For a population to grow birthrate must be greater than _______________.
Death rate
The number of individuals a given environment can support based upon the resources available is referred to as _____________.
What is carrying capacity?
Human population size has ________ over time.
increased
The variety of different species that exist in a particular biological community is called ________
Species biodiversity
Burning fossil fuels adds greenhouse gasses to the atmosphere and contributes to climate change.
When people exit or leave the country this is called ___________
Exponential growth occurs when . . .
Organisms have unlimited resources and mates and limited competition and number of predators
Explain why families, historicaly, had more children on average than families in present day.
Death rates were higher so they needed to have more children to ensure some would survive.
Give an example of one way biodiversity benefits humans.
Earth’s best natural resources (wood, food, etc.)
Provides us with medicine and other valuable resources
Keeps ecosystems healthy and resilient (strong)
Explain how deforestation impacts biodiversity.
Deforestation destroys organisms habitat and threatens their survival.
Give an example of an ABIOTIC factor that limits population growth.
Temperature
Precipitation
Weather
pH
Salinity
Human disturbances
The most common kind of growth in stable ecosystems that is represented by an S-curve is called ____________ growth.
Logistic growth
What factors reduced death rates?
Give two examples of ecosystem services that are provided by ecosystems that are biodiverse.
Food production
Nutrient cycling and soil structure
Purifying water
Storing carbon
Regulating pests and pollinating crops
Buffering effects of extreme weather events
Farmers can practice regenerative farming and plant many types of plants that can remove more CO2 from the atmosphere instead of planting large fields of a single crop. Farmers can also use low-till methods when plowing to improve soil quality.
Give an example of an BIOTIC factor that limits population growth.
Competition
Predation
Parasitism
Disease
The graph shown below is called a ___________ curve and represents _____________ growth.
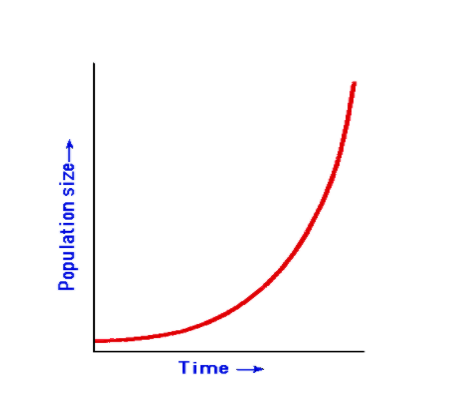
J-curve; exponential growth
Humans continued to have a large number of children but the death rate decreased due to improved nutrition and medicine. As a result, the human population grew exponentially.
Explain the difference between species diversity and genetic diversity.
Species biodiversity is the number of different species in the biosphere.
Genetic diversity is the total of all the different forms of genes present in a particular species.
Explain the difference between bioaccumulation and biomagnification.
Bioaccumulation occurs when pollutants collect in the body tissues of organisms.
Biomagnification is a process in which pollutants are concentrated as the pollutants pass through trophic levels.
Populations can decrease in size if the death rate is greater than the birthrate OR . . .
