This gas makes up approximately 78% of all the gases in the atmosphere.
Nitrogen
Source
The source of all incoming energy on Earth.
the Sun
The name for gases that cause an increase in global temperatures as their concentration increases.
Greenhouse Gases
This gas being added to the atmosphere is responsible for the development of life outside the oceans.
Oxygen
O3 is the chemical formula for this molecule.
Ozone
Example processes include: formation of fossil fuels, photosynthesis, and diffusion.
Sinks
The impact on global temperatures from an increase in atmospheric CO2 levels in the atmosphere.
Increase
The lowering of the pH of the ocean because CO2 is absorbed via diffusion.
Ocean acidification
This process is both a source and a sink in the carbon cycle.
Diffusion
This human activity contributes high levels of greenhouse gases to Earth's atmosphere.
Burning fossil fuels
Places where carbon is stored or can be found, including the ocean, rocks, the atmosphere, plants, and animals.
Reservoirs
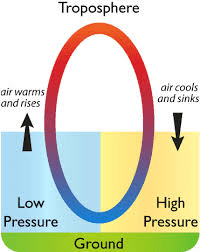 This form of energy transfer causes the pattern shown in the diagram.
This form of energy transfer causes the pattern shown in the diagram.
The reasons for sea level rise.
1. Melting land ice
2. Thermal expansion of the ocean
This action was taken to help restore the ozone layer.
Banning CFCs / the Montreal Protocol
This geologic phenomenon adds large quantities of several gases, such as sulfur dioxide, to the atmosphere.
Volcanoes / volcanic eruptions
Carbon in the atmosphere is most commonly found as this compound/molecule.
Carbon dioxide
These naturally occurring surfaces on Earth have a high albedo.
Ice / snow
This source of pollution is often credited with causing acid rain.
Burning fossil fuels.
The greater concentration of these ions makes a substance more acidic.
Hydrogen
The ozone layer can be found in this layer of the atmosphere.
Stratosphere
This process is done by plants that removes carbon dioxide from and adds oxygen to the atmosphere.
Photosynthesis
The reason for global cooling after a large meteor impact or volcanic eruption.
Gas/dust/ejecta would block the energy from the Sun and lower global temperatures.
3 examples of changes caused by an increase in global atmospheric temperatures.
- ice caps melting
- glaciers melting
- increased ocean temperatures
- increased atmospheric temperatures
- sea level rise
- increased intense weather events/storms
- increased likelihood of droughts
- increased likelihood of heatwaves
The name of the bacteria that first performed photosynthesis in the Earth's oceans, eventually adding oxygen gas to the atmosphere.
Cyanobacteria