The smallest unit of life
What is the cell?
The drawing for the Bohr model of Boron
What is see white board for teacher response
Attraction of molecules of the same substance
What is cohesion?
The monomer for carbohydrates
What is monosaccharide?
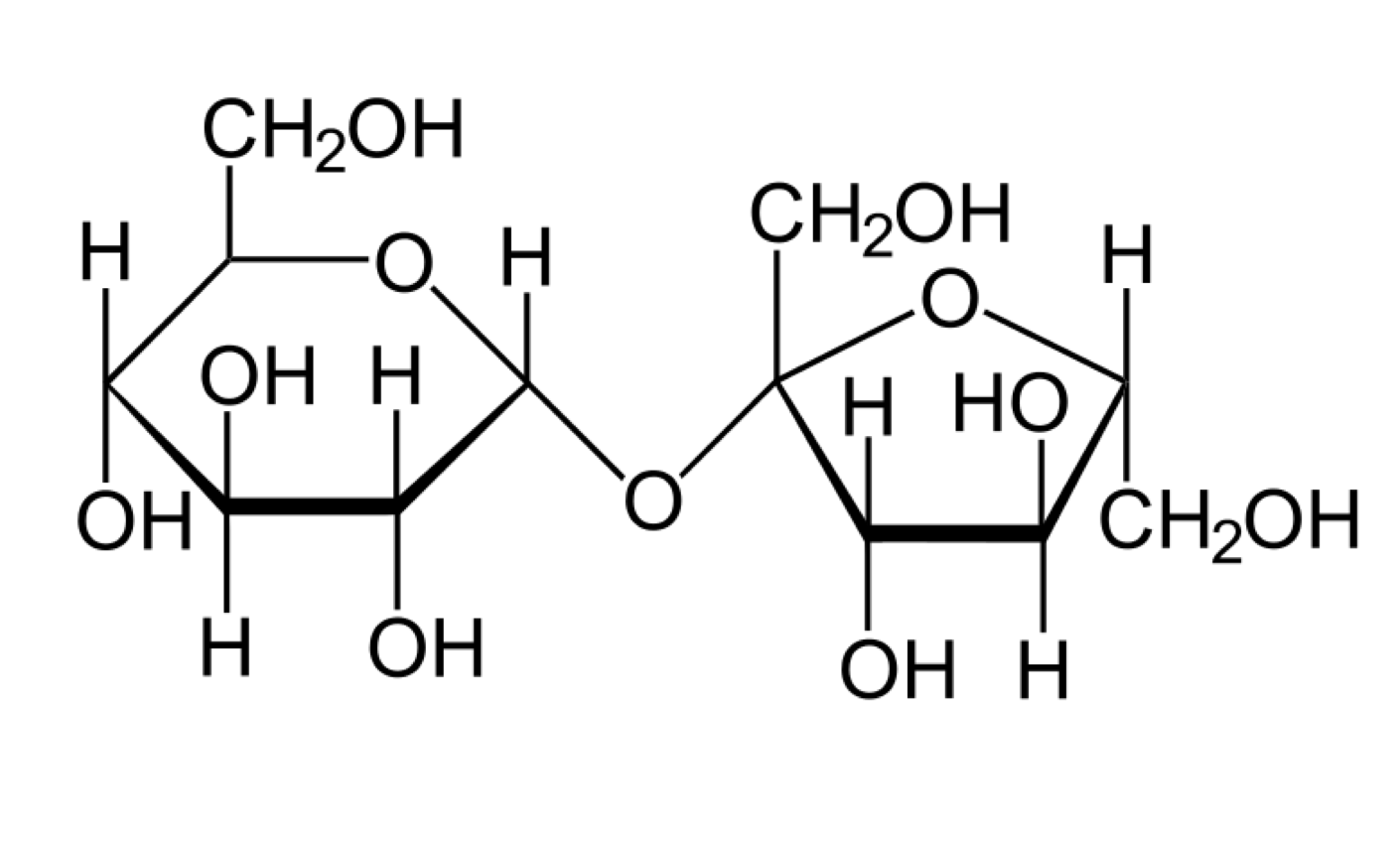
What is a disaccharide or carbohydrate?
The need for new organisms to replace the ones that are dying off
What is reproduce?
The subatomic particles involved in bonding.
What is valence electrons?
Attraction of molecules of different substances
What is adhesion?
The monomer for Lipids.
What is glycerol and fatty acids?

What is DNA?
The change of an immature species to an adult, occurs over time, often adding more cells in process
What is growth and development?
The three subatomic particles and their respective charges.
What is a positive proton, neutral neutron and a negative electron?
The ability of water to resist temperature changes,
What is heat capacity?
The monomer for proteins?
What is amino acids?
The four LEVELS of a protein.
What is primary, secondary, tertiary, and quarternary?
Organisms either are producers (produce own food) or consumers (eat a producer) because they need this.......
What is use energy?
The differences between a covalent and ionic bond. (at least 3)
What is
covalent bonds share electrons between nonmetals, stronger
ionic bonds gain and lose electrons, between metal and nonmetal, not as strong as covalent
This property of water allows for surface tension.
What is cohesion?
The monomer for nucleic acids.
What is nucleotide?
The element nucleic acids have that the other macromolecules do not.
What is phosphorous?
The ability to respond to outside stimuli
What is react to the environment?
The total amount of atoms in 2 C6H12O6
What is 48?
This property of water allows capillary action.
What is adhesion?
One difference between a saturated and unsaturated fat.
What is saturated fats have TONS of hydrogens, SINGLE bonds and "bad fats" while unsaturated have less hydrogens, double bonds and "good fats."
The differences between DNA and RNA. (at least 2)
DNA - double stranded, RNA - single
DNA - deoxyribose sugar, RNA - ribose
DNA - genetic code, RNA - makes proteins