Identify the type of epithelial tissue shown below:
Simple Squamous:
Single, flat layer of cells
This connective tissue contains macrophages and mast cells
Blood
This type of muscle is found in your stomach and digestive tract
Smooth Muscle
What are the two types of nerve tissues?
Neurons and Neuroglia

B. Vascular
Within the four major categories or groupings of tissues, there are both vascular and non vascular examples
Which letter represents the basal surface?
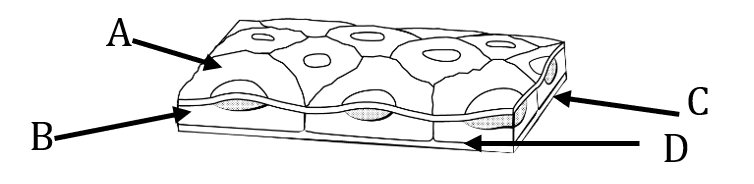
D
(Letter A is the free or apical surface, B is the epithelium proper, C represents the basement membrane)
The 2 types of fibers found in connective tissues are...
Collagen fibers and elastic fibers
This is the only type of muscle that can contract voluntarily
Skeletal
This type of cell is responsible for converting stimuli to impulses and passing impulses through the body
Neuron
What type of connective tissue is characterized by droplets of oil filling most of the cell’s space?
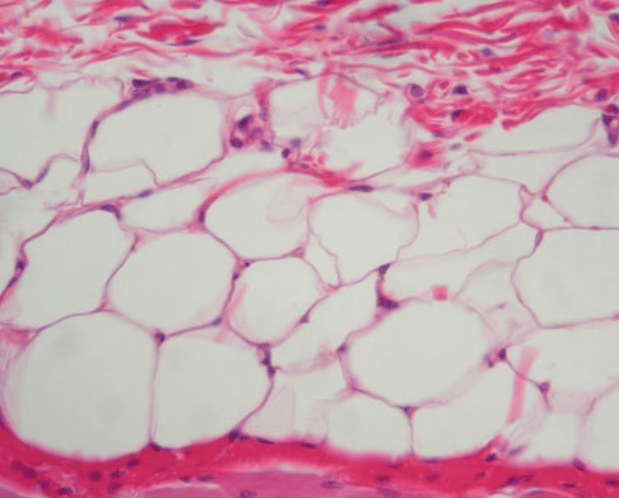
Adipose Tissue
The type of epithelial tissue that changes shape when stretched
Transitional
(This type has greater flexibility/ elasticity and is found in the bladder)
This type(s) of connective tissue has cells within lacuna (a small cavity or space within a tissue that houses a cell)
Cartilage and Bone
(I will give credit for either)
The image below shows what type of tissue?
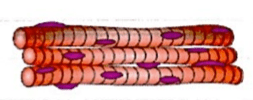
Skeletal Muscle
(Both skeletal and cardiac are striated but cardiac muscle cells appear as shorter, branched fibers while skeletal muscle cells are longer and unbranched)
This type of nerve tissue makes up 90% of your nervous tissue
Neuroglia
What is the gel-like or watery substance found in the extracellular matrix?
Ground Substance
This type of epithelial secretes mucous and is found in the lining of the digestive tract.
Simple Columnar Epithelium
(While Cuboidal is also known to secrete substances, it is primarily found in the kidneys)
This cell type develops into bone
Osteocytes
Why is it considered dangerous to have scar tissue in your heart/cardiac muscle?
Scar tissue has very little flexibility/elasticity so the heart would not be able to expand and contract as well
Head trauma that results in damage to neurons and neuroglia cells is called . . .
A concussion
Describe 2 types of membranes found in or on the body.
There are 3 total:
- Cutaneous- covers body surface, mucous- moist and found in body cavities that open to the outside environment
- serous- completely enclosed in ventral body cavity prevents friction with organs
- synovial- protects joints
The image below shows a salivary gland - these are what type of gland? How do you know?
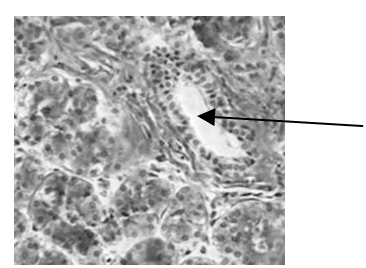
Exocrine gland (Specifically Merocrine) because the secretory product exits the cell via vesicles through a duct without causing any damage or loss of cellular material to the gland itself.
Endocrine products are secrete to the blood and then travel longer distances to reach their targets
(Both use exocytosis)
Name 2 characteristics of all connective tissues.
They are all formed from the same type of stem cell (Mesenchyme) and all mostly composed of extracellular matrix.
(I would also accept that functionally they provide support, bind tissues together, provide insulation, and protection)
Compare and contrast skeletal muscle tissue and smooth muscle tissue.
Skeletal muscle tissue is striated and voluntarily controlled. Smooth muscle tissue is non-striated and involuntarily controlled. Both are involved in movement.
Why can't neurons regenerate?
They are too specialized - they made evolutionary compromises to specialize and increase their ability to pass information very quickly - lack of regeneration was one of the compromises.
(This is not on your quiz or in your notes, but we did talk about it in class)
Draw a picture of a pseudostratified tissue
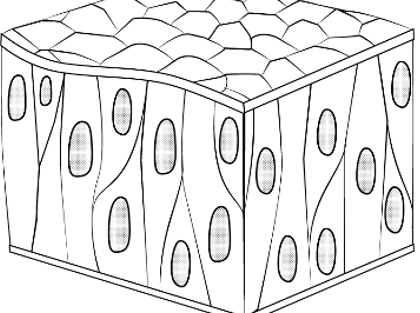
pseudostratified tissues are a single layer of cells that look like more than one layer because the nuclei are in different positions/not lined up.
-Found in your upper respiratory tract