from their original igneous, sedimentary, or earlier metamorphic form
What is the cycle that mentions metamorphic rocks, sedimentary rocks, and ingenious rocks?
The Rock Cycle.
What is the softest rock in the rock cycle?
sedimentary.
- What are igneous rocks?
- What are the two main kinds of igneous rock?
Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava.
The two main kinds of igneous rocks are intrusive igneous rocks, which form from magma that cools below the Earth's surface, and extrusive igneous rocks, which form from lava that cools on the Earth's surface.
A clastic rock is:
A.a rock formed from the cementation of transported grains
B.a rock formed from evaporation of sea water
C.transformed by heat into limestone
D.transformed by pressure into limestone
A.a rock formed from the cementation of transported grains
- Which of the following rocks represents the highest metamorphic grade?
a.slate
b.schist
c.phyllite
d.gneiss
gneiss
How many types of rocks are there in the rock cycle?
3
Which of the following rocks can be considered gradational between an igneous rock and a metamorphic rock?
A.geniss
B.quartzite
C.migmatite
D.schist
C.migmatite
- Which of the following is NOT an extrusive igneous rock?
A. Basalt
B. Andesite
C. Obsidian
D. Granite
D. Granite
Which one of the following features is NOT associated with sedimentary rocks?
A.bedding
B.foliation
C.fossils
D.all may be associated with sedimentary rocks
D.all may be associated with sedimentary rocks
- Metamorphic rocks with segregated light and dark minerals are called _______.
a.slate
b.schist
c.phyllite
d.gneiss
gneiss
TRUE or FALSE: old rocks turn into new ones.
true
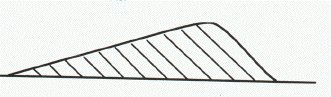
In the cross section of a sand dune given above, the wind was blowing?
A.<-------
B.-------->
C.<------->
D.cannot determine direction from information given.
B.-------->
The tendency for variations in current velocity to segregate sediments on the basis of particle size is called _____.
A.lilthification
B.compaction
C.metamorphism
D.sorting
D.sorting
- In contact metamorphism there is a ____________ .
a. local heat source
b. frictional heat source
c. regional heat source
local heat source
What is the hardest rock in the rock cycle?
metamorphic.
he temperature (at least a minimum estimate) from which the melt cooled is reflected by the _________ of the rock.
A.mineralogy
B.texture
C.color
D.density
A.mineralogy
Vesicles in an igneous rock form from:
A.escaping gases
B.phenocrysts settle to the bottom of the magma chamber
C.falling ash
D.all of the above
A.escaping gases
Which of the following processes is not an important cause of subsidence during the development of a sedimentary basin?
A.cooling and contraction of the crust
B.deposition of sediments
C.erosion of sediments
D.tectonic down faulting
C.erosion of sediments
- Which mineral is responsible for the strong foliation in a schist?
a.quartz
b.calcite
c.mica
d.foliate
mica
What is the rock cycle driven by?
Earth's internal heat engine.
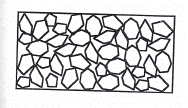
The diagram above most likely represents a ___________.
A.extrusive igneous rock
B.intrusive igneous rock
C.clastic sedimentary rock
D.chemical sedimentary rock
C.clastic sedimentary rock