Patient Care
What is the formula for wavelength?
λ = c/f
what is the reciprocal unit for msec?
kHz
What are the units for Period?
seconds or msec or µs
What is the dominant form of attenuation?
Absorption
What is the reciprocal of PRP?
PRF
What is B?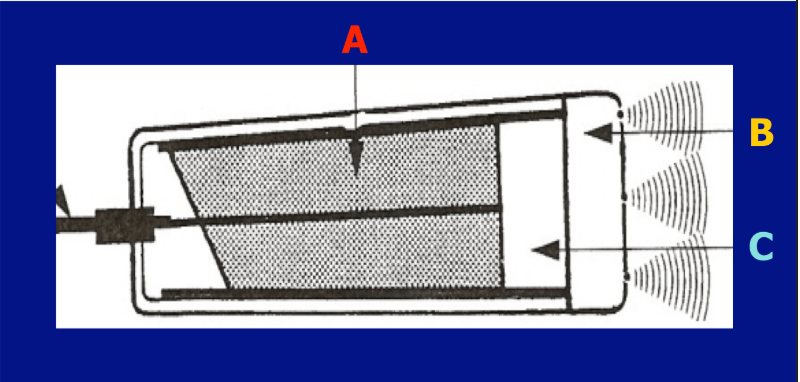
matching layer
How would you fix this image?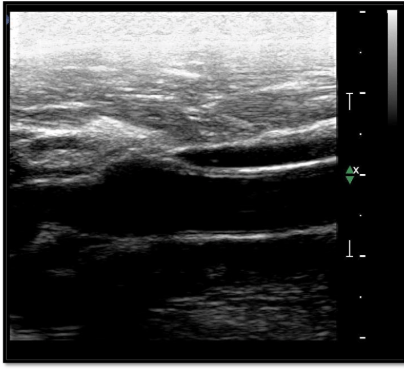
Move near field TGCs to the left and far field TGCs to the right
What is the scientific notation for 2,700?
2.7 x 10^3
What is the formula for axial resolution?
SPL/2
Ultrasound can be defined as a _______________, ______________ wave.
longitudinal, mechanical
Frequency and Period are both determined by the.....
source
Absorption _____ with increasing frequency
increases
The far zone is also referred to as the ___________ zone.
Frauenhofer
What is the difference between amplification and compensation?
amplification - all echoes equally increased
compensation - increases deeper echoes more
How many km are in 3000 m?
3 km
What is the formula for duty factor (DF)?
Duty factor(%) =
(PD (µs)/ PRP (µs)) x 100
What is the speed of sound in soft tissue?
1540 m/sec or 1.54 mm/µs
Does air or bone have a higher propagation velocity?
bone
What is the redirection of US waves in many different directions when they encounter structures that are small or irregular compared to the wavelength of sound?
- It occurs when the sound beam hits heterogeneous tissue, small reflectors, or rough surfaces.
Scattering.
This image was produced by which type of transducer?
curvilinear array (or curved linear)
Define "Standard Precautions"
A set of guidelines to minimize the exposure and risk of health care workers when in contact with a patient.
What is the reciprocal of 0.5 msec?
2 kHz
What is the formula for fractional bandwidth (FBW)?
FBW = Bandwidth (BW) / Operating frequency (Fc)
What is the audible frequency range of sound?
20–20,000 Hz
What is the The 3dB Rule?
A 3 dB INCREASE in output power will DOUBLE the beam intensity.
A 3 dB DECREASE in output power will HALF the beam intensity.
The area indicated by the red arrow can be described as __________ which indicates that there are ___________ reflected signals.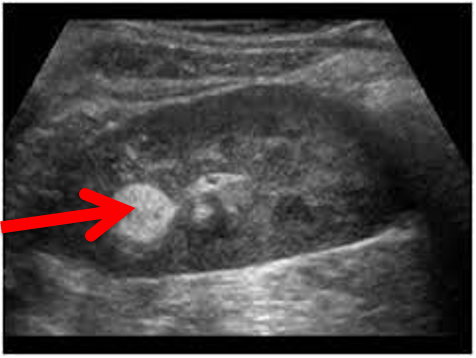
hyperechoic, highly
The reciprocal of frame time is _______.
And the reciprocal of seconds is _______.
Frame rate
Hertz
How is the frequency of a continuous wave transducer determined?
Determined by the frequency of the electrical signal created by the ultrasound system (electrical 𝑓 = acoustic 𝑓)
In this mode of ultrasound, the Y axis is depth and derived from “time of flight”.
B mode aka grayscale aka B scan
What is the formula for amplitude?
Amplitude = (max - min) / 2
Ultrasound frequencies are anything higher than _____ Hz
The frequency range used in diagnostic ultrasound is _________
20,000 Hz (20kHz)
2 - 12 MHz
If there is a large difference between 2 impedances, there will be nearly total what?
reflection
What is the 13 usec rule?
