controls all the activities of the cell and stores the genetic information
Nucleus
Name this organelle:
endoplasmic reticulum (smooth and rough)
Does not require energy to transfer in and out of the cell
What is passive transport
What is it called when food coloring moves from a high concentration to a low concentration?
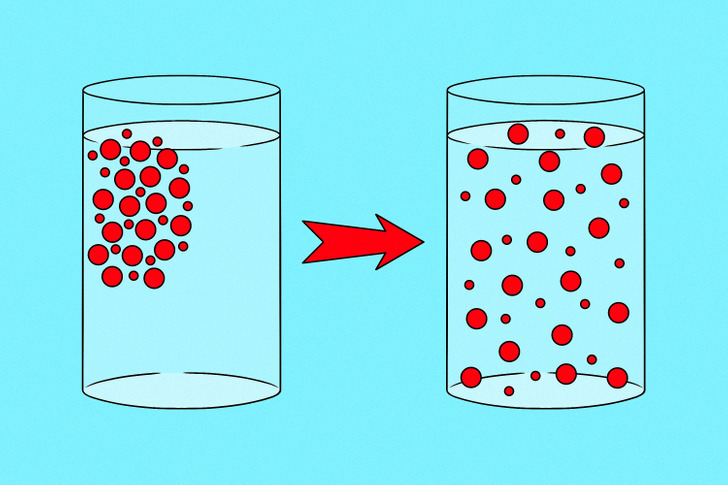
Diffusion
The part of the cell cycle in which the nucleus divides.
What is mitosis?
What is the term that describes how different structured cells have specific functions?
Cell Specialization (Differentiation)
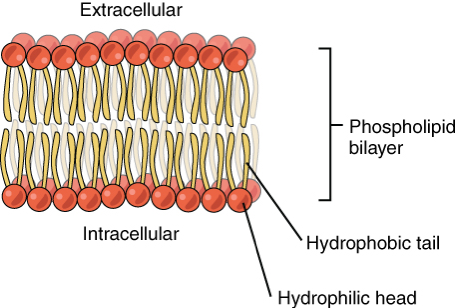 What is this a picture of?
What is this a picture of?
Cell membrane - lipid bilayer
This organelle converts glucose and other organic molecules into a form of usable cell energy called ATP.
Mitochondria
Simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis are examples of what type of transport?
What is passive transport
Describe the movement across concentration gradients in passive transport compared to active transport
Active - Against the gradient
Happens during S phase of interphase?
What is DNA replication?
What is one way stem cells may be used in the future?
Prevent disease, treat cancer, regeneration, research, etc.
the "jelly" like fluid that fills a cell
cytoplasm
These structures may be found floating freely in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum and makes proteins
Ribosomes
Diffusion of water is called?
Osmosis
When the cell needs to use energy to move things across the membrane
Active transport
The stage of the cell cycle when chromosomes separate.
Anaphase
A disease of unregulated cell division.
What is Cancer?
This organelle sorts and packages proteins and ships them to their final destinations.
Golgi apparatus
In what place are the ribosomes manufactured
Nucleolus
A glucose molecule travels from a high to low concentration through a protein channel. What type of passive transport is occurring?
Facilitated Diffusion
There is an equal flow of water entering and exiting the cell. This term is called what?
Isotonic
The part of the cell cycle when the nucleus breaks down and chromosomes appear.
What is prophase?
Programmed cell death
Apoptosis
What type of cell contains a nucleus?
Eukaryotic Cell
This organelle reels in the spindle fibers to separate the chromosomes
Centrioles
List the three types of active transport
Endocytosis, Exocytosis, Molecular Pumps
What is the term that refers to the cell's ability to maintain stable conditions? Ex: cell transport
Homeostasis - Feedback mechanisms
Describe the difference in cytokinesis for plant vs. animal cells
Plant - cell plate formed
Animal - pinching of cell membrane (cleavage furrow)
These are set places within the cell cycle where the cell is stopped before proceeding onto the next step. Give an example.
Checkpoint - G1, S, G2, Mitosis
Spherical structures that are used to breakdown waste products in an animal cell
Lysosomes
What is the main function of the cell? In what organelle does this take place?
Ribosomes - make proteins
A cell which contains 35% salt is sitting in a solution that contains 45% salt. In which direction will the water move in order to reach homeostasis? What is this called?
Water will move out of the cell - Hypertonic
A saltwater crab is placed into a freshwater pond. Describe what will happen to the crab - what is this called?
Cells will flood with water - Hypotonic
Where does G1 and G2 phases occur in the cell cycle? What is their function?
Interphase - to grow and produce proteins
Why may ethics be a concern when using Embryonic Stem Cells? (Hint: What may make them controversial to use?)
ESC are used from a human zygote (fertilized egg) that is undergoing differentiation.