The classic debate over whether our traits are shaped more by genes or experience.
What is nature vs. nurture?
The two main divisions of the nervous system.
What are the central and peripheral nervous systems?
The brief electrical charge that travels down an axon.
What is an action potential?
The oldest part of the brain that controls heartbeat and breathing.
What is the brainstem?
The biological clock that regulates our sleep-wake cycle.
What is the circadian rhythm?
A testable prediction based on a theory and research.
What is a hypothesis?
Studies comparing identical and fraternal twins to study heredity and environment.
What are twin studies?
The system that controls voluntary muscle movement.
What is the somatic nervous system?
The space between neurons where neurotransmitters cross.
What is the synapse?
The lobe responsible for reasoning, decision-making, and personality.
What is the frontal lobe?
The sleep disorder marked by sudden attacks of overwhelming sleepiness.
What is narcolepsy?
The principle requiring participants to be told the true purpose of a study after it ends.
What is debriefing?
The principle that certain traits are passed on because they help an organism survive and reproduce.
What is natural selection?
The division that activates the “fight or flight” response.
What is the sympathetic nervous system?
Drugs that block neurotransmitter receptor sites.
What are antagonists?
The part of the limbic system involved in forming new memories.
What is the hippocampus?
This phase of sleep is when the brain is least active.
What is NREM 3?
A research method that examines one individual or group in depth.
What is a case study?
This controversial and discredited movement sought to “improve” the human population by controlling breeding for desirable traits.
What is eugenics?
The division that calms the body after stress.
What is the parasympathetic nervous system?
The process of neurotransmitters being reabsorbed after firing.
What is reuptake?
The “little brain” that coordinates balance and movement.
What is the cerebellum?
Vivid experiences that occur as a person falls asleep. They can involve visual, auditory, or physical sensations, and can be quite intense and realistic.
What are hypnagogic sensations?
The variable that is measured in an experiment.
What is the dependent variable?
The study of how the environment can affect gene expression without changing DNA.
What is epigenetics?
The part of the nervous system that controls glands and internal organs.
What is the autonomic nervous system?
These neurons connect the sensory and motor neurons.
What are interneurons?
The brain’s ability to reorganize after injury or experience.
What is plasticity / neuroplasticity?
Also known as sleepwalking, this disorder causes individuals to move or walk around during deep NREM sleep.
What is somnambulism?
The standard deviation of this Bell Curve is ____.
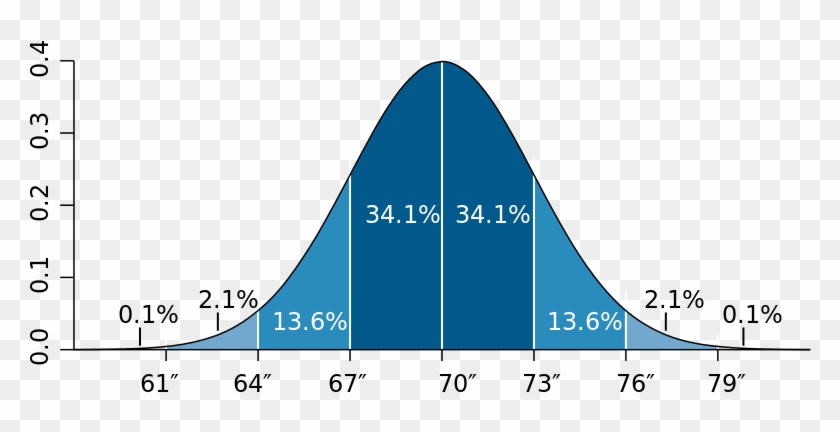
What is 3?
This psychological approach explains behavior in terms of natural selection and how adaptive traits promote survival.
What is the evolutionary perspective?
The chemical messengers of the endocrine system that interact with the nervous system such as Ghrelin and Adrenaline.
What are hormones?
An oversupply of this transmitter can lead to migraines.
What is Glutamate?
The structure that connects the two hemispheres of the brain.
What is the corpus callosum?
This theory suggests dreams are the brain’s way of making sense of random neural activity
What is the activation-synthesis theory?
The committee that reviews psychological research for ethical concerns before it’s conducted.
What is the Institutional Review Board (IRB)?
This term describes the proportion of variation among individuals that can be attributed to genes.
What is heritability?
This disease is caused by a deterioration of the myelin sheath and causes the failure of the central nervous system to communicate with the peripheral nervous system.
What is Multiple Sclerosis?
Once a dendrite is triggered, ion channels open and ions flood in toward the soma/cell body. These ions have a _______________ charge.
What is postive?
The area of the brain that controls language production.
What is Broca’s area?
The theory that sleep helps strengthen and store memories.
What is the consolidation theory?
A numerical measure that describes the strength and direction of a relationship between two variables.
What is a correlation coefficient?