Pulse round trip time = 13µs for each cm of distance from the source to the reflector
What type of beam results from this phase delay profile - (give 2 descriptions)?
focused, un-steered beam
What are the 5 processes that happen in the receiver? List them in the order in what they happen.
Amplification
Compensation
Compression
Demodulation (detection)
Rejection
What are the 2 costs (drawbacks) of harmonic imaging?
Decreased amplitude in the far field
Decreased axial resolution
What are 2 formulas for intensity?
Intensity = Power / area
or
Intensity = Amplitude2 / area
Propagation velocity ______ with increasing bulk modulus.
increases
Name the 7 Sound Wave Parameters?(measurable attributes) and which are determined ONLY by the source.
Frequency, Period, Wavelength, Propagation speed, Amplitude, Power, Intensity
Frequency and Period are determined only by the source
The rate at which an ultrasound beam loses intensity as it travels through a medium (expressed per unit distance) is the definition of _________.
Attenuation coefficient
Calculate the pulse duration for a pulsed wave that has a period of 3 msec and rings (“is on”) for 4 cycles.
12 msec
Focal length is another name for:
NZL
(near zone length)
*** focal length and focal zone are 2 DIFFERENT THINGS
What is the formula for calculating the frequency of a pulsed wave transducer?
f0 =
crystal propagation speed (mm/usec) /
2 x crystal thickness (mm)
Compressibility ______ with increasing bulk modulus.
decreases
These waves have the same ________, but different ________.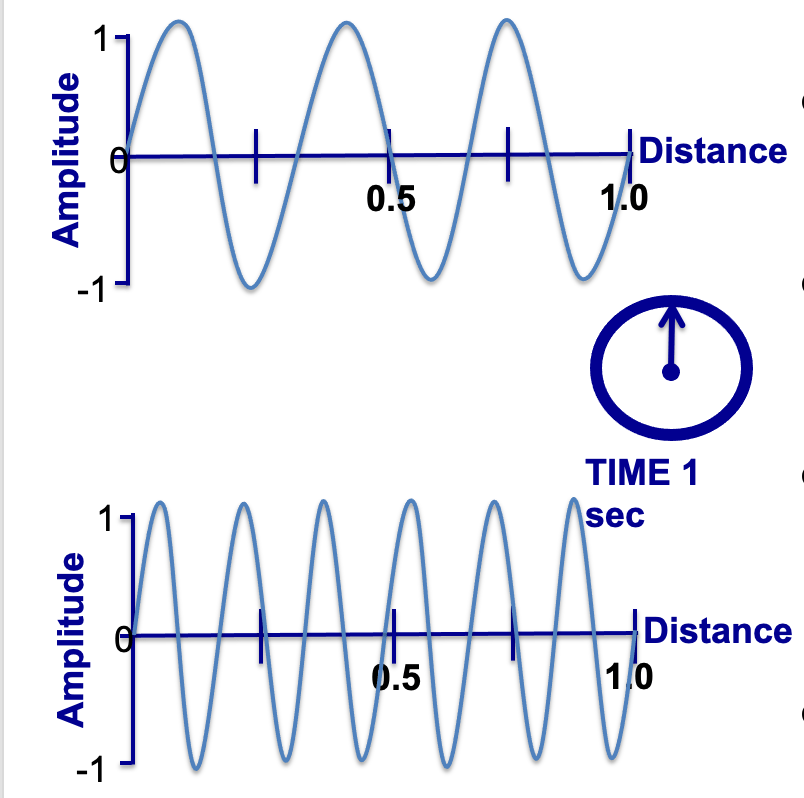
Propagation velocity, frequencies (or wavelength)
Snell's law is used to determine:
the presence and angle of refraction
For array transducers -
describe the difference between sequencing and phasing
Sequencing - Operated by applying voltage pulses to groups of elements in succession creating the image frame from one side to the other
Phasing - used for steering and focusing and operated by applying voltage pulses to most or all of the elements with small (< 1 µs) time differences between them
Calculate Log 50
1.7
Log 50 = Log (100/2)
= Log 100 - Log 2
= Log 2 - 0.3
= 1.7
What are the 2 forms of the formula for the change in decibels
Power form: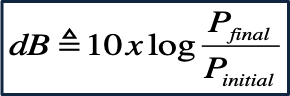
Amplitude form:
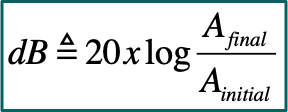
The blue and red waves have _______ interference. They both have an amplitude of 2V, so the green wave has an amplitude of ______V.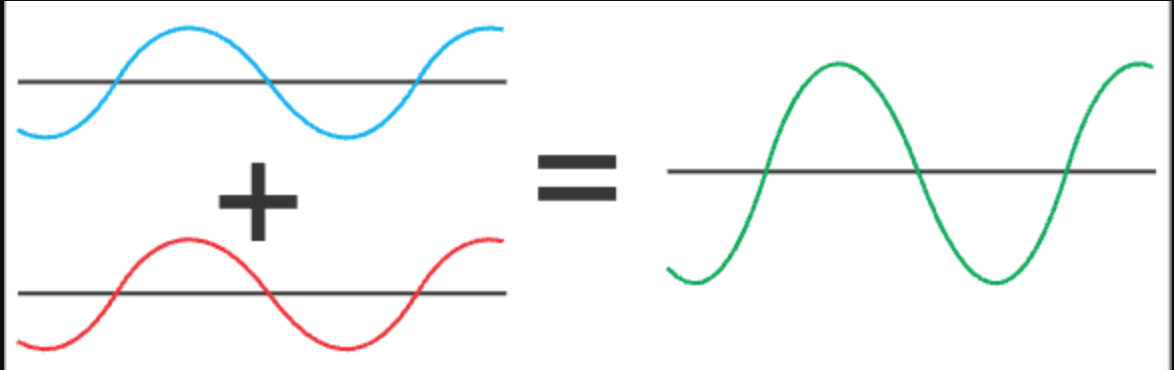
constructive, 4V
What are the two requirements for refraction to occur at the interface of 2 media?
1. Oblique incidence
2. Different propagation speeds
If "F" is 4 V, "A" is 5msec and the "C" is 20msec, calculate the DF.
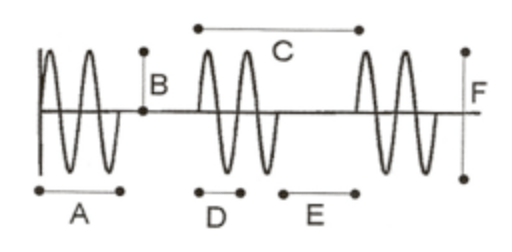
0.25 or 25%
______ and ______ describe transducer design, while ______ and ______ describe transducer operation.
linear; curved
sequencing, phasing
Which operation feature uses 1 transmit beam that is a little wider than normal and divides it into 2 creating 2 receive lines in the same space?
Parallel processing
What are 2 formulas used to calculate the NZL?
NZL = D2 / (4 x wavelength)
and
NZL =(D2 x f0) / 6 - for soft tissue
What happens to the wavelength when it moves from a medium with lower propagation velocity to a medium with higher propagation velocity?
Wavelength increases
Define "attenuation coefficient"
Attenuation that occurs with each centimeter the sound wave travels
Unit: dB/cm or dB/cmMHz
Both ______ and ________ resolution are determined by beamwidth, but in 2 different dimensions.
lateral and elevational
What is the formula for the intensity reflection coefficient (IRC)?
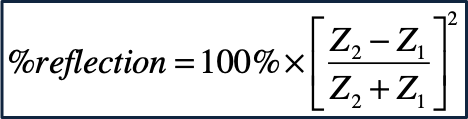
What happens to the beam intensity if the beam area is increased by a factor of 4?
Decreases by a factor of 4.
What sound beam incident angle gives the strongest reflection?
0 degrees
Name 3 adjustments a sonographer can make that will decrease the frame rate
increase depth
use multi-focus
widen the sector
What characteristics of the transducer will produce a higher beam divergence vs. a lower beam divergence?
Higher beam divergence (shallow depth of field) - smaller crystal diameter and lower frequency
Lower beam divergence (broad depth of field) - larger crystal diameter and higher frequency
Name 5 adjustments a sonographer can make that changes the amount of output power the machine allows
Frequency
Imaging mode
Depth
Image sector size
Focus
This gallstone demonstrates what 2 main types of attenuation?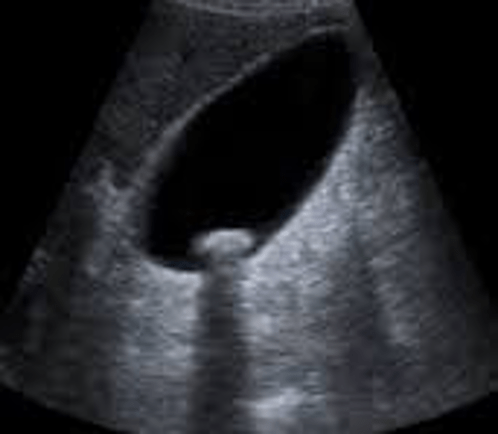
Absorption and reflection
To obtain the longest focal zone you need a _____ crystal diameter and a _______ frequency
large, high