What are the Vedas in early Hinduism?
Collections of hymns, prayers, and rituals used to honor the gods
In Buddhism, what is the purpose of meditation?
To control the mind and gain wisdom.
Why does Arjuna hesitate to fight in the Bhagavad Gita?
He doesn't want to kill his family on the other side of the battlefield.
The term “caste” comes from...
The Portuguese word casta, meaning “race” or “lineage”
What is karma?
Energy that is based on a person’s actions and choices.
What is the atman in Hindu belief?
The eternal soul that connects every being to Brahman.
The Eightfold Path provides Buddhists with...
a plan for how to learn to change one’s expectations and desires and thus end suffering.
What advice does Krishna give Arjuna?
To fight, because it is his dharma (purpose) as a warrior.
Who are the Dalits?
People outside the varna system who faced discrimination; also known as Untouchables.
Dharma refers to...
The moral duty or responsibility in life.
According to the Upanishads, what is Brahman?
Brahman is truth, the ultimate reality, the source of existence. Brahman is the universe and is present in all things.
According to the Four Noble Truths, what is the cause of suffering?
(150 for each correct answer)
Expectations and desires
Svadharma means...
One's personal duty based on social role or varna
The rationale for the poor treatment of lower castes and Dalits is connected to the cycle of _______.
samsara
What is the ultimate goal for Buddhists who follow the Eightfold Path?
To reach nirvana, a state of peace and freedom from suffering
What is the goal of moksha in Hinduism?
To be released from the cycle of rebirth (samsara) and unite with Brahman.
What role did Buddhist monks and nuns play in their communities?
They taught householders and modeled righteous living.
As Vedic society became more complex, people started asking deeper questions about life and existence. Hinduism evolved to address these questions. New ideas were written down in the _________, religious texts created by Hindu sages and philosophers.
Upanishads
Put the following four social classes in order from highest to lowest:
Shudra, Brahmin, Vaishya, Kshatriya
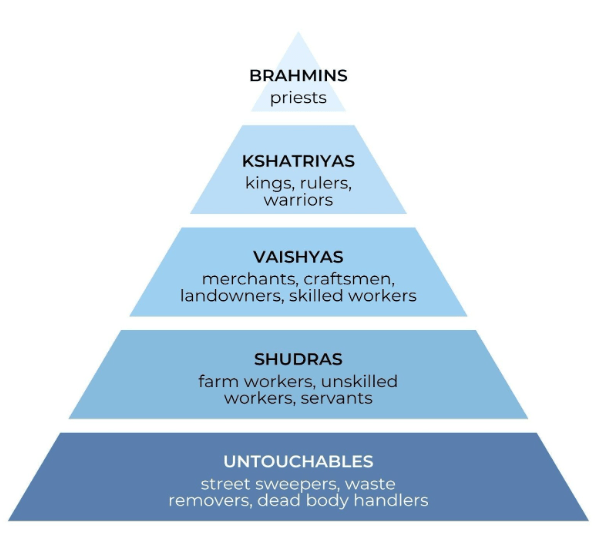
What change has occurred in modern times regarding the caste system?
Discrimination is illegal in India, but prejudice and inequality still continue at times
Explain how samsara and moksha are connected.
Samsara is the cycle of birth, death, and rebirth that continues until a person reaches moksha. Moksha is freedom from that cycle (samsara). It happens when a person has fulfilled their dharma, their purpose, and no longer needs to be reborn.
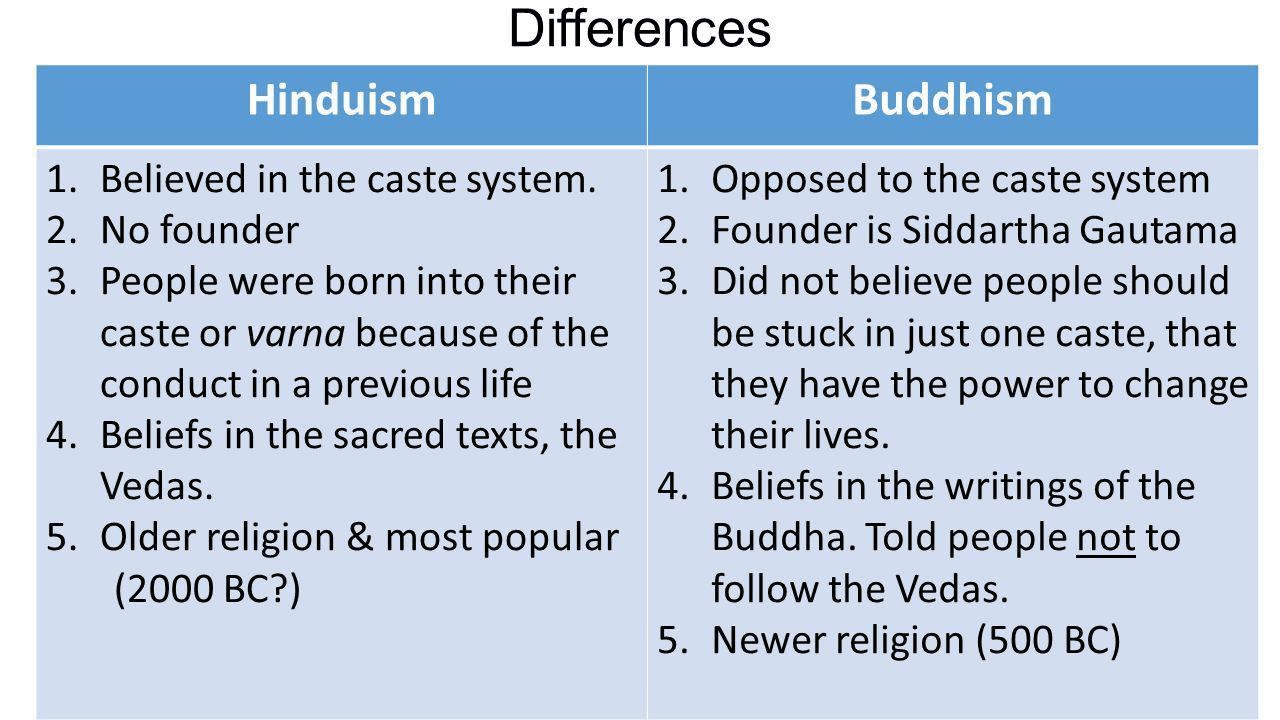
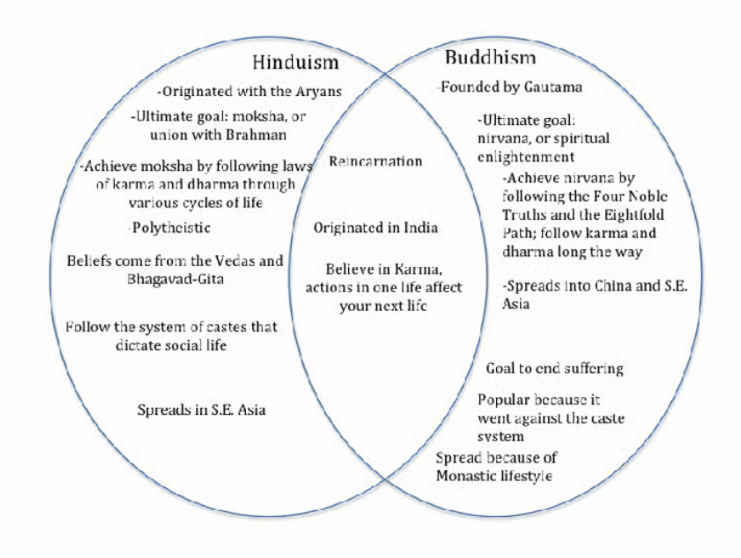
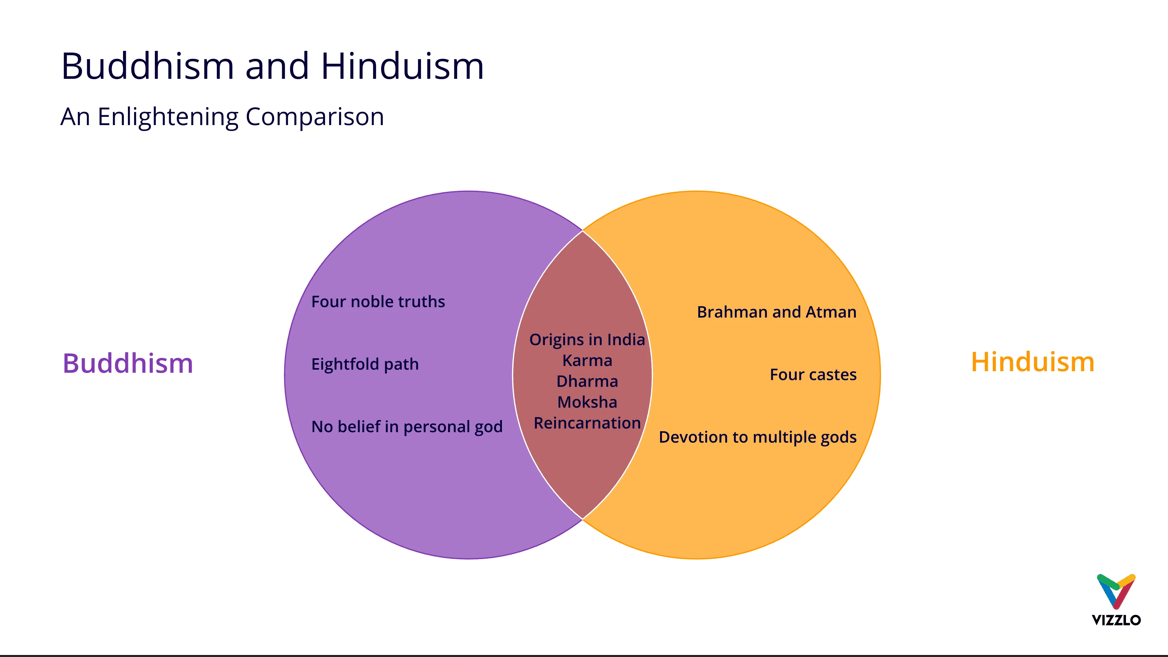
Explain a difference between Hinduism and Buddhism.
The leader of India’s independence movement against Great Britain, who called Dalits “Harijan,” which means children of God.
Mahatma Gandhi
1. Explain how Hindu beliefs helped shape India’s caste system.
2. Then describe one result these beliefs had on people in the Dalit (Untouchable) class.
(250 for each correct response)
1. Hindu beliefs in karma and samsara helped shape India’s caste system because people thought their social position was based on actions from past lives. Those born into higher castes were believed to have earned good karma, while those in lower castes or the Dalit group were thought to have bad karma from past lives.
2. As a result, Dalits (Untouchables) were treated unfairly, forced to do the hardest jobs, and excluded from temples and public spaces.
Who is Siddhartha Gautama better known as?
the Buddha, which means "the enlightened one"