Using a ______ frequency will improve spatial resolution.
High
Hepatofugal flow in the portal veins indicate
Portal hypertension
The first artery off of the aortic arch
Brachiocephalic/Innominate
Normal PSV for renal arteries
<180 cm/s

This waveform in the vertebral artery suggests
Ipsilateral subclavian artery stenosis
ALARA stands for
As Low As Reasonably Achievable
Diabetic patients are most likely to develop peripheral arterial disease in what lower extremity arteries
Crural arteries (PTA, ATA, Pero A)
This vein connects the cephalic and basilic veins
Median cubital vein
Diameter measurement range of an ectatic PROXIMAL aorta
2.5 cm - 3.0 cm

This waveform indicates a ______ occlusion
Distal
Another name for scale
Nyquist limit
Celiac artery stenosis that resolves with deep inspiration is indicative of extrinsic compression from the
Median arcuate ligament
The first branch off of the ECA
Superior thyroid artery
>70% stenosis velocity for internal carotid artery
>230 cm/s
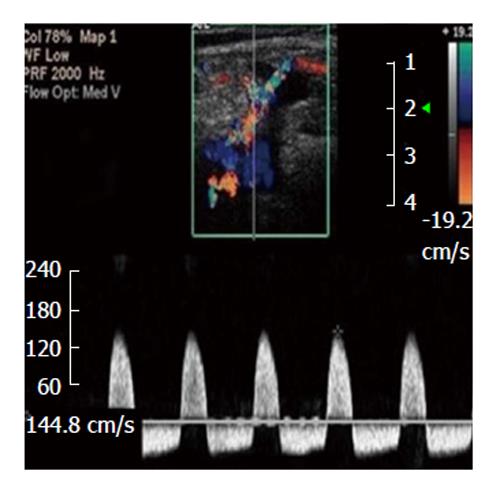
This waveform was most likely taken in a
Pseudoaneurysm neck
Persistence is also known as
Temporal Compounding
A recovery time of 2-6 minutes post exercise ABI indicates
Single level disease
Peroneal veins travel behind this bone
Fibula
PSV of >80% in-stent restenosis of popliteal artery
>275 cm/s

This waveform is known as
Tardus Parvus
There will be NO Doppler shift when the angle of insolation is __ degrees.
90
The most common artery to supply blood to the residual sac in a type II endoleak
This vessel drains blood from the colon
Inferior mesenteric vein
ICA/CCA ratio criteria for > 20% in-stent restenosis of ICA
>2.15
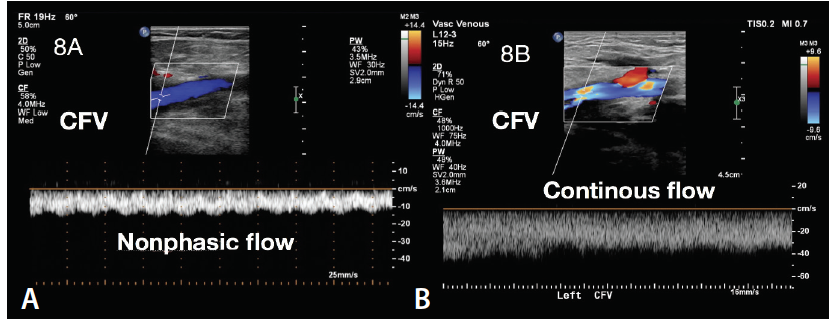
This type of venous flow may indicate 1 or 2 things (can you get both?)
Obstruction from DVT in a proximal vein OR extrinsic compression of a proximal vein