This neurotransmitter is associated with mood regulation and can lead to bouts of depression.
What is Serotonin?
Lobe of the cerebral cortex placed just behind the forehead; directs language processions and higher order thinking such as decision making.
What is the Frontal Lobe?
An everyday term for compulsive substance use that continues despite harmful consequences.
What is addiction?
This disorder involves the inability to fall or stay asleep.
What is insomnia?
This lobe is responsible for processing visual information.
What is the occipital lobe?
Initiating the reward system, this neurotransmitter regulates emotion and can be a cause for substance addiction and schizophrenia.
What is Dopamine?
a limbic system neural structure that is located below the thalamus; directs the endocrine system and temperature.
What is the Hypothalamus?
This class of drugs regresses neural activity and slows body functions.
What are depressants?
This stage of sleep is most associated with dreaming due to spiked brain activity.
What is REM sleep?
Which lobe contains the primary motor cortex?
What is the frontal lobe?
This neurotransmitter is most associated with muscle movement and memory.
What is Acetylcholine?
Often referred to as the 'little brain,' it's function includes processing sensory input, balance and movement, and nonverbal learning and communication.
What is the Cerebellum?
This class of drugs alter your state of consciousness and distort perception and evoke sensory images.
What are hallucinogens?
This term refers to your biological clock as it regulates sleep/wake cycles in a 24hr period.
What is circadian rhythm?
What is neuroplasticity?
This neurotransmitter promotes relaxation and calmness as well as sleep/wake cycles. It is also affected by alcohol.
What is GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid)?
This area of the brain is responsible for the production of speech and language.
What is the Broca's area?
This class of drugs increases neural activity and speed up body functions.
This disorder is characterized by breathing repeatedly stopping and starting, often without the person knowing, leading to poor sleep quality, daytime fatigue, and serious health risks like heart problems.
What is sleep apnea?
The limbic system includes the following EXCEPT: Hippocampus, Amygdala, Hypothalamus, or Pons
What is pons?
The body's natural painkillers and mood elevators, reducing the perception of pain and stress while promoting feelings of pleasure and well-being
What are Endorphins?
A cerebral cortex area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations.
What is the somatosensory cortex?
natural or semi-synthetic drugs used for pain relief and causes euphoria, sedation, and slowed breathing; they include morphine, codeine, and heroin.
What are opiates?
Sleep stage 3 (NREM 3) is characterized by what kind of brain waves?
What are delta waves?
Areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor and sensory functions.
What are association areas?
What is happening in this image?
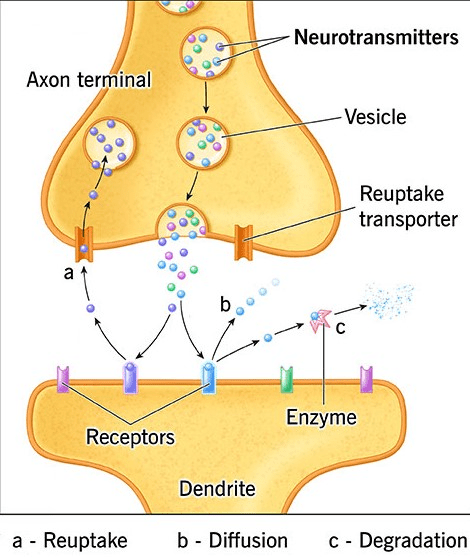
(answers may vary) This is the neurotransmitter system where neurotransmitters are released and received in the synapse.
This small section is responsible for fear and aggression as well as the "fight-or-flight" responses.
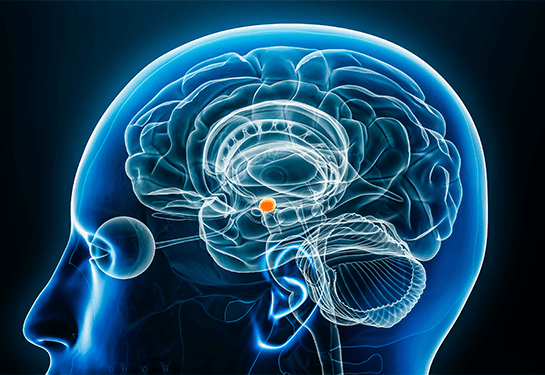
What is the Amygdala?
A class of central nervous system depressant drugs used historically as sedatives, sleeping pills, and anesthetics.
What are Barbiturates?
These disorders are characterized by the malfunction of normal paralysis to stop one from acting out dreams, sleep speaking or walking.
What are REM sleep behavior disorders?
A thin layer of interconnected neural cells responsible for higher-level thinking.
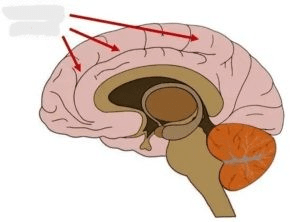
What is the cerebral cortex?