What are the three different types of attention?
Sustained, Divided and Selective Attention
What are the two types of perceptual processing?
Top-down and bottom-up
What is the main biological influence on visual perception?
Depth cues
Give one biological, one psychological, and one social influence on taste perception.
Biological = genetics
Psychological = perceptual set/appearance
Social = culture
Give one example of synaesthesia
Hearing a sound and seeing a colour, tasting words, feeling shapes when touching textures, etc
What is the difference between each type of attention
Sustained - focusing on 1 stimuli
Divided - focusing on more than 1 stimuli
Selective - focusing on 1 stimuli and actively ignoring any other stimuli
What is the difference between the two types of processing?
Top-down: Using prior knowledge to inform your perception/stimulus information
Bottom-up: Using sensory/stimulus information to form knowledge
Which monocular depth cue makes parallel lines appear to converge in the distance?
Linear perspective
If parents enjoyed, I did too - showing genetic/biological influence on taste
What perceptual distortion is NOT considered a disorder?
Synaesthesia
What type of attention/s were explored in the word search practical?
How was each perceptual processing seen in the puzzle practical?
What are gestalt principles?
Psychological factors that help us organise and interpret stimuli into something meaningful
Explain why labelling the same cola drink as “Coke” vs. “Pepsi” can cause different taste perceptions
Perceptual set (expectations from labels/branding) alters the interpretation of sensory input, even though it is the same!
Give one example of behaviour shown by someone with spatial neglect
Eating food only on one side of the plate, shaving one side of the face, drawing only half a picture, etc
What was a random error in the experiment?
Distractions, participant-related variables, etc
The group with the picture used the picture to form the corners/positioning. The group without used the colours to figure out the positioning
 What gestalt principle is this?
What gestalt principle is this?
Closure
What were the three factors that influenced our judgement of flavour?
Perceptual set, colour intensity and texture
Is spatial neglect caused by problems with the eyes?
No, it is an attention disorder caused by brain damage
Explain how a conversation at a party demonstrates two types of attentions.
Selective = focusing on one conversation despite being noise/distractions in the background
Divided = noticing your name/something happening in another conversation while still listening to the first.
What is the process of perception?
Selection, Organisation and Interpretation
How do visual errors like the Müller-Lyer illusion and the Ames Room happen?
Misapplying depth cues
When we grew up with something (demonstrated through easier to identify the flavour), we liked it more (rated higher) - suggesting culture has a big influence on taste
Someone was asked to copy this drawing. What type of perceptual distortion and what brain damage does this person have?
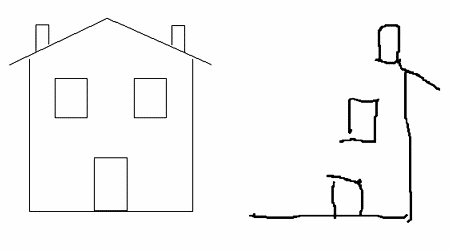
Spatial neglect to the left side (right brain damage to parietal lobe).