Water’s polarity leads to this type of bonding, which is essential for its high cohesion and surface tension
What are hydrogen bonds?
These are the four major types of macromolecules in biological systems.
What are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids?
The double-helix shape of DNA is stabilized by these bonds between nitrogenous bases.
What are hydrogen bonds?
These four elements make up about 96% of living matter.
What are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen?
This type of reaction builds polymers by removing a water molecule.
What is a dehydration synthesis (or condensation) reaction?
Water moderates temperature because of this property, which requires a lot of energy to raise its temperature.
What is high specific heat?
The monomers of proteins are called this.
What are amino acids?
Explain why enzymes lose function at extreme temperatures or pH levels.
What is: These conditions disrupt the protein’s tertiary and quaternary structures, altering the active site?
These two elements are often involved in hydrogen bonding due to their high electronegativity.
What are oxygen and nitrogen?
This type of reaction breaks down polymers into monomers.
What is hydrolysis?
This phenomenon allows water to move against gravity through the xylem in plants, combining cohesion and adhesion.
What is capillary action
This type of bond forms between amino acids during protein synthesis.
What is a peptide bond?
Which macromolecule contains nitrogen but not necessarily phosphorus, and what functional groups are involved?
What is protein; it includes an amino group and a carboxyl group?
Which element forms the backbone of all biological macromolecules, and why is it especially suited for this role?
What is carbon; it can form four covalent bonds, allowing for complex and diverse molecular structures?
DAILY DOUBLE!
Dehydration synthesis links monomers by forming this kind of bond.
What is a covalent bond?
This property of water allows it to stick to itself, creating surface tension.
What is cohesion?
DAILY DOUBLE!!
Describe the difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids at the molecular level and relate it to membrane fluidity.
What is: Saturated fats have no double bonds (solid at room temp), while unsaturated fats have cis-double bonds that increase membrane fluidity?
Hemoglobin has quaternary structure. What does this mean in terms of protein organization?
What is: It consists of multiple polypeptide subunits bonded together?
Explain how the electronegativity difference between oxygen and hydrogen leads to water’s polarity.
What is: Oxygen is more electronegative, pulling electrons closer and creating partial charges that make water polar?
Compare anabolic and catabolic processes in the context of dehydration and hydrolysis.
What is: Anabolic builds molecules via dehydration synthesis; catabolic breaks them down via hydrolysis?
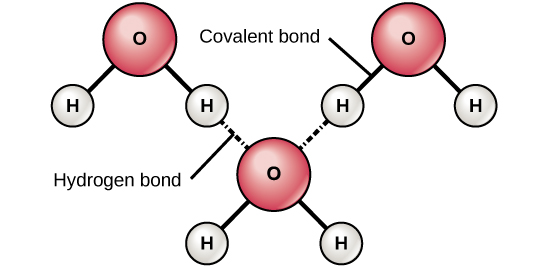
What would 3 molecules of water that are frozen look like, including charges and bonds?
Nucleic acids are directional. What are the two distinct ends called, and what is their biological significance?
What are the 5' (phosphate) end and 3' (hydroxyl) end; they determine direction of replication and transcription?
Structural differences between DNA and RNA affect their function. Name two structural differences and relate them to function.
What is: DNA is double-stranded and uses deoxyribose (stable for storage), RNA is single-stranded and uses ribose (more reactive for protein synthesis)?
Living organisms require a consistent nitrogen source. Describe the process by which atmospheric nitrogen becomes bioavailable and name one organism involved.
What is nitrogen fixation by nitrogen-fixing bacteria (e.g., Rhizobium)?
During protein synthesis, a dehydration reaction links amino acids. Describe the process and bond formed.
What is: The carboxyl group of one amino acid bonds to the amino group of another, forming a peptide bond and releasing water?