Emigration is greater than immigration
Identify what each of the letters in the diagram represents:
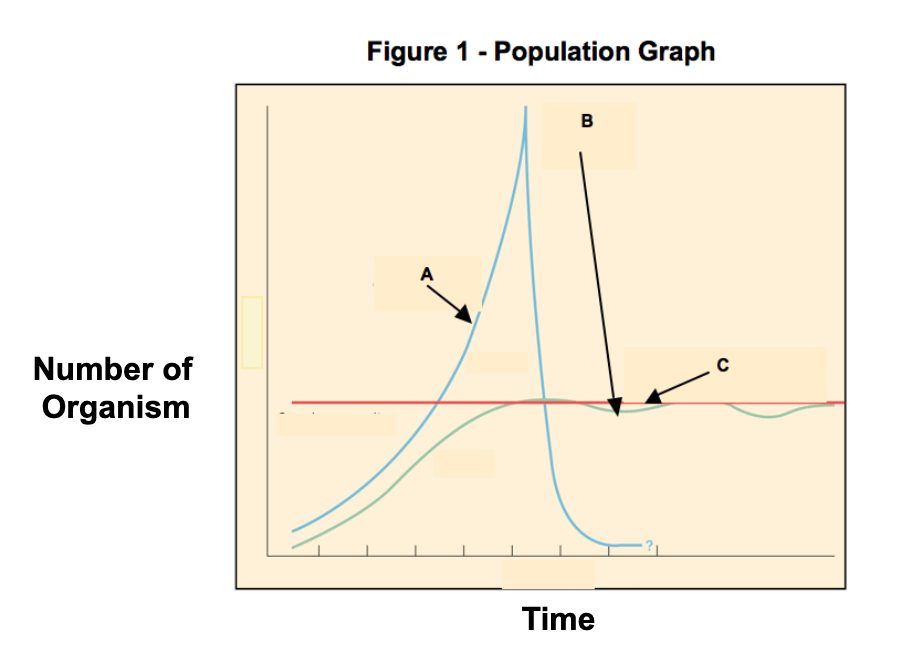
A = J-curve/exponential growth
B = S-curve/logistic growth
C = carrying capacity
Describe how the human population growth curves changed as a result of the industrial revolution.
Human population growth was stable so resulted in an S-curve prior to the industrial revolution. After the industrial revolution the human population grew exponentially which resulted in a J-curve.
Explain how biodiversity makes an ecosystem more resilient. (HINT: Think about when you were each assigned a different tree and an insect affected only the Douglas fir trees in the forest.)
When ecosystems are biodiverse they are less likely to be severely impacted by limiting factors such as competition, diseases, etc.
Use the diagram below to help you explain why pregnant women are advised NOT to eat lots of tuna.
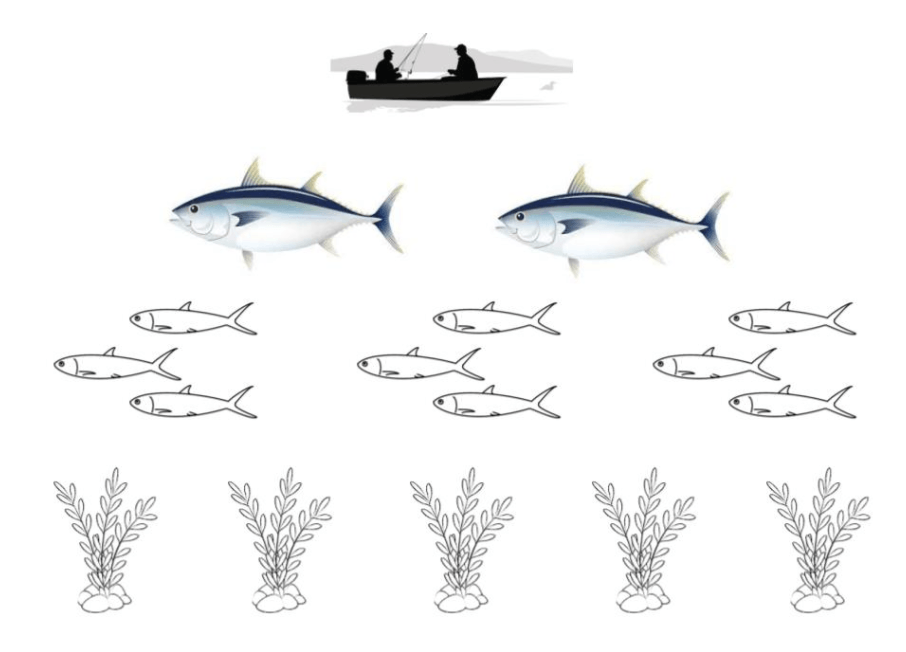
Biomagnification is a process in which pollutants are concentrated as the pollutants pass through trophic levels. The mercury is first absorbed by the water plants and then ingested by the small fish and then the larger fish like the tuna. As a result, there is lots of mercury in the tuna that can harm the growing baby if the mother eats too much tuna.