Physical Geography vs. Human Geography
Physical Geography: the study of physical features of the earth's surface
Human Geography:The study of where and why human activities are located where they are
Place
A specific point on Earth distinguished by particular characteristics.
Environmental Possibilism
the belief that a physical environment plays a role in the development of a society, but is NOT the ONLY factor at work
Map Projection
a method of taking a 3D object and putting in on a 2D plane
Graduated Symbol
Time-Space Compression
the idea that the world feels smaller than it used to because of increased technology in transportation and communication
Density
the number of things divided by the measurement of area
Environmental Determinism
the belief that a physical environment is THE reason that some societies are strong while others are weaker
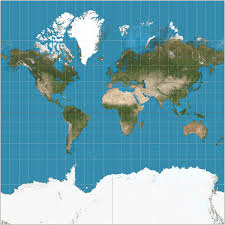
Mercator Projection
Qualitative vs. Quantitative
Qualitative: subjective information that is opinion based, is usually descriptive, and often expressed as text
Quantitative: objective data that is fact based, usually measurable and usually expressed in numbers
Spatial Perspective
Where something occurs
Region
a place larger than a point and smaller than a planet that is grouped together because of a measurable or perceived common feature.
Types
Scale on a map vs. Scale of analysis
Map: how distance on a map compares to distance on the ground
Analysis: refers to the area of the world being studied (Local, Regional, National, Global)
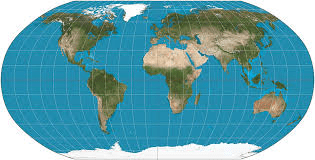
Robinson Projection
GIS vs. GPS
GIS (Global Information Systems): software that captures, manages, analyzes, and displays data in layers.
GPS (Global Positioning System): a system that measures distance from a series of satellites to determine location on the planet
Clustered
Gathered closely together in a group
Distance Decay
the idea that the interaction between two places declines as the distance between them increases
Ecological Perspective
The relationship between living things and their Environments.
Reference Map
maps that emphasizes the location of places (without data attached).
Isoline
Relative Location vs. Absolute Location
Relative: describing the position of a place as compared to (or relative to!) another landmark
Absolute: describing where something is using the exact site on an objective coordinate system
Region
a place larger than a point and smaller than a planet that is grouped together because of a measurable or perceived common feature
Site vs. Situation
Site: The physical character of a place, including its geographic characteristics.
Situation: the location of a place relative to the places that are around it
Types of Thematic Maps (5)
Isoline, Chloropleth, Dot Distribution, cartogram, graduated symbol
Types of regions (4)
Formal (uniform/Homogenous)
Functional
Vernacular/perceptual
